Tutorial on Root Locus
-
Upload
ivan-yerovi -
Category
Documents
-
view
271 -
download
5
Transcript of Tutorial on Root Locus
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
1/30
Chapter 7:
The Root Locus Method
Tutorial Session
EE4314 - Summer 2008
Prof. K. Alavi
TA: An Vo
Content
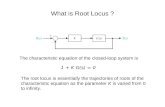
Characteristic Equation
Definition of Root-locus
Angle and Magnitude Condition
Sketching Root Locus
Change In Pole-zero Configuration
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
2/30
Closed loop system
consider a general form of closed loop system:
)(sR )(sC)(sE )(sG
)(sH
with transfer function:)()(1
)(
)(
)(
sHsG
sG
sR
sC
+=
Characteristic equation
0)()(1 =+ sHsG
or:
1)()( =sHsG
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
3/30
Root locus
The root locus is the path of the roots of
the characteristic equation in the s-plane as
a system parameter is changed.
Example : system definitionconsider a closed loop system:
)(sR )(sC)(sE1K
)10(
2
+ss
K
after reduction:
)(sR )(sC
K
K
++102
21KKK=
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
4/30
Example : table of pole positions
Norman S. Nisse (2004).
Control Systems Engineering, 4th edition
John Wiley & Sons
0102 =++ Kss
Example : poles in s-plane
Norman S. Nisse (2004).
Control Systems Engineering, 4th edition
John Wiley & Sons
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
5/30
Example : root locus
Norman S. Nisse (2004).
Control Systems Engineering, 4th edition
John Wiley & Sons
Angle and magnitude condition
because
1)()( =sHsG
)()( sHsG is complex
amplitude condition:
,...2,1,0)12(180)()( =+= kksHsG
angle condition:
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
6/30
Angle and magnitude condition
The values ofs that fulfill both the angle andmagnitude conditions are the roots of the
characteristic equation (closed-loop poles).
Root locus property
A locus of the points in the complex plane
satisfying the angle condition alone is the
root locus.
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
7/30
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
8/30
Example : vector representation of G(s)
consider a closed loop system:
)(sR )(sC
)2)(1(
)4)(3(
++
++
ss
ssK
Example : angle and magnitude
=
++
++=
)2)(1(
)4)(3()(
ss
ssKsG
)12(180)2()1()4()3( +=+++++= kssss
amplitude condition:
angle condition:
1)2)(1(
)4)(3()( =
++++=
ss
ssKsG
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
9/30
Example
Check, if pointbelongs to root locus
32 js +=
+==+=+
180)12(55.70
43.1089057.7131.564321
k
Norman S. Nisse(2004).
Control Systems Engineering, 4th edition
John Wiley & Sons
NO
Example
Check, if point belongs to root locus2
22 js +=
=+ 1804321
33.0)22.1)(22.1(
)22.1(
2
2
21
43=== LL
LLK
For which value ofK?
YES
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
10/30
Sketching the root-locus plot
1. Locate the poles and zeros of G(s)H(s) on the s plane.
The root locus is symmetrical about the real axis
The number of branches of the root locus equals the number of
the closed-loop poles
The root locus begins at the finite and infinite poles of G(s)H(s)
and ends at the finite and infinite zeros of G(s)H(S)
Example : construction of root locus
consider a closed loop system:
)(sR )(sC
)2)(1(
)4)(3(
++
++
ss
ssK
for this system system:
1)( =sHand)2)(1(
)4)(3()(
++
++=
ss
ssKsG
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
11/30
Example
Norman S. Nisse (2004).
Control Systems Engineering, 4th edition
John Wiley & Sons
Example
Norman S. Nisse (2004).
Control Systems Engineering, 4th edition
John Wiley & Sons
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
12/30
Sketching the root-locus plot
2. Determine the asymptotes of the root loci on the
real axis.
The root locus approaches straight lines as asymptotes as the
locus approaches infinity. The equation of the asymptotes is
given by the real-axis intercept, a, and angle, a, as follows
zerosfinite#polesfinite#
zerosfinitepolesfinite
=a
,...2,1,0zerosfinite#polesfinite#
)12(
=
+
= kk
a
Example: finding asymptotes
consider a closed loop system:
)(sR )(sC
)4)(2)(1(
)3(
+++
+
ssss
sK
real axis intercept:
34
14)3()421( =
=a
angles of the lines:
3
)12(
+=
ka
33
5,,
3
==a
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
13/30
Example : finding asymptotes
Norman S. Nisse (2004).
