Unit 1 Jwfiles
description
Transcript of Unit 1 Jwfiles
-
Unix programming
Term:2008-2009
III B.Tech II semester
Unit-I PPT Slides
Text Books: (1)unix the ultimate guide
by Sumitabha Das
(2)Advanced programming in unix environment by Stevens
*
-
INDEX
UNIT-I PPT SLIDES
Srl. No. Module as per Session planner Lecture No. PPT Slide No.
Introduction to Unix file system L1 1-8vi editor L2 9-15file handling utilities-cp, mv,ln L3 16-194. Rm, unlink, mkdir, rmdir, find L4 20-24
5. security by file permissions L5 25-30
6. process utilities L6 31-33
7 .disk utilities L7 34-38
8. ulimit , unmask L8 39-40
9. networking commands L9 4146
*
-
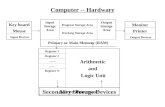
What is UNIX?
A computer operating system. It is designed to be used by many people at the same time (multi-user). Runs on a variety of processorsIt provides a number of facilities:management of hardware resourcesdirectory and file systemloading / execution / suspension of programs*
-
1.3. Why Use UNIX?
multi-tasking / multi-usernetworking capabilitygraphical (with command line)easy to program portable (PCs, mainframes,
super-computers)continued
*
- File: s a container for storing information.A file is of 3
types.Ordinary file: It contains data as a stream of characters. It
is of 2 types.Text file: contains printable characters.Binary file:
contains both printable & non printable characters.Directory
file: contains no data but it maintains some details of the files
& subdirectories that it contains.
*
- Every directory entry contains 2 components.1.file name.2.a
unique identification number for the file or directory.Device file:
It represents the device or peripheral.
*
-
The UNIX File System
A simplified UNIX directory/file system:/
bin
dev
lib
User
usr
tmp
User2
User1
User3
*
. . .
. . .
- /Bin: contains executable files for most of the unix
commands./Dev: contain files that control various input &
output devices./Lib: contains all the library functions in binary
form./Usr: contains several directories each associated with a
particular user./Tmp: contain the temporary files created by unix
or by any user./Etc: contains configuration files of the system.
*
-
vi Editor
vi is a full screen text editor. It was created by Bill Joy.Bram Moolenaor improved it and called it vim (vi improved).Invoking vi:$Vi file name*
-
Modes of operation
Vi has 3 mode of operation.1.Command mode: In this mode all the keys pressed by the user are interpreted as commands. It may perform some actions like move cursor, save, delete text, quit vi, etc.
2.Input/Insert mode: used for inserting text.start by typing i; finish with ESC*
-
Modes of operation
Ex mode or last line mode:Used for giving commands at command line. The bottom line of vi is called the command line.*
-
Basic Cursor Movements
hmove cursor one place to left
jdown one
kup one
lright one
wmove forward one word
bback one word
*
-
Finishing a vi Session
Get to command mode (press ESCs)
ZZsave changes to the file and quit
(no RETURN)
:q!quit without saving
(press RETURN):wq! Saves the file & quit.
*
-
Inserting Text
Move to insertion point
Switch to input mode: i
Start typing; BACKSPACE or DELETE
for deletion
ESCfinish; back in command modeNo RURN
*
-
Deletion
Must be in command mode.
xDelete character that cursor is on.
ddDelete current line.
DDelete from cursor position to
end of lineuUndo last command
*
-
File handling utilities
Cp (Copying Files)To create an exact copy of a file you can use the cp command. The format of this command is:cp [-option] source destination
Eg:
Cp file1 file2
Here file1 is copied to file2.
Eg:
Cp file1 file2 dir
File1 file2 are copied to dir.
*
- Copying Files
Cp turns to interactive when i option is used & destination file also exists.
$cp -i file1 file2
overwrite file2 (yes/no)?
Y at this prompt overwrites the file.
*
- mv (Moving and Renaming Files)
Used to rename the files/directories. $mv test sample
Here test is renamed as sample.
*
- ln (link):Used to create links (both soft & hard links).It
creates the alias & increase the link count by one.$ln file1
file2ln wont work if the destination file also exists.
*
- Rm (Deleting Files and Directories)To delete or remove a file,
you use the rm command. For example,
$rm my. listing
will delete my.listing.
With i option removes the files interactively.
$rm i file1
With r option recursively removes directories.
$rm r dir1
*
- mkdir: used to create one or more directories.$mkdir book
Creates the directory named book.
$mkdir dbs doc dmcCreates three directories.
*
- rmdir (remove directories ):Removes empty directories.$rmdir
book
removes directory named book if it is empty.
$rmdir dbs doc dmcRemoves 3 directories.
*
- find: It recursively examines a directory tree to look for
matching some criteria and then takes some action on the selected
files.
Syntax:
find path_list selection_criteria actionTo locate all files named a. out use$find / -name a. out print
/ indicates search should start from root directory.*
- To locate all c files in current directory
$find . -name *.c print
To find all files begin with an uppercase letter use$find . name [A-Z]* print
Find operators:
Find uses 3 operators
!,-a ,-o
*
-
Security by file permissions
Unix follows a 3-tiered file protection system.
owners permission others permission
- r w x r - x r - -
Type of file groups permissions
Each group represents a category. There are 3 categories-owner ,group ,others.
