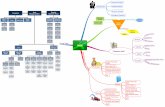
Unit 2 Mind Map Assignment
-
Upload
christian-andrade -
Category
Documents
-
view
52 -
download
0
Transcript of Unit 2 Mind Map Assignment

Chapter 3: FederalismFederalism - a system of government in which
power is divided between a national (federal) government and various regional governments.o Dual - views the Constitution as giving a
limited list of powers (foreign policy/national defense).
o Cooperative - federalism as a system of intergovernmental relationships in delivering governmental goods and services to the people and calls for cooperation among various levels of government.
o Marble cake - conceives federalism as a mixed set of responsibilities in which all levels of government are engaged in a variety of issues.
o Permissive - the states’ share rests on the permission and permissiveness of the national government.
o New - made by Nixon and Reagan, saying that the power of the federal government is limited in favor of the broad powers reserved to the states
Alternatives to Federalism - unitary systems, confederations
Advantages - checks the growth tyranny, allows unity without uniformity, encourages experimentation, provides training and
Federal Courts -o National supremacy - the federal government
has power over the states when laws are conflicted.
o Preemption - the right of a national law or regulation to preclude enforcement of a state or local law or regulation.
Centralists vs. Decentralists - o Centralists - people who favor national action
over state and local action. Rejected idea of the Constitution as an
interstate compact, its viewed as supreme law
National government speaks for everyone and states do not.
o Decentralists - people who favor state or local action over national action. States’ rights - powers expressly or
implicitly reserved to the states Devolution revolution - the effort to slow
the growth of the national government by returning many functions to the states
Federal Grants - supply state and local governments with revenue, establish minimum national standards, equalize resources among states, and attack national problems, but minimize the growth of federal agencies.o Categorical-Formula Grants - For specific
purposes (e.g. roads, airports, housing, bilingual education). National government agrees to pay a portion of the costs of these, and states pick up the balance --

Powers of the National Government - o Delegated - regulate commerce, implied
powers create banks. o Elastic Clause - saying that they have
rights to make laws that are “necessary and proper” to carry out the execution of the government.
o Expressed - powers specifically specified in the Constitution.
o Inherent - powers in foreign affairs to grow out the existence of the national government.
o Commerce Clause - gives Congress the power to regulate all business activities that cross state lines or affect more than one state or other nations.
o Federal Mandates - a requirement the national government imposes as conditions for receiving federal funds.
Powers of the States -o Reserved powers - powers not delegated to
the national government is reserved and given to the states.
o Concurrent Powers - powers that the Constitution gives to both the national and state governments (levy taxes)
Interstate Relationships - o Full faith and credit- requires each state to
recognize the civil judgments rendered by the courts
o Extradition - the legal process saying the
McCulloch vs. Maryland- Chief Justice John Marshall wrote the opinion for this landmark case defining the powers of a state over the federal government.o The facts are these:
The State of Maryland voted to tax all bank business not done with state banks. This was meant to be a tax on people who lived in Maryland but who did business with banks in other states. However, the State of Maryland also wanted to tax the federal bank.
Andrew McCulloch, who worked in the Baltimore branch of the Bank of the United States, refused to pay the tax. The State of Maryland sued, and the Supreme Court accepted the case.
Chief Justice John Marshall wrote that the federal government did indeed have the right and power to set up a federal bank. Further, he wrote, a state did not have the power to tax the federal government.
Gibbons vs. Ogden - the Court said that the federal commerce clause outranked a state law that had granted a monopoly to one group of people.o The facts are these:
The majority opinion, written by Marshall, said that the U.S. Constitution had a commerce clause that allowed the federal government to regulate



