Triangles - Study Pointmedians of a triangle is called its centroid. Characteristics of Centroid (i)...
Transcript of Triangles - Study Pointmedians of a triangle is called its centroid. Characteristics of Centroid (i)...

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles85
CHAPTER
6We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius
Triangles
A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle.
We denote a triangle by the symbol . In fig. ABC has
(i) three vertices namely, A,B and C
(ii) three sides namely, AB, BC, CA
(iii) three angles namely, A , B and C .
Types of Triangles on the basis of sides
(i) Equilateral triangle. A triangle whose all the three
sides are equal is called equilateral.
In the figure ABC is an equilateral triangle in
which AB = BC = CA
(ii) Isosceles triangle. A triangle having two sides
equal is called an isosceles triangle.
In the figure, ABC is an isosceles triangle in which
AB = AC.
(iii) Scalene triangle. A triangle whose sides are of
different lengths. In the figure ABC is a triangle in
which AB BC CA.
Types of Triangles on the Basis of Angles
(i) Obtuse-angled triangle. A triangle in which one
angle is an obtuse angle, is called an obtuse angled
triangle. In figure, ABC is a triangle in which 090B .
(ii) Acute angle triangle a triangle in which all angles
are less than 900 in measures is called acute angled
triangle.

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles86
(iii) A right angled triangle : A triangle in which one
angle is of exact 900 is called right angle triangle.
Some Other Important Terms of Triangles
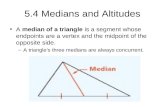
(a) Median. A median of a triangle is the line segment
joining the mid-point of side with the opposite
vertex.
(b) Centroid. The point of intersection of all the three
medians of a triangle is called its centroid.
Characteristics of Centroid
(i) Centroid is the point at which the medians of triangle
meet.
(ii) The medians of a triangle are concurrent.
(iii) The centroid divides the medians in the ratio 2 : 1.
(iv) The median of an equilateral triangle are equal.
(v) The medians of an equilateral triangle coincide with
the “altitudes”.
(c) Altitudes. The altitude of a triangle is the
perpendicular drawn from a vertex to the opposite
side.
(d) Orthocentre. The point of intersection of all the
three altitudes of a triangle is called its orthocenter.
Characteristics of Orthocentre
(i) Orthocentre is the point at which the altitudes of a
triangle meet.
(ii) The altitudes of a triangle are concurrent.
(iii) Orthocentre of an acute triangle lies in the interior of
the triangle.
(iv) Orthocentre of an obtuse triangle lies in the exterior of
the triangle.
Orthocentre of a right triangle lies on the
vertex of the right angle.
(e) Angle bisectot: the angle bisector of an angle of a
triangle is a line that divided the angle in two equal
part
(f) Incentre of a triangle. The point of intersection of
the bisectors the internal angles of a triangle in
called its incentre.
Characteristics of Incentre
(i) The point at which the three angle bisectors of a
triangle intersect is called the „incentre‟.

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles87
(ii) The triangle may be acute, obtuse, or right, the angle
bisectors of a triangle must meet at a point lying inside
the triangle.
(iii) The incentre of a triangle lies in the interior of the
triangle.
(iv) The bisectors of the angles of a triangle are
concurrent.
(v) From the incentre we can draw a on opposite sides.
(vi) We can call this perpendicular as “inradius”
(g) Perpendicular bisector: the perpendicular
bisector of a triangle is perpendicular drawn from
the opposite vertex and divide the opposite side in
two equal parts.
(h) Circumcentre of a triangle. The point of
intersection of the perpendicular bisectors of the
sides of a triangle is called its circumcentre.
Characteristics of Circumcentre
(i) The point at which the perpendicular bisectors of the
sides of a triangle meet is called the cicumkcentre of
the triangle.
(ii) The right bisectors of the sides of a triangle are
concurrent.
(iii) With circumcentre as centre, we can drawn a circle
passing through the vertices of a triangle.
(iv) The distance from centre to the vertices is called the
„circumradius‟.
The circle thus drawn with circumentre as centre
and circumradius as radius is called
„circumcircle‟.
(i) Perimeter. The sum of lengths of the sides of a figure is its perimeter. Perimeter of ABC = AB
+ BC + CA.
Asseingment-1
1. Prove that the sum of the angles of a triangle is 1800.
2. In ABC , 075B ,
032C find A .
3. In the figure, show that 0360 FEDCBA

