Thermodynamics and thermophysical properties of liquid Fe-Cr alloys Thermodynamics and...
-
Upload
mary-williamson -
Category
Documents
-
view
240 -
download
0
Transcript of Thermodynamics and thermophysical properties of liquid Fe-Cr alloys Thermodynamics and...

Thermodynamics Thermodynamics and thermophysical and thermophysical properties of liquid Fe-Cr alloysproperties of liquid Fe-Cr alloys
Rada NovakovicRada Novakovic
National Research
Council (CNR–IENI)
Genoa, Italy

Mixing behaviour of liquid binary alloys: energetic & structural factors
Observable indicators: Phase diagrams. Empirical factors – physical, chemical & structural
properties of alloy constituents (liquid metals), melting points, volume, first shell coordination, radius size, valence difference, electronegativity difference...
Thermodynamic functions – heat capacity, enthalpy, activity, excess Gibbs energy.
Microscopic functions – concentration fluctuations in the long wavelength limit & CSRO (Warren-Cowley short range order) parameter.
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

What kind of input data are necessary for modelling?
1. Thermodynamic dataon mixing: heat capacity; enthalpy; entropy; Gibbs
energies (integral & excess).partial quantities: activities (or chem. potentials). 2. Phase diagram informationtype of alloy system: segregating or compound
forming3. Thermophysical data: molar volume, surface
tension, viscosity of pure components.4. Structural data: coordination number; neutron
diffraction data to be transformed into the microscopic functions
5. Experimental data on Thermo-Physical properties of alloys: for a comparison with theoretical results
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

The Fe-Cr system
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Thermodynamic data of the Fe-Cr liquid phase [11Xiong] An improved thermodynamic modeling of the Fe–Cr system
down to zero kelvin coupled with key experiments[86Mas] The Fe-Cr phase diagram[76Hul;81AB;82HS;87AS] previous assessments of the p.d.[93BLee] The reassessment of the Fe-Cr phase diagram[93BLee] T=1873K: The optimised term of the excess Gibbs free energy;the enthalpy of mixing [84Bat]; the activities [80Mar;69Fru;69Gil;98Zai]. [06Vre] The presence of interm. - phase [06Ter] The melting, the enthalpy of mixing, thermal diffusivity - by atomic
simulations
Comment: The Cr-Fe phase diagram can be considered as COMPLETE (although some measurements in the liquid phase are necessary).
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Results of calculations
- phase energ. favoured ( AB )
Weak influence on the energetics of the Fe-Cr liquid phase.
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Results of calculations
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

SURFACE TENSIONSURFACE TENSION
SURFACE TENSION MODELS
Binary systems
Ternary systems
Geometric models
EXAMPLES: Fe-Cr, Al-Nb-Ti

Surface properties of liquid binary alloys:
surface segregation & surface tension
Butler(1932) published the paper proposing his well known equation:
( i = A, B), that gives the relation between the surface tension and thermodynamics of liquids in which the bulk and surface phases are in equilibrium.
bi
si
i
Bi
a
aTkln
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

and combining with
and taking into account the bulk (surface) phase activity coefficients obtained by Fowler_Guggenheim method asand
the and xs can be calculated. The surface tension can be calculated inserting xs into the Butler’s equation.
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, September 19-23, 2011,
Lerici (SP), ItalyLerici (SP), Italy
)]}1ln([ln)]1ln(){[ln/( xxSRT Bss
BBB
)lnln( BBAAxsM xxRTG
)}1ln()1ln()21{ln(2
ln sssss
sB xx
z
}ln)1ln()21{ln(2
ln sssss
sA xx
z
Subtracting Butler’s equ. for both components,)}ln(lnln){ln/( xxSRT A
ssAAA

Surface tension calculations of binary systems
* Models based on Butler’s equation
- Regular solution
- Subregular solution
- “Central” atom
- Compound Formation Model (CFM)
- Self Aggregating Model (SAM)
An interface Liquid / Gas :
& * Probabilistic Models
Singh et al.
Monolayer or Multilayers

Surface tension calculations of ternary systems
* Models based on Butler’s equation
- Regular solution- Subregular solution- “Central” Atom- Compound Formation Model (CFM)- Self Aggregating Model (SAM)
An interface Liquid / Gas
:
& * Geometric Models (from thermodynamic
calculations of mixing properties in the bulk)
SYMMETRIC- Kohler; Colinet; Muggianu
ASYMMETRIC- Toop; Bonnier; Hillert;
GENERALIZED - Chou
Monolayer

