Endocrine system and nutrition; Nutrition and endocrine system
Topic 2 Endocrine System
Transcript of Topic 2 Endocrine System
-
7/29/2019 Topic 2 Endocrine System
1/7
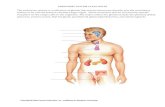
X INTRODUCTIONIn this topic, we will proceed with the discussion on the endocrine system. Theendocrine system executes various physiological processes through chemicalmessengers called hormones. The endocrine system is a collection of glands thatsecrete hormones which are necessary for normal bodily functions. Theendocrine system, as shown in Figure 2.1, comprises the pituitary, parathyroid,thyroid, adrenals, pancreas and ovaries or testes. The hypothalamus in the brainreceives information from nerve cells about both the internal condition of the
body and the external environment. It then responds to those conditions over the
endocrine system by using the pituitary gland to relay directions to other glands.
TTooppiicc
22X
EndocrineSystem
By the end of this topic, you should be able to:
1. Explain the role of hormones in humans;
2. Describe animal hormones and their functions;
3. Identify plant hormones and their functions; and
4. Differentiate between animal and plant hormones.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
-
7/29/2019 Topic 2 Endocrine System
2/7
TOPIC 2 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM W 33
Figure 2.1: The endocrine systemSource: http://www.drstandley.com
ROLE OF HORMONES IN HUMANS
An endocrine gland or ductless gland is a group of specialised cells that producesand secretes hormones into the bloodstream. Only small concentrations ofhormones are needed for their effectiveness. Table 2.1 lists several endocrineglands and some of their secreted hormones which help to maintain homeostasiswithin the human body.
2.1
-
7/29/2019 Topic 2 Endocrine System
3/7
X TOPIC 2 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM34
Table 2.1: Major Human Endocrine Glands and Their Secreted HormonesSite of secretion Hormone
Pituitary gland ADH, Oxytocin, GH, TSH, FSH, Prolactin
Thyroid gland Thyroid hormone
Parathyroid gland Parathyroid hormone
Adrenal Adrenalin
Pancreas Insulin, Glucagon
Ovaries Estrogens, Progesterone
Testes Testosterone
Endocrine glands are located in strategic areas around the body. Their hormonesregulate a vast range of activities including blood glucose concentration, heartrate, metabolism, growth rate, reproduction and water balance.
To further our understanding of endocrine glands and hormones, let us take alook at the following scenario.
Fight or FlightImagine that you suddenly see a tiger in a jungle. What will you do? Do youwant to fight with the tiger? Maybe you should run as fast as you can, awayfrom the tiger? Do you want to fight or take flight? Whatever your decision, ithas something to do with interaction between the endocrine system andnervous system. Impulses are sent through the nervous system so the adrenalglands get the message to secrete adrenaline hormone. Consequently, the
breathing and heart rate increase which causes the transportation of oxygenand glucose into the body cells to become rapid. Eventually, more blood ispumped to the muscles and the brain. As a result, a quick decision can bemade by the brain, and there is an increase in energy production and bloodpressure.
-
7/29/2019 Topic 2 Endocrine System
4/7
TOPIC 2 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM W 35
ANIMAL HORMONES
Although hormones will reach the entire parts of the body through blood
circulation, each hormone will have its own target organ. Due to this, eachhormone has its own specific function. Lets take a look at Table 2.2 on animalsmain hormones and their functions.
Table 2.2: Main Animal Hormones and Their FunctionsHormone FunctionsAntidiuretichormone (ADH)
x Promotes reabsorption of water by kidneys
Oxytocin x Stimulates contraction of uterus
x Stimulates milk flow from the mammary glands
Growth hormone(GH)
x Stimulates growth
x Stimulates metabolic functions
Thyroidstimulatinghormone (TSH)
x Regulates growth of thyroid glands and its hormone secretion
Folliclestimulatinghormone (FSH)
x Stimulates production of ova and sperm
x Stimulates estrogens secretion in ovaries
x Stimulates testosterone secretion in testes
Prolactin x Stimulates mammary glands to secrete milk
Thyroid hormone x Stimulates and maintain metabolic processes
Parathyroidhormone
x Raises blood calcium level
x Regulates bone formation
Adrenaline x Prepares body for action such as increasing blood glucose, heartrate and metabolic rate
Insulin x Lowers blood glucose concentration
Glucagon x Raises blood glucose concentration
Estrogens x Promote development and maintenance of female secondary sexcharacteristics
x Stimulate uterine lining growth
x Control menstrual cycle and pregnancy
Progesterone x Controls menstrual cycle and pregnancy
Testosterone x Promotes development of testes and male secondary sexcharacteristics
2.2
-
7/29/2019 Topic 2 Endocrine System
5/7
X TOPIC 2 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM36
Study, think and matchthese keywords!Get more information by borrowing books in the library or surfing theInternet to group these keywords. These keywords represent endocrineglands, hormones and functions of those hormones. Then, summarisethem in the table below.
Endocrine gland Hormone Function
ACTIVITY 2.1
-
7/29/2019 Topic 2 Endocrine System
6/7
TOPIC 2 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM W 37
PLANT HORMONES
Plant hormones are also known as plant growth substances. Unlike animalhormones, plant hormones are not manufactured in special organs. Instead, theyare made by cells in many different parts of the plant. They regulate manyaspects of plant growth and development, from seed formation and germinationto the maturity and death of the plant. There are five major types of planthormones: auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid and ethene. Table 2.3
below provides a brief explanation of their respective functions.
Table 2.3: Plant Hormones and Their FunctionsHormone Production Site and Functions
Auxins Synthesised in the apical meristems to promote primary growthby increasing the rate of cell elongation.
Gibberellins Formed in young leaves to stimulate the growth of shoots andleaves.
Cytokinins Synthesised in the roots and transported to other parts of theplant. When combined with auxins, it stimulates cell division.
Abscisic acid Synthesised in chloroplast to promote dormancy in some seedsand stimulates the closing of stomata.
Ethene/Ethylene Released from ripening fruit, nodes of stems, ageing leaves and
flowers. Involved in seed dormancy, fruit ripening and leafabscission.
2.3
ACTIVITY 2.2
Test your knowledge on the major types of plant hormones bymatching the hormones below to each function.
Auxin Ethylene Cytokinins
Function HormonesRipen fruit
Shoot growth
Increase stem length
-
7/29/2019 Topic 2 Endocrine System
7/7
X TOPIC 2 ENDOCRINE SYSTEM38
Endocrine system is a collection of glands that secretes hormones, which arenecessary for normal human bodily functions such as digestion, metabolism,growth, reproduction, heart rate and water balance.
Plant hormones act either to stimulate or to inhibit certain parts of plants.
Animal hormones
Endocrine gland
Endocrine system
Plant hormones
Kent, M. (2000). Advance biology. New York: Oxford University Press.
Mader, S. S. (2010). Biology. New York: McGraw-Hill.
SELF-CHECK 2.1
Describe the role of hormones in the cycle of a girls life until shebecomes a woman, gets married and gives birth.