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles88
4. In the figure, prove that 0360 cba
5. The angles of a triangle are in the ratio 3 : 5 : 10. Find the measures of each angle of the triangle.
6. The sum and difference of two angles of a triangle are 1280 and 22
0 respectively. Find all the angles
of the triangle.
7. If the bisector of the angle B and C of a ABC meet at a point O, then prove that BOC =
900 +
2
1 A .
8. In ABC , B > C , if AM is the bisector of BAC and AN BC, prove that MAN = 2
1 (
CB ).
9. Fill in the blanks
(a) The sum of three angles of a triangle is ……..
(b) If two angles of a triangle are 510 and 38
0, the third angle is equal to ……….
(c) If the angles of a triangle in the ratio 2 : 2 : 5, then the angles are……..
(d) The angles of a triangle are 3x – 5, 2x + 55 and 5x – 50 degrees then x is equal to…………
(e) A triangle cannot have more than……………..right angles.
(f) A triangle cannot have more than…………obtuse angle.
10. Which of the following statements are true or false?
(a) An exterior angle of a triangle is less than either of its interior opposite angles.
(b) Sum of the three angles of a triangle is 1800.
(c) A triangle can have two right angles.
(d) A triangle can have two acute angles.
(e) A triangle can have two obtuse angles.
(f) An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
Exterior angle of a Triangle:
Definition. If the side BC of a triangle ABC is
produced to ray BD, then ACD is called an
exterior angle of triangle ABC at C, and is denoted
by exterior ACD . A and B are called remote
interior angles or interior opposite angles.
Note : At each vertex there are two exterior angles
Theorem . If a side of a triangle is produced, then the exterior angle so formed is equal to
the sum of the two interior opposite angles.
Given A ABC whose side BC has been produced to D forming exterior angle ACD .
To prove ACDBA
Proof. In ABC
0180 ACBBA ….(1)
0180 ACDACB ….(2) (straight angle)
From (1) and (2), we get
ACBBAACDACB
BAACD

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles89
ACDBA
IX ACADEMIC QUESTIONS Subjective
Assengment-2
1. In the figure, find BED .
2. In figure, prove that CBAx .
3. In the figure, find x and y, if AB || DF and AD ||
FG.
4. In the figure, prove that DE || BF.
5. In the figure, AB || DG, AC || DE, EDH = 250
and BAC = 200, Find x and y.
6. In the figure, CD AB, ABE = 1300 and
BAC = 700. Find x and y.

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles90
7. If ABD = 1250 and ACE = 130
0, then BAC
= …….
Congruent Figures
The geometric figures are said to be congruent if they are exactly of the same shape and size.
(a) Congruent segments. Two segments are congruent if they are of the same length and conversely.
Hence in Fig. AB CD
A B
C D
(b) Congruent angles. Two angles are congruent if they have equal measures and conversely.
Hence in fig. FDEBAC
(c) Congruent circles. Two circles are congruent if they have equal radii and conversely.
Hence in fig.
If r1 = r2
Then c1 circle c2 circle
Rules for Congruent triangles
Rules 1. (SAS) When two sides and the included angle are given
In DEFandABC
If AB = DE, DA , AC = DF
Then DEFABC .

