Tissue ID- ing Practice
description
Transcript of Tissue ID- ing Practice
Tissue IDing Practice
Tissue ID-ing PracticePractice for the histology test
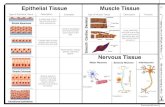
Simple squamous
Description: Single layered flattened cell, nuclei is centered
Function: to allow passage for materials where security is not important; secretes lubricating substances
Location: Kidney, air sacs of the lungs
2.?
Simple Cuboidal
Description: Single layered cubelike cells
Function: to absorb and secrete
Location: Kidney, ovary surface
Simple Columnar
Description: single layer tall cells with round to oval nuclei..a little bit of cilia
Function: To secrete and absorb mucus
Location: stomach, anal canal
Pseudostratified epithelium
Description: Looks like simple columnar but with more cillia and contains goblet cells..differing heights
Function: To secrete mucus through ciliary function
Location: linings of the trachea, male sperm carrying duct
Stratified Squamous
Description: Multi-layered with a squamous apical surface
Function: To protect underlying tissues from abrasion
Location: Mouth, linings of the esophagus
Transitional Epithelial
Description: resembles both stratified squamous and cuboidal; basal cells are cuboidal and columnar
Function: to allow organs to expand when contained with urine
Location: bladder
Hyaline
Description: Smooth firm matrix
Function: support and reinforce
Location: trachea, larynx
Elastic
Description: Similar to hyaline, but more elastic fibers in matrix
Function: Maintains shape of structure and allow flexibility
Location: external ears (pinna)
Fibrocartilage
Description: Matrix is similar but less firm than hyaline
Function: ability to absorb compressive shock.
Location: intervertebral discs, discs of knee joint
Osseous (Bone) Tissue
Description: hard, calcified matrix containing collagen fibers
Function: Bone supports and protects: lever for muscles to act on
Location: Bones
Blood
Description: Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix
Function: transport respiratory gasses and nutrients
Location: within blood vessels
Nervous Tissue
Description: branching cells surrounded by supporting cells (neuroglia)
Function: Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors; control activity
Location: brain, spinal cord, nerves
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
Description: Striated, long, cylindrical
Function: Voluntary movement, facial expression, control
Location: attached to bones
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
Description: Striated, branching, has intercalated discs
Function: Involuntary control; propels blood into circulation.
Location: Walls of heart
Smooth Muscle Tissue
Description: central nuclei, no striations, sheet-like
Fuction: Propels substances along internal passageways; involuntary control
Location: Walls of hollow organs
Areolar Tissue
Description: Gel-like matrix with all three fibers: Elastic, Collagen and fibroblast fibers
Function: wrap and cushion organs; provide protection and holds tissue fluid
Location: under epithelia
Adipose Tissue
Description: Made up of close packed adipocytes which are fat cells. Nuclei pushed to the side
Function: Provides reserve fuel and organ protection
Location: Breast, within the abdomen