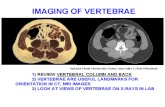
Thorax Part 2 Vertebrae, Spinal cord, Lymph nodes, Thymus.
-
Upload
austin-walsh -
Category
Documents
-
view
219 -
download
0
Transcript of Thorax Part 2 Vertebrae, Spinal cord, Lymph nodes, Thymus.

Thorax Part 2Vertebrae, Spinal cord, Lymph nodes, Thymus

Be able to spell & define:
1. Vertebra / vertebrae 11. paralysis2. Intervertebral disk 12. paraplegia3. Degenerative 13. quadriplegia4. Cervical 14. lumbar puncture5. Thoracic 15. lymph / lymphoid6. Lumbar 16. thymus7. Sacrum 17. T-cells8. Coccyx 18. Helper T-cells9. Meninges 19. Killer T-cells10. Cerebrospinal fluid
MQ #2
when fin’d

5. Vertebrae, aka spine, vertebral column
Functions:1. Support head2. Attach ribs3. Protects spinal cord
1 vertebra2 vertebrae


Each vertebra is separated by a disc of cartilage
(intervertebral disk)1 inch diameter x ¼ inch thick
Spinal cord

This disc cushions like a shock absorber
Prevents bone rubbing against bone

As we age….1. Disks thin > loss of height2. Become less flexible3. Become more prone to injury

Degenerative Disk Disease• https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q_5U7skcQeM
•Area of spine most affected•6 possible S/S• Tx’s

5 areas of vertebral column
1. cervical vertebrae• Neck bones• C1 – C7• Smallest vertebrae

5 areas of vertebral column
2. thoracic vertebrae• Bones of chest/upper back• T1 – T12• Larger than cervical• Ribs attach here

5 areas of vertebral column3. lumbar vertebrae
• Bones of lower back• L1 – L5• Largest vertebrae

5 areas of vertebral column
4. sacrum• Wedge-shaped• 5 fused vertebrae• Back of pelvis• Hips attach here

5 areas of vertebral column
5. coccyx• Tailbone• 4 fused vertebrae

5 minutes to create a mnemonicC (soft) T L S C (hard)
CindyTookLisa’sSugar
Cookies

Scoliosis = condition of being crooked
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PEtGUESDTAo
Girls > boysTeens
Can be asymptomaticCan interfere c organs

6. Spinal Cord• Extension of brain > L2• White, soft, delicate nerve tissue• Protected by meninges, CSF & vertebrae• ≈ 1 cm diameter (pinky)• Cells CANNOT regenerate ***
CSF = cerebrospinal fluid
Meninges = 3 layers of membranes
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gg0F67mnTys



6. Spinal Cord 2 main functions:1. Reflex center (brain to & from body)2. Conduction pathway (brain to & from body)

Same 3 sections as Vertebral Column Top 3:
1. Cervical2. Thoracic3. Lumbar (thru L2)

Off the SC, are branches known as SPINAL ROOTS/NERVES.
• It is from these SPINAL ROOTS/NERVES that all other nerves appear.

Spinal roots in the CERVICAL area control what?

Spinal roots in the THORACIC region control what?

Spinal roots in the LUMBAR area control what?

Beyond L2, the SC ‘frays’ into the ‘cauda equina’ …. Any guess what that means?

The nerves from the cauda equina (in the sacral area) control what?

Paralysis• PARALYSIS = loss of control/sensation/voluntary movement• Severing (cutting) of SC will result in paralysis BELOW the injury• WHERE in SC determines degree of paralysis• The HIGHER in the SC, the GREATER the loss of fxn

AT THE PRESENT TIME….
•A severed spinal cord CANNOT regenerate.•PERMANENT. Hope is on the horizon…

Photo paralysis / SC
5

Paralysis: paraplegia, quadriplegia• Paraplegia = Loss of control near chest / waist area• Quadriplegia = Loss of control in neck (WORST!!!)• Aka TETRAPLEGIA
-plegia = paralyzedpara- = pair, near
quadri- = 4
How alike? How different?
7

Tony Dowels
http://www.wtsp.com/video/3458485754001/53147622001/Vote-and-help-paralyzed-student-win-custom-van

Curing Paralysis
• Invivo, future cure http://www.wxyz.com/about-us/as-seen-on/new-invivo-therapeutics-technology-could-mean-a-cure-for-paralysis
6

Lumbar Puncture aka ‘SPINAL TAP’•NEEDLE is inserted between 2 VERTEBRAE,
thru the MENINGES until reaching the CSF. • A sample of CSF is withdrawn by the NEEDLE.• Test the CSF for WBC, PATHOGENS, etc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=O_RjwNMZws8

Epidurals• local anesthetic is injected near the spinal
cord/nerve roots to block sensations of pain in regions such as the abdomen, hips, legs, or pelvis
Not ONLY during L&D
3
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zIoCKN9Bt-I

Appearance of normal CSF: CLEAR, like water• LP & epidural are ALIKE: • Needle into intervertebral space• Sterile technique• Know what you’re doing!• Not near Sp. Cord!
• LP & epidural are DIFFERENT: • In LP, CSF is REMOVED• In E, meds are ADDED

7. Lymph Nodes

What is
lymph?
• Straw-colored fluid containing WBC’s• Moves around in a NETWORK of LYMPH VESSELS similar to
(and parallel to) BLOOD VESSELS• Bathes TISSUES & drains LYMPH VESSELS into
BLOODSTREAM• SLOW moving (heart/blood much faster!)• Lymph has NO heart to pump• Our MUSCLE MOVEMENTS move lymph
4

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qTXTDqvPnRk
• British pronunciation of• Capillaries (ka PILL or ees)• Circulatory (SIR cu LIT tory)

http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/anatomyvideos/000084.htm
Lymph System & Breast CA

Lymph Nodes (NOT glands!)• Little ‘bumps’ along lymph vessels. (Picture garbage cans.) • Lymph is filtered (pathogens, abnormal cells, etc.)• Contain WBC’s (picture Army barracks)• Arm pit, neck, behind ear, groin, beneath sternum, etc.
My Lymph Nodes are Swollen…what does that mean? READ THIS!

8. Thymus

Thymus

Thymus • Small, lymphoid structure (similar to….?• Beneath sternum, near heart• Infancy & Childhood: BIGGEST! • Makes special WBC’s called T-cells.• Puberty: shrinks in size• -ectomy in adults > no problem• -ectomy in childhood > severe immune deficiency

Thymus • T-cells = are special WBC’s that are made in the BONE MARROW then travel to the THYMUS to MATURE

ThymusMATURE T-cells leave the THYMUS and travel to the SPLEEN, TONSILS & LYMPH NODES where they FIGHT INVADERS
Why were these cells named
“T-cells”?

2 types of T-cells
1. Helper T-cells• “scouts”• “whistle-blowers”• “organizers”
2. Killer T-cells• “assassins”• Kill virus-making cells
HIV kills T-cells, esp the HELPER T-cells

Thymus&
T-cells

Thymus&
T-cells
What’s important in the reading section at the end of the page?

MQ 2….When? On what?