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles91
Rule 2 (SSS). When three sides are given
In DEFandABC
If AB = DE, BC = EF, CA = FD
Then DEFABC .
Rule 3 (ASA). When two angles and the included side is given
In DEFandABC
If EB , BC = EF, FC
Then DEFABC .
Rule 4 (R.H.S). When Right Angle – Hypotenuse – Side are given
In DEFandABC
If EB = 900, BC = EF, CA = FD
Then DEFABC .
Congruence Relations of Triangles
(i) Reflexive ABCABC (congruence relation is reflexive) Every triangle is congruent to itself.
(ii) Commutative If DEFABC , then ABCDEF (congruence relation is commutative)
(iii) Transitive If DEFABC , and PARDEF then PARABC (congruence relation
is transitive)
Note : Since the congruence relation is reflexive, commutative and transitive, it is an equivalence
relation.

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles92
IX ACADEMIC QUESTIONS Subjective
Asseingment-3
1. Prove that ABC is isosceles if altitude AD bisects BC.
2. Prove that ABC is isosceles if median AD is
perpendicular to BC.
3. In the fig. it is given that AB = CF, EF = BD and AFE =
DBC . Prove that CBDAFE .
4. ABCD is a quadrilateral in which AD = BC and CBADAB . Prove that :
(i) BACABD
(ii) BD = AC
(iii) BACABD
5. In the fig. AC = AE and AB = AD and BAD = EAC .
Prove that BC = DE.
6. In fig. l || m and M is the mid point of the line segment AB.
Prove that M is also the mid-point of nay line segment CD
having its end points on l and m respectively.

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles93
7. In fig. It is given that BC = CE and 21 . Prove that
DCEGCB .
8. In fig. AD and BC are perpendicular to the line segment AB
and AD = BC. Prove that O is the mid point of line segment
AB and DC.
9. In the figure C is the mid point of AB
CBEBAD
DCBECA
Prove that (i) EBCDAC (ii) DA = EB
10. In the fig. BM and DN are both perpendiculars to the
segments AC and BM = DN. Prove that AC bisects BD.
11. In fig., PS = PR, QPRTPS . Prove that PT = PQ.
12. In fig. AD = AE and D and E are points on BC
such that BD = EC. Prove that AB = AC.
13. In the fig. AD CD and BC CD. If AQ = BP
and DP = CQ. Prove that CBPDAQ .

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles94
14. In the fig. AB = AC, ACDABD Prove that BD = CD.
15. In fig. PQRQPR and M and N are respectively on
sides QR and PR of PQR such that QM = PN. Prove that
OP = OQ, where O is the point of intersection of PM and
QN.
16. In the fig. AB = AC. BE and CF are respectively the
bisectors of B and C . Prove that FCBEBC .
17. AD and BE are respectively altitude of ABC such that AE = BD. Prove that Ad = BE.
18. AD, BE and CF, the altitudes of ABC are equal. Prove that ABC is an equilateral triangle.
19. AD is the bisector of A of a triangle ABC, P is any point on AD. Prove that the perpendicular
drawn from P on AB and AC are equal.
20. ABCD is a parallelogram, if the two diagonals are equal, find the measure of ABC .
21. Fill in the blanks in the following so that each of the following statements is true.
(i) Sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are………….
(ii) Angle opposite to equal sides of a triangle are…………
(iii) In an equilateral triangle all angles are…………..
(iv) In a ABC if A = C , then AB = ……….
(v) If altitudes CE and BF of a triangle ABC are equal, then AB = ……….
(vi) In an isosceles triangle ABC with AB = AC, if BD and CE are its altitudes, then BD is
…………. CE.
(vii) In right triangles ABC and DEF, if hypotenuse AB = EF and side AC = DE, then
ABC ……………
22. Which of the following statements are true and which are false.
(i) Sides opposite to equal angles of a triangle are unequal.
(ii) Angles opposite to equal sides of a triangle are equal.
(iii) The measure of each angle of an equilateral triangle is 600.