Control Systems Engineering, 4th edition
John Wiley & Sons
sketching the root-locus plot3. Find the points where the root loci may cross the
imaginary axis.
a) Use the Rouths stability criterion
b) Let s=j in characteristic equation, equate both the real part andimaginary part to zero, and then solve for and K.
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
14/30
Example :j-axis crossing
consider a closed loop system:
)(sR )(sC
)4)(2)(1(
)3(
+++
+
ssss
sK
closed-loop transfer function of the system:
KsKsss
sKsT
3)8(147
)3()(
234
+++++
+=
Example :j-axis crossing
Routh table:
65.90720652 ==+ KKK
59.107.20235.8021)90( 22 jssKsK ===
-74.6456 9.6456
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
15/30
Example :j-axis crossing
Norman S. Nisse (2004).
Control Systems Engineering, 4th edition
John Wiley & Sons
1.59
Closed loop system is stable
if K
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
16/30
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
17/30
Example : break-away point
Norman S. Nisse (2004).
Control Systems Engineering, 4th edition
John Wiley & Sons
-0.435
sketching the root-locus plot5. Taking a series of test points in the broad
neighborhood of the origin of the s plane, sketch the
root loci.
if accurate shape of the root-loci is needed MatLab
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
18/30
Example num = [1];den = [ 1 1];rlocus(num, den)
Examplenum = [1];
den = conv([1 1],[1 2]);
rlocus(num, den)
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
19/30
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
20/30
Example
num = [1];
den = conv([1 0],[1 1]);
den = conv(den,[1 3]);
rlocus(num, den)
Addition of zeros
num = [1 4];
den = conv([1 0],[1 1]);
den = conv(den,[1 3]);
rlocus(num, den)
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
21/30
Addition of zeros
num = [1 2];
den = conv([1 0],[1 1]);
den = conv(den,[1 3]);
rlocus(num, den)
Addition of zeros
num = [1 0.5];
den = conv([1 0],[1 1]);
den = conv(den,[1 3]);
rlocus(num, den)
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
22/30
Root-locus plot: MatLab
% open-loop system
clear;
num = [0 0 4];
den = [1 2 0];
% root locus plot
rlocus(num,den)
v=[-5 1 -3 3]; axis(v); axis('square')
grid
title('root-locus plot')
% r: complex root locations, K: gai vector[r K] = rlocus;
Root-locus plot: MatLab
-5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 1-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
30.160.340.50.640.76
.
0.94
0.985
0.160.340.50.640.760.86
0.94
0.985
1234
root-locus plot of the system
Real Axis
ImaginaryAxis
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
23/30
Root-locus plot: MatLab
% open-loop system
clear;
num = [0 1 1];
den = [1 2 3 4];
% root locus plot
sys = tf(num, den);
rltool(sys)
Root-locus plot: MatLab
-1.8 -1.6 -1.4 -1.2 -1 -0.8 -0.6 -0.4 -0.2 0-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5Root Locus Editor for Open-Loop 1 (OL1)
Real Axis
ImagAxis
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
24/30
example :
construction of root locusconsider a closed loop system:)(sR )(sC
32
)2(2 ++
+sK
G(s) has a pair of complex conjugated poles at:
21 js +=and
21 js=
change in pole-zero configuration
A slight change in the pole-zero
configuration may cause significant
changes in the root-locus configurations.
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
25/30
change in pole-zero configuration
change in pole-zero configuration
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
26/30
change in pole-zero configuration
change in pole-zero configuration
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
27/30
change in pole-zero configuration
change in pole-zero configuration
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
28/30
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
29/30
change in pole-zero configuration
Problems
Prob 9 and 10: E7.26 & 7.27 Plot root locus
using matlab
Prob 11: See section 7.6/page 444 and
7.7/447
Example 7.11/ page 452
-
7/27/2019 Tutorial on Root Locus
30/30
impulse(sys)
step(sys)
References
Lecture notes, Dr. Darek Korzec