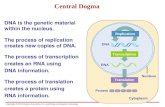
DNA Info DNA in the nucleus is safe But DNA in the cytoplasm can be destroyed.
Transcription and Translation. If DNA never leaves the nucleus, how can the DNA message get to the...
-
Upload
dora-preston -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
Transcript of Transcription and Translation. If DNA never leaves the nucleus, how can the DNA message get to the...
If DNA never leaves the nucleus, how can the DNA message get to the site of protein production, the ribosome?
Answer: The DNA message is copied to RNA during the process of Transcription
D. The Structure of RNA
1. RNA is single stranded
2. The sugar in RNA is Ribose, not deoxyribose as in DNA
3. The DNA nucleotide thymine is replaced by the RNA nucleotide Uracil
E. RNA’s Functions: Two Types, Two Jobs
1. m-RNA (messenger RNA) delivers the copied DNA from the nucleus to the Ribosome- the site of protein synthesis
2. t-RNA (transfer RNA) picks up specific amino acids in the cytoplasm and delivers them to the ribosome
F. Steps in Protein Synthesis1. DNA molecule unzip where the desired gene is located
2. Free floating RNA nucleotides pair with the DNA strand forming m-RNA (Transcription)
3. The m-RNA leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome
4. A specific t-RNA delivers a specific amino acid to the ribosome (Translation)
5. The m-RNA codon matches with the t-RNA anticodon bringing the amino acid into its proper place
6. When the next amino acid is in place, the two are joined in a condensation reaction
7. The process is repeated until a stop code is read and a complete protein is formed
G. Mutation- change in the genetic
code 1. Gene Mutation or Point Mutation- a nucleotide base is added, subtracted or changed to produce a change in the amino acid sequence of a protein
A change in a single base in the DNA strand will result in a change in the m-RNA strand and the resulting protein
Normal Hemoglobin
DNA
GGA CTC CTC
RNA
CCU GAG GAG
Amino Acids
Proline Glutamic Acid Glutamic Acid
Sickle Cell Hemoglobin
5 6 7
GGA CAC CTC CCU GUG GAG Proline Valine Glutamic Acid
2. Chromosome Mutation- involves a change in many genesa) Deletion- part of a chromosome is lost
b) Inversion- part of a chromosome is flipped around
c) Translocation- part of a chromosome is added to another chromosome
3. Somatic & Germ Mutationsa) Somatic mutations: change that occurs in body cells. Affects only the individual. Ie. cancer
b) Germ Mutations- changed in the genetic code of gametes that will affect the individuals offspring
4. Mutagens- substances capable of causing damage to DNA
5. Most mutations are harmful