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles95
(iv) If the altitude from one vertex of a triangle bisects the opposite side, then the triangle is
isosceles.
(v) The bisectors of two equal angles of a triangle are equal.
(vi) If the bisector of the vertical angle of a triangle bisects the base, then the triangle may be
isosceles.
(vii) If any two sides of a right triangle are respectively equal to two sides of other right triangle,
then the two triangles are congruent.
(viii) Two right triangles are congruent if hypotenuse and a side of one triangle are respectively
equal to the hypotenuse and a side of the other triangle.
23. ABC and DBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC. Show that ACDABD .
24. If ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC. Prove that the perpendicular from the vertices B
and C to their opposite sides are equal.
25. If the altitudes from two vertices of a triangle to the opposite sides are equal. Prove that the triangle
is isosceles.
26. In a right angled triangle, one acute angle is double the other. Prove that the hypotenuse is double
the smallest side.
Inequalities in a Triangle
(i) If two sides of a triangle are unequal, the longer side has greater angle opposite to it.
(ii) If two angles of a triangle are unequal, the greater angle has the longer side opposite to it.
(iii) The sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles96
IX ACADEMIC QUESTIONS Subjective
Assignment-4
1. Prove that the difference of any two sides of a triangle is less than the third.
2. Show that of all the line segments that can be drawn to a given line from a given point not lying on
it, the perpendicular line segment is the shortest.
3. In a right angled triangle, prove that the hypotenuse is the longest side.
4. In the figure, AD is the bisector of A , show that AB > BD.
5. In figure PR > PQ and PS bisects QPR . Prove that
PSQPSR .
6. In the fig. PQ > PR. QS and RS are the bisector of Q and
R respectively. Prove that SQ > SR.
7. In the fig. yx , show that NM .

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles97
XI SCIENCE & DIP. ENTRANCE Subjective
Assignment (MCQ) – 5
1. In the figure AB||CD, 0128ABE ,
020BED , what is the value of EDC ?
(a) 128o
(b) 148o
(c) 108o
(d) 130o
2. In the given figure AB||CD, 030EFC and
0100ECF , then BAF is equal to
(a) 070 (b)
080
(c) 0100 (d)
0130
3. In ABC, when BC is produced on both ways, the exterior angles are 0102 and
0134 , what is
the value of A
(a) 036 (b)
056
(c) 0106 (d)
0112
4. In the figure calculate the value of „y‟ if 05x
(a) 450 (b) 50
0
(c) 600
(d) 900
5. In the figure the value of 0x is
(a) 1000
(b) 1090
(c) 1150
(d) 1200
6. The angles of a triangle are 010x2 , 020x and 010x , which type of
triangle it is?
(a) Equilateral Triangle (b) Right Angled Triangle
(c) Acute Angle Triangle (d) Obtuse Angle Triangle
7. In the trapezium ABCD, EF||AD, what is the value of ACD ?
(a) 070 (b)
060
(c) 050 (d)
040
8. In the figure CE is perpendicular to AB. 020ACE and
050ABD , what is the measure of
BDA ?
(a) 050 (b)
060
(c) 070 (d)
090

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles98
9. In the figure what is the relation of x in term of ,a b and c ?
(a) cbax (b) 90cbax
(c) x 180 a b c
(d) cba180x
10. PN QR and PM is bisector of P in PQR, then ( RQ ) is equal to
(a) MPN (b) MPN2
(c) MPN2
1
(d) MPN
3
1
11. The bisector of exterior angles B and C meet at „O‟, what is BOC
(a) 0120 (b)
080
(c) 045 (d)
040
12. The bisectors of exterior angles of ABC intersect at „O‟ and form a BOC which is always
(a) Acute Angle
(b) Right Angle
(c) Obtuse Angle
(d) None of these
13. The bisectors of interior angles of a triangle forms an angle which is always
(a) Acute Angle
(b) Right Angle
(c) Obtuse Angle
(d) All of these
14. In a triangle ABC, the internal bisectors of angles B and C meet at „P‟ and the external
bisectors of the angles B and C meet at Q, then the BQCBPC is equal to
(a) 090 (b) A2/190
(c) A2/190 (d) 0180
15. In the figure what is the value of cba ?
(a) 090 (b)
0180
(c) 0270 (d)
0360
16. In the figure PM is bisector of P and PN is perpendicular on QR
then the value of MPN is
(a) 030 (b)
040
(c) 060 (d)
0100
17. BM and CM are interior bisectors of B and C while BN and CN are exterior bisectors of
B and C respectively. Which is correct?
(a) 0110BMC
(b) 070BNC
(c) 0180BNCBMC

