Uncompressed lossless lossy audio
Click here to load reader
-
Upload
jonny-williams -
Category
Education
-
view
755 -
download
2
description
Transcript of Uncompressed lossless lossy audio

Uncompressed
Lossy & Lossless
audio

Lossy & Lossless
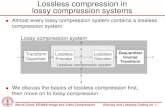
• Lossy Codec: refers to a codec that sacrifices file quality for the sake of compression.
• Lossless Codec: does not destroy any data, regardless of whether or not the data is necessary for the file’s integrity.

Uncompressed audio files
• Uncompressed audio files are large, original studio-quality digital-audio files. They are flexible file formats designed to store more or less any combination of sampling rates or bitrates. This makes them suitable file formats for storing and archiving an original recording if storage space is no concern.

Uncompressed audio files• AIFF (Audio Interchange File Format) - An audio file format standard used
for storing sound data for personal computers and other electronic audio devices. The format was co-developed by Apple Computer and is most commonly used on Apple Macintosh computer systems. Standard AIFF is a leading format used by professional-level audio and video applications, and unlike the better-known lossy MP3 format, it is non-compressed (which aids rapid streaming of multiple audio files from disk to the application), and lossless. Like any non-compressed, lossless format, it uses much more disk space than MP3—about 10MB for one minute of stereo audio at a sample rate of 44.1 kHz and a sample size of 16 bits.
• WAV (Waveform Audio File Format) - A Microsoft audio file format standard for storing audio on PCs. It is the main format used on Windows systems for raw and typically uncompressed audio. shortcoming identified in WAV is its inability to hold any metadata describing its audio contents. File size is also limited to 4Gb.

Lossless audio files• Lossless audio files are another form of studio-quality digital-
audio format, but they are compressed. A lossless compressed format stores data in less space by eliminating unnecessary data. Lossless compression still retains low-level resolution of a standard CD. The advantage is that it takes up less room on your computer than an uncompressed format, and unlike lossy codecs, it does not remove any information from the audio stream and is suitable both for everyday playback and for archiving audio collections.
• Development in lossless compression formats aims to reduce processing time while maintaining a good compression ratio.

Lossless audio files• FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec) – The FLAC format is
currently well supported by many software audio products, and is the only free lossless audio compression format that has any hardware support.
• ALAC (Apple Lossless compression) – ALAC is an audio codec developed by Apple for lossless data compression of digital music. After initially keeping it proprietary for many years from its inception in 2004, in late 2011 Apple made the codec available open source and royalty-free.

Lossy compression
• Lossy compression enables even greater reductions in file size by removing some of the data. Lossy compression typically achieves far greater compression than lossless compression by simplifying the complexities of the data. This of course results in a reduction in audio quality, but a variety of techniques are used, mainly by exploiting psychoacoustics, to remove the data that has least effect on perceived quality.
• For many everyday listening situations, the loss in data (and thus quality) is imperceptible. Most formats offer a range of degrees of compression, generally measured in bit rate. The lower the rate, the smaller the file and the more significant the quality loss.

Lossy compression• AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) – AAC was designed as an improved-performance
codec relative to MP3. File format is typically .mp4 or .m4a (audio only). AAC is the format used by iTunes
• ATRAC (Adaptive TRansform Acoustic Coding) – Sony’s audio compression algorithm used to store information on MiniDisc and other Sony-branded audio players.
• MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer-3) – One of the most popular music formats, due to it being able to be played or nearly all portable music players.
• MP3 is a lossy format, designed to remove parts of the music that the human ear find hard to hear. A number of techniques are used to allow ~10:1 compression compared with uncompressed audio. MP3 s allow encoding at a range of ‘bit rates’, ′these are typically between 128 and 320 kilobits per second. Variable Bit Rate (VBR) is now also commonly used, here the bit rate alters through the music depending on the demands of the music.

Lossy compression
• OGG Vorbis – Vorbis is an open and free audio compression which normally goes under the name format of OGG. Due to the free nature, Ogg Vorbis format has proved popular among the open source communities, along with its claimed best quality lossy audio codec (at certain bitrates).
• WMA (Windows Media Audio) – WMA is Microsoft’s audio file format. A WMA file is almost always encapsulated in an Advanced Systems Format file. The resulting file may have the Filename extension .wma or .asf (.wma being used being used if audio only). Windows Media Audio supports DRM which has led to itself as a competitor to the AAC format used by iTunes.