tutor oil n fat
-
Upload
naminiasoiv -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of tutor oil n fat

8/6/2019 tutor oil n fat
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/tutor-oil-n-fat 1/9
OIL AND FAT ( CPB 30203- Sem July 2011 )
TUTORIAL
CHAPTER 1
1. List down all type edible oils and its source available in the world
y Vegetables Oils and Fats
y Land Animals Fats
y Marine Animals Fats
y Synthetic Fats
1. Vegetables Oils and Fats
Fruit Pulp / Mash fatsy such as Palm Oil , Olive and avocado, coconut
Seed Kernel fats
y Major source of oil and fats
y such as palm kernel oil,, corn oil, sunflower oil and etc
2. Land Animals Fats
Lard-Hog (pig)
Tallow(cattle and sheep)
Milk or butter(cow)
3. State the method to differentiate types of edible oil.

8/6/2019 tutor oil n fat
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/tutor-oil-n-fat 2/9
3. Explain the lipid, glyceride, fatty acids and minor components are available
in edible oil.
Show the interconnection among these components.
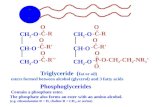
GLYCERIDE y Occurs about 97 % as triglycerides-triester of glycerols with fatty acids
y 2% as diglycerides
y 1% as monoglycerides
Tri, di and mono consists of 1 mol of glycerols esterified with 3mol,
2mol, or 1 mol of fatty acid
FATTY ACID
y Fatty acid that form the triglycerides of naturally occurring oil & fats with
predominant even numbered, straight chain, aliphatic monocarboxylic acid
with chain length ranging from C4 to C24 y Distinguish by:
Chain length
Number & position of double bonds
Position of the fatty acids within the glyceride molecule.
y the simplest lipids that exhibit the above properties
y carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon tail (fatty acids).y usually contain an even number of carbons
y If double bonds are present (unsaturation), they're usually cis.y pKa of fatty acids' carboxyl groups about 4.5

8/6/2019 tutor oil n fat
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/tutor-oil-n-fat 3/9
4. List down all application of oil palm tree.
Palm oil, like other vegetable oils, can be used to create biodiesel,
Vegetable Oil-Based as Engine Oils.
Vegetable Oils in Paint and Coatings.
Poly-Ol based products
Food ingredients products
5. Sketch and name functional group of carboxylic acid.
carboxylic acid
A carboxyl group (or carboxy) is a functional group consisting of a carbonyl
(RR'C=O) and a hydroxyl (R -O-H), which has the formula -C(=O)OH, usually
written as -COOH or -CO2H.

8/6/2019 tutor oil n fat
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/tutor-oil-n-fat 4/9
6. Write the names of carboxylic acid ranging from C8 to C20
7. Sketch and identify the saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.

8/6/2019 tutor oil n fat
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/tutor-oil-n-fat 5/9
8. Explain the behavior of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids
y Unsaturated fatty acids differ in number and position of double bonds and its
configuration.
y Common fatty acid are know with trivial name such as: butyric, lauric,
palmitic, oleic,stearic, linoleic, linolenic.
y Crude oil contains significant amount of Free fatty acid(FFA)
Therefore these oils are called unsaturated fats. Because of the kinks in the
hydrocarbon tails, unsaturated fats can¶t pack as closely together, making them
liquid at room temperature. Many people have heard that the unsaturated fats are
³healthier´ than the saturated ones. Hydrogenated vegetable oil (as in shortening
and commercial peanut butters where a solid consistency is sought) started out as
³good´ unsaturated oil. However, this commercial product has had all the double
bonds artificially broken and hydrogens artificially added (in a chemistr y lab-ty pe
setting) to turn it into saturated fat that bears no resemblance to the original oil
from which it came (so it will be solid at room temperature).
In unsaturated fatty acids, there are two ways the pieces of the hydrocarbon tailcan be arranged around a C=C double bond. In cis bonds, the two pieces of the
carbon chain on either side of the double bond are either both ³up´ or both
³down,´ such that both are on the same side of the molecule. In trans bonds, the
two pieces of the molecule are on opposite sides of the double bond, that is, one
³up´ and one ³down´ across from each other.

8/6/2019 tutor oil n fat
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/tutor-oil-n-fat 6/9
9.Explain about lipid and its physical and biochemical properties
Lipids: Fats, Oils, Waxes, etc. All Lipids are hydrophobic: that¶s the one
property they have in common. This group of molecules includes fats and oils,
waxes, phospholipids, steroids (like cholesterol), and some other related
compounds.
Fats and oils are made from two kinds of molecules: glycerol
(a ty pe of alcohol with a hydroxyl group on each of its three
carbons) and three fatty acids joined by dehydration
synthesis. Since there are three fatty acids attached, these are
known as triglycerides. ³Bread´ and pastries from a ³bread
factor y´ often contain mono- and diglycerides as ³dough
conditioners.´ Can you figure out what these molecules wouldlook like? The main distinction between fats and oils is
whether they¶re solid or liquid at room temperature, and this,
as we¶ll soon see, is based on differences in the structures o
the fatty acids they contain.
Structure of Fatty Acids
The ³tail´ of a fatty acid is a long
hydrocarbon chain, making it
hydrophobic. The ³head´ of themolecule is a carboxyl group
which is hydrophilic. Fatty acids
are the main component of soap,
where their tails are soluble in oily
dirt and their heads are soluble in
water to emulsify and wash away
the oily dirt. However, when the
head end is attached to glycerol to
form a fat, that whole molecule is
hydrophobic.