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles99
(d) All are correct
18. In a ABC, AB = 5cm, AC = 5cm and A = 50o, then B =
(a) 35o (b) 65
o (c) 80
o (d) 40
o
19. If two sides of a triangle are unequal then opposite angle of larger side is
(a) greater (b) less (c) equal (d) half
20. The sum of attitudes of a triangle is_______ than the perimeter of the triangle
(a) greater (b) less (c) half (d) less
21. In the given figure, PQ = QR, QPR = 48o, SRP = 18
o, then PQR =
(a) 48
o (b) 84
o (c) 30
o (d) 36
o
22. In the given figure, PQR is an equilateral triangle and QRST is a square. Then PSR =
(a) 30
o (b) 15
o (c) 90
o (d) 60
o
23. Can we draw a triangle ABC with AB = 3cm, BC = 3.5cm and CA = 6.5cm?
(a) Yes (b) No (c) Can‟t be determined (d) None of these
24. Which of the following is not a criterion for congruence of triangles?
(a) SSA (B) SAS (c) ASA (d) SSS
25. In the given figure, AB BE and EF BE. Also BC = DE and AB = EF. Then
(a) BD = FEC (b) ABD = EFC (c) ABD = CMD (d) ABD = CEF
26. In quadrilateral ABCD, BM and DN are drawn perpendicular to AC such that BM = DN. If BR
= 8cm, then BD is

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles100
(a) 4cm (b) 2cm (c) 12cm (d) 16cm
27. In the given figure PQ > PR, QS and RS are the bisectors of Q and R respectively.
(a) SQ = SR (b) SQ > SR (c) SQ < SR (d) None of these
28. In the figure, PS is the median, bisecting angle P, then QPS is_______
(a) 110
o (b) 70
o (c) 45
o (d) 55
o
29. In the given figure x and y are
(a) x = 70
o, y = 37
o (b) x = 37
o, y = 70
o (c) x + y = 117
o (d) x – y = 100
o
30. In the given figure BD AC, the measure of ABC is
(a) 60
o (b) 30
o (c) 45
o (d) 90
o

011-26925013/14+91-9811134008+91-9582231489
NTSE, NSO Diploma, XI Entrance
Triangles101
ANSWER
Assignment – 1
2. A = 71o 5. 30
o, 50
o, 100
o 6. 52
o, 53
o, 75
o
9. (a) 180o (b) 91
o (c) 40
o, 40
o, 100
o (d) 18
o (e) one (f) one
10. (a) False (b) True (c) False (d) True (e) False (f) True
Assignment – 2
1., BED = 82o 3. x = 60
o, y = 55
o 5. x = 115
o, y = 20
o 6. x = 40
o, y = 20
o
7. 75o
Assignment – 3
20. 90
21. (i) equal (ii) equal (iii) 60 (iv) BC (v) AC
(vi) Equal to (vii) EFD
22. (i) False (ii) True (iii) True (iv) True (v) True
(vi) True (vii) True (viii) True
Assignment – 5
1.c 2.d 3.b 4.b 5.d 6.b 7.a 8.b 9.c 10.d 11.c 12.a
13.c 14.d 15.d 16.a 17.d 18.b 19.a 20.b 21.b 22.b 23.b 24.a
25.a 26.d 27.b 28.c 29.b 30.d