o Revenue Sharing - General grant of money to states to spend as they please ➞ even more leeway than block grants. Associate these with Nixon and Reagan -- more New Federalism. As budget deficits skyrocketed in late 80s, these ended -- “no more revenue to share.”
Federalist #10 - Madison begins perhaps the most famous of the Federalist papers by stating that one of the strongest arguments in favor of the Constitution is the fact that it establishes a government capable of controlling the violence and damage caused by factions. Madison defines that factions are groups of people who gather together to protect and promote their special economic interests and political opinions. Although these factions are at odds with each other, they frequently work against the public interests, and infringe upon the rights of others.
Federalist #51 - Madison begins his famous federalist paper by explaining that the purpose of this essay is to help the readers understand how the structure of the proposed government makes liberty possible. Each branch should be, for the most part, in Madison's opinion, independent. To assure such independence, no one branch should have too much power in selecting members of the other two branches. If this principle were strictly followed, it would mean that the citizens should select the president, the legislators, and the judges. But,
o Criticisms - Conservatives have fewer objections to big government when individuals have a choice in determining how government will affect them. Vouchers for school, choices in prescription drug benefit plans, and options to manage Social Security savings are examples.
Socialism - an economic and governmental system based on public ownership of the means of production and exchange.
Libertarianism - an ideology that cherishes individual liberty and insists on minimal government, promoting a free market economy, a noninterventionist foreign policy, and an absence of regulation in moral, economic, and social life.
Social Capital - The concept of social capital highlights the value of social relations and the role of cooperation and confidence to get collective or economic results. The term social capital is frequently used by different social sciences. It is a wide term, and that is why it can be defined accentuating different aspects depending on the perspective. In general terms, we could say that social capital is the fruit of social relations, and consists of the expectative benefits derived from the preferential treatment and cooperation between individuals and groups.
Chapter 5: American Political Landscape Ethnocentrism - belief in the superiority of one’s
nation or ethnic group. Political Socialization - the process by which we
develop our political attitudes, values, and beliefs.

U.S. vs. Lopez - Alfonzo Lopez, a 12th grade high school student, carried a concealed weapon into his San Antonio, Texas high school. He was charged under Texas law with firearm possession on school premises. The next day, the state charges were dismissed after federal agents charged Lopez with violating a federal criminal statute, the Gun-Free School Zones Act of 1990. The act forbids "any individual knowingly to possess a firearm at a place that [he] knows...is a school zone." Lopez was found guilty following a bench trial and sentenced to six months' imprisonment and two years' supervised release.
Chapter 4: Political Culture Political Culture - the widely shared beliefs,
values, and norms about how citizens relate to government and to one another. POLITICAL CULTURE IS LEARNED IN OUR FAMILIES!
Shared Values -o Natural rights - the rights of all people to
dignity and wortho Liberty, Equality, Individualism, Respect for
the Common Person, Democratic Consensus, Justice and the Rule of Law, Patriotism, Optimism, and Idealism
o Political Values and Economic Change- there has been a change in industrial transformation. The New Deal directly influenced the Great Depression.
Political Ideology - a consistent pattern of beliefs about political values and the role of government.
Liberalism - a belief that government can and should achieve justice and equality of
Regional Differences - the South (Sun Belt): affected by Civil Rights revolutions in the 1960’s. More African Americans that aren’t registered voters. Country: the Civil War made the South to be Democratic and the North Republican, because of Lincoln. “The decline of the South in the Democratic party would reorder the American party system and realign the electorate.”
State and Local Identity - some states contain 1\8 of the population, giving larger states many reps. and electoral votes. This is reversed for smaller states like Wyoming, receiving only 1 in each category.
Places - (1) urban- highly populated, central cities, (2) suburban- surrounding are of a central city, (3) rural- small towns, often associated with farming
Race and Ethnicity - the less common races and ethnicities become minorities, causing them to receive less attention and funding and respect causing them to lead to “big government”.
Religion - fundamentalists- Conservative Christians who are more active and influenced 2000/2004 elections. Protestants=51.3%, Catholics=23.9%, None- 16.9%
Gender - government and politics= mostly controlled by men, but since women suffrage women are becoming more equal, (1) gender gap- the difference between the political opinions of men and women. Includes sexual orientation.
Family Structure - traditional= married, has children and stayed together
Education - people who have failed to learn the democratic and capitalist ideals are more likely to oppose them compared to the well-educated
Wealth and Income - in the U.S. greater wealth correlates to Republican, but some are republican