*
-
Security by file permissions
Each category contains read ,write ,execute permissions .rwx->presence of all permissions.r-x->absence of write permissionr-- -> absence of write ,execute permissionChmod: changing file permissionchmod sets a files permissions (read, write and execute) for all three categories of users (owner, group and others)
*
- Syntax:
chmod category operation permission file(s)
The command contains three components:
category of a user (owner, group or others) operation to be performed (assign or remove a permission)Permission type (read, write or execute)*
- Abbreviations used by chmod:
Category operation
u-user +-assign permission
g-group --remove permission
o-others =-assigns absolute permission
a-all
permissions
r-read permission
w-write permission
x-execute permission
*
- Absolute assignment:
Absolute assignment by chmod is done with the = operator. Unlike the + or operator s, it assigns only those permissions that are specified along with it and removes other permissions.
If u want to assign only read permission to all three categories and remove all other permissions from the file small use
chmod g-wx,o-x small
Or simply use = operator in any of the following ways.
*
-
chmod ugo=r small
chmod a=r small
Chmod =r small
The octal notation:
Chmod also takes a numeric argument that describes both the category and the permission. The notation uses octal numbers. Each permission is assigned a number like
read permission-4, write permission-2, execute permission-1
*
-
Process utilities
Ps (process status):Display some process attributes.$psPID TTY TIME CMD
1078 pts/2 0:00 bash
Ps presents a snapshot of the process table.*
-
Process utilities
Ps with f option displays a fuller listing that includes the PPID.Ps with u option followed by user-id displays the processes owned by the user-id.Ps with e option displays the system processes.*
- Who: know the usersDisplays the users currently logged in the
system.$whoWhoami: Show you the owner of this account$whoamiW: Tell
you who is logging in and doing what!$w
*
- Finger: Displays the information about the users.$finger user
Find out the personal information of a user
$finger nameTry to find the persons info. by his/her name
finger email-addressTry to find the persons info across the network
*
-
Disk utilities
Du: disk usageDu estimate the file space usage on the disk.It produces a list containing the usage of each subdirectory of its argument and finally produces a summary.$du /home/usr1*
-
Disk utilities
Df: displays the amount of free space available on the disk. The output displays for each file system separately.$dfMount:Used to mount the file systems.Takes 2 arguments-device name ,mount point.*
-
Disk utilities
Mount uses an option to specify the type of file system.To mount a file system on the /oracle directory on Linux system use$mount t ext2 /dev/hda3 /oracle
$mount t iso9660 /dev/cdrom /mnt /cdrom
$mount t vfat /dev/hda1 /msdos
$mount t msdos /dev/fd0 /floppy
*
-
Disk utilities
Umount: unmounting file systemsUnmounting is achieved with the umount command. which requires either file system name or the mount point as argument.$umount /oracle$umount /dev/hda3Unmounting a file system is not possible if the file is opened.*
- ulimit: user limitIt contains a value which signifies the
largest file that can be created by the user in the file
system.When used by itself it displays the current setting.$ulimit
unlimited
User can also set the ulimit value by using
$ulimit 10
*
-
unmask:
When u create files and directories, the default permissions that are assigned to them depend on the systems default setting. Actually this default is transformed
By subtracting the user mask from it to remove one or more permissions. This value is evaluated by umask without arguments.
$umask
022
*
-
Networking commands
ftp: file transfer protocolftp is used to transfer files. It can be usedwith host name.
$ftp Saturn
Connected to Saturn
220 Saturn ftp server
Name (Saturn: summit ): Henry
Password: ******
*
- To quit ftp use close and then bye or quit.ftp>close
221 good bye
ftp>byeTransferring files:Files can be of 2 types.
Uploading( put & mput):To upload ur web pages & graphic files to website.The put command sends a single file to the remote machine.
*
- ftp>binary
200 type set to I
ftp>put penguin. gifTo copy multiple files use mput.
ftp>mput t*.sqlDownloading files: get & mgetTo download the files from remote machine use get & mget.ftp>get ls-lR.gzftp>_*
-
Networking commands
telnet: Remote login
If u have an account on the host in a local network (or on internet ),u can use this with the host name or the ip address as argument.
$telnet Saturn
Trying to 192.168.0.1
Connected to Saturn
*
- Login:----Password:-----U can quit telnet by using exit
command.telnet prompt:
When telnet used without Ip address the system displays a telnet> prompt . U can invoke a login session from here with open.
telnet> open 192.168.0.8
Trying to 192.168.0.8
Connected to 192.168.0.8
*
-
Networking commands
rlogin: remote login without passwordrlogin is the Berkley's implementation of the remote login facility.U can log on to ur own identical remote account without using either the user name or password.$rlogin JupiterLast login :.rlogin is terminated with ctrl+d or exit or logout.*










![Mc-unit 2 Jwfiles[1]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/577ce4e81a28abf1038f5f8d/mc-unit-2-jwfiles1.jpg)