8/6/2019 tutor oil n fat
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/tutor-oil-n-fat 7/9
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are made
from glycerol, two fatty
acids, and (in place of
the third fatty acid) a
phosphate group with
some other molecule
attached to its other end.
The hydrocarbon tails of
the fatty acids are still
hydrophobic, but the
phosphate group end of
the molecule is
hydrophilic because of the oxygens with all of
their pairs of unshared electrons. This means that phospholipids are soluble in both
water and oil.
An emulsifying agent
is a substance which is
soluble in both oil and
water, thus enabling the
two to mix. A ³famous´
phospholipid is lecithin
which is found in egg
yolk and soy beans. Egg
yolk is mostly water
but has a lot of lipids,
especially cholesterol,
which are needed by
the developing chick.Lecithin is used to
emulsify the lipids and hold them in the water as an emulsion. Lecithin is the basis
of the classic emulsion known as mayonnaise.

8/6/2019 tutor oil n fat
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/tutor-oil-n-fat 8/9
Our cell membranes are made mostly of
phospholipids arranged in a double layer
with the tails from both layers ³inside´
(facing toward each other) and the heads
facing ³out´ (toward the water y
environment) on both surfaces.
Steroids
The general structure of cholesterol
consists of two six-membered rings side-
by-side and sharing one side in common, a
third six-membered ring off the top corner of the right ring, and a five-membered ring
attached to the right side of that. The
central core of this molecule, consisting of
four fused rings, is shared by all steroids,
including estrogen (estradiol),
progesterone, corticosteroids such as cortisol (cortisone), aldosterone, testosterone,
and Vitamin D. In the various ty pes of steroids, various other groups/molecules are
attached around the edges. Know how to draw the four rings that make up the
central structure.
Lipoproteins are clusters of proteins and lipids all tangled up together. These act
as a means of carr ying lipids, including cholesterol, around in our blood. There are
two main categories of lipoproteins distinguished by how compact/dense they are.
LDL or low density lipoprotein is the ³bad guy,´ being associated with deposition
of ³cholesterol´ on the walls of someone¶s arteries. HDL or high density
lipoprotein is the ³good guy,´ being associated with carr ying ³cholesterol´ out of
the blood system, and is more dense/more compact than LDL.

8/6/2019 tutor oil n fat
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/tutor-oil-n-fat 9/9
10. Explain non polar hydrophobic and polar hydrophilic tail?
A hydrophilic molecule or portion of a molecule is one that is ty pically charge-
polarized and capable of hydrogen bonding, enabling it to dissolve more readily in
water than in oil or other hydrophobic solvents. Hydrophilic and hydrophobic
molecules are also known as polar molecules and nonpolar molecules,
respectively. Some hydrophilic substances do not dissolve. This ty pe of mixture is
called a colloid. Soap, which is amphipathic, has a hydrophilic head and a
hydrophobic tail, allowing it to dissolve in both waters and oils.
Nonpolar substances are hydrophobic and will not mix with water. Plasma
membranes are composed largely of phospholipids which are composed of a polar,
hydrophilic phosphate "head" and a hydrophobic fatty acid "tail." These molecules
spontaneously arrange such that the heads point out toward the extracellular matrix
(outside of the cell) and inwards toward the cytoplasm, with the fatty acid tails onthe inside. Polar and charged particles (ions) cannot pass through the fatty acid
region and need to be shuttled in through proteinaceous channels. Some of the
most important chemicals used by our body are either polar or ionic (charged), so
these are ver y critical for sustaining life. These include water, the potassium,
sodium and calcium cations and the chloride and phosphate anions. Nonpolar
substances can freely pass through.
11. Sketch palm oil fruit dissection diagram and label the parts
12. Describe the process of extraction oil from Oil Palm Fruits.
13. Why sterilization is crucial in extraction process of oil palm fruits
14. For DOBI analysis why 446 Nm absorbance was used to be the benchmark
of the analysis.
15. How does oxidation process can cause poor bleachability of edible oil
16. Sketch and explain the Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME).
17. Explain how anerobic process bacteria digested the waste.
18. Why the arrangement of POME¶s pond should have anaerobic process
pond at beginning and follow by aerobic process pond?