Topic 2 – The Ecosystem 2.1 - Structure IB Topics 2.1.1-2.1.7.
-
Upload
vivien-harmon -
Category
Documents
-
view
233 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Topic 2 – The Ecosystem 2.1 - Structure IB Topics 2.1.1-2.1.7.

2.1 - StructureIB Topics 2.1.1-2.1.7
Topic 2 – The Ecosystem

Key Words (define and provide a local example of each)
Biotic Abiotic Trophic Level Producer Consumer Autotroph Heterotroph Carnivore Herbivore Omnivore
Species Population Community Habitat Ecosystem Niche Competition Mutualism Parasitism Predation

Biotic and Abiotic ComponentsBiotic
All living components of the ecosystem
Ex:
Abiotic All non-living
components of the ecosystem
Ex:

Food Chains The position an organism occupies in a
food chain is called the trophic level.



Local Food Chain Example:Make your own food chain with Wisconsin species.

Food Webs Ecosystems
contain many interconnected food chains


Pyramid of Numbers A graphical model
of the number of organisms in a food chain


Pyramid of Biomass A graphical model
of the amount of biomass present in a food chain at a certain point in time

Pyramid of Productivity A graphical model
of the rate of energy production over time

Top CarnivoresBioaccumulation
Toxins (pesticides, etc.) can be retained in fat tissue
Biomagnification
Each successive trophic level gains more toxin

2.2 – Measuring Abiotic ComponentsIB Topics 2.2.1-2.2.2
Topic 2 – The Ecosystem

Significant Abiotic FactorsTerrestrial Ecosystem
Includes: land Temperature Light intensity Wind speed SOIL• particle size• moisture• drainage• mineral content
Marine Ecosystem
Includes: Oceans, estuaries, salt marshes and mangroves salinity temperature wave action dissolved
oxygen pH
Freshwater Ecosystem
Includes: lakes, rivers, streams,
wetlands turbidity temperature flow velocity pH dissolved
oxygen

2.3 – Measuring Biotic ComponentsIB Topics 2.3.1-2.3.5
Topic 2 – The Ecosystem

Estimating abundance of organisms Counting the
number of organisms is almost always done using an estimate

Lincoln Index A mathematical
model to estimate population size
Capture-mark-release-recapture

Example 1
13 deer were caught and marked
14 deer were caught the second time and 5 were marked
Example 2
75 Ladybugs were caught and marked
80 Ladybugs were caught the second time and 3 were marked

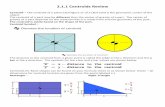
Quadrats A square of area
used to measure the population of non-mobile organisms Can help to
calculate population density and percentage cover

Diversity1. The number of
different species
2. The number of individuals of each species

Simpson’s Diversity Index Used to compare
diversity between areas
High value of D implies stable ecosystem
Low value of D implies unstable ecosystem

2.4 – BiomesIB Topics 2.4.1-2.4.2
Topic 2 – The Ecosystem

Biomes A collection of
ecosystems that share similar climactic conditions

Rainforest
Desert Tundra Temperate Forest
Grassland
Prevailing Climate
Location
Sun Exposure
Precipitation
Limiting Factors

Rainforest
Desert Tundra Temperate Forest
Grassland
Prevailing Climate
Hot, Humid, Rainy
Hot, Dry Cold Seasonal Varied by location
Location Near Equator
Varied, where no
precip
Poles 40-60o N Latitude
Varied, where some precip
Sun Exposure
High Varied, usually
high
Low Medium, Seasonal
Varied
Precipitation
High None Snow Medium, Seasonal
Low
Limiting Factors
Too much precip.
Not enough water
Too cold, permafrost
Seasons Low precip

2.5 – FunctionIB Topics 2.5.1-2.5.7
Topic 2 – The Ecosystem

Photosynthesis

Respiration


Energy Flow Through the Ecosystem








Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)The amount of
energy produced by producers

Net Primary Productivity (NPP)The amount of
energy stored by producers and available to consumers

Gross Secondary Productivity (GSP)The amount of
energy consumed by consumers

Net Secondary Productivity (NSP)The amount of
energy stored by consumers and available to the next trophic level

Simplified Example:

2.6 – ChangesIB Topics 2.6.1-2.6.7
Topic 2 – The Ecosystem

Carrying Capacity The maximum
number of organisms an ecosystem can support sustainably over a long period of time

Limiting Factors Factors that limit
the amount of individuals in an ecosystem

Tolerance Species will be most abundant within a
certain range of a limiting factor

Population CurvesS Curve
Reaches carrying capacity and stabilizes J Curve
Unchecked population growth

Limiting Factors Density-
dependent factors Limit population
size more as population increases

Limiting Factors Density-
independent factors Limit population
size regardless of population size

r-strategists Opportunistic
species Inhabit
unstable/changing environments
Reproduce early/often, mature quickly
Slow growing/maturing species
Few offspring Long lifespans
K-strategists
C-strategists In between r & K


Survivorship Curve

SuccessionA natural increase in the complexity of
the structure and species composition over time



SuccessionPrimary
Occurs on uncolonized substrate (rock)
Secondary Occurs where a
previous community has been destroyed


Zonation Different
types of ecosystems in a gradient due to elevation or resources Ex: Altitude
zonation on a mountain


Climax Community A stable, complex
ecosystem in a late stage of succession
Characteristics:

2.7 – Measuring ChangesIB Topics 2.7.1-2.7.3
Topic 2 – The Ecosystem

Environmental Impact Assessment
Before any development gets permission to begin, an EIA must be done
Predicts the potential impacts on habitats, species, and ecosystems



Baseline Study Habitat type Species list Species diversity Endangered
species Land use Hydrology Human population Soil quality