Geometric modelsKohlerKohler
ToopToop
ChouChou
31)31(1)31(3
1323
)23(3)23(2
3212
)12(2)12(1
21 xsxsxsxs
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
XX
);()()1;(1
)1;(1 32
3
32
223
2321113
1
31112
1
2
XX
X
XX
XXXXX
X
XXX
X
X xsxsxsxs
3/2232
323/1132
312/1122
21 )()()()()()( XXxs
XXxs
XXxsxs XXXXXX


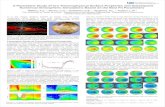
Iso-surface tension lines of liquid Al-Ti-Nb alloys calculated by the Butler equation for the regular solution model at 2073 K. The square symbol represents the composition location of the Ti46Al46Nb8 (at.%) in the Gibbs triangle and the corresponding surface tension calculated value
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Surface tension reference data of Cr
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Surface tension reference data of Fe
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Results of calculations
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Results of calculations
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Results of calculations
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Microscopic functions (B-T) & Thermodynamics
For ideal solution the SCC(0) becomes
The CSRO parameter and SCC(0) are related to each other by
where Z is the coordination number.
BAidCC ccS )0(
1
1
)1(1
1)0(
Zcc
S
BA
cc
1
,,
1
,,
1
,,
2
2
)0(
NPTB
BBA
NPTA
AAB
NPTA
Mcc C
aaC
C
aaC
C
GRTS
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Microscopic functions & local arrangements of atoms in the melt
SCC(0) and CSRO parameter indicate chemical order & segregation (phase separation):
SCC(0) – the nature of mixing
CSRO parameter – the degree of order
Criteria for mixing behaviour
1. SCC(0) < SCC(0, id) presence of chemical order
SCC(0) > SCC(0, id) segregation
2. -1 < CSRO < 0 ordering in the melt
CSRO = -1 complete ordering
0 < CSRO < 1 segregation
CSRO = 1 phase separation
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Results of calculations
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

The interdiffusion coefficient (Dm) can be given in terms of the SCC(0) by
For “ideal” alloys, SCC(0)= SCC(0,id)= cAcB, then
and finally combining the last two eqs. it is obtained,
The criteria for mixing behaviour:SCC(0) > SCC (0, id) segregation Dm < Did
SCC(0) < SCC (0, id) presence of chem. order Dm > Did
)0(
)0()( **
CC
idCC
ABBAm S
SDcDcD
idABBAABBAm DDcDcDcDcD )( **
)0(
)0(
CC
idCC
id
m
S
S
D
D
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Results of calculations
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Viscosity Viscosity () of liquid alloys - the atomic level structure and interactions.
The composition dependence of of liquid alloys in respect to the linear low (ideal mixture):
- a linear variation (simple liquids, e.g. Ag-Au, Sn-Pb, Bi-Pb) - positive deviations (compound forming alloys, H <<0)- negative deviations (segregating alloys, H >>0).
Sometimes the viscosity of binary liquid alloys exhibits “strange” behaviour (Bi-Ga, Bi-Cu, Ga-Hg..), i.e. the same behaviour as their thermodynamic functions (according to the theory should be opposite!)
00BBAAid cc

In the framework of the QLT the viscosity, , is related to the SCC(0) and diffusion by:
For a thermodynamically ideal mixture,SCC(0)=SCC(0,id)=c(1-c) previous equ. becomes:
with
and for the viscosity of pure components (Stokes-Einstein)
Assuming 1 = 2 = =1, it is obtained the Stokes-Einstein type relation for diffusion and viscosity:
)0()(
CC
BA
A
B
B
A
id
B
S
CCCC
D
Tk
)(A
B
B
Amid
Bid
CC
D
Tk
idBB
BidB
BBid
AA
BidA
BA D
Tk
rD
Tkand
D
Tk
rD
Tk
33
idAB
idBA
idm DcDcD
Tk
DD BidB
idA

Recently, we proposed the following viscosity
equation:
where mi and i (i=A,B) are parameters that can be calculated from the experimental data.
)0())exp()exp(
(CC
BA
ABB
B
BAA
A
id
B
S
CC
Cm
C
Cm
C
D
Tk

Results of calculationsviscosityviscosity of some binary systems

Modelling of the interfacial properties of molten Pb / FeCr substrate system: Application of the
Phase Field Method
Study of thermodynamics and thermophysical properties of the Fe-Cr, Fe-O, Pb-O, Fe-Cr-Pb, Fe-Cr-Pb-O systems
Model formulation and implementation Collection of input parameters for the Pb-Fe and Pb-Cr systems Simulations, analysis of model parameters and validation with
experimental micrographs for the Pb-Fe and Pb-Cr systems Extension of the model and implementation towards ternary
system Pb-Fe-Cr Collection of input parameters for the Pb-Fe-Cr system Simulations for the interface between molten Pb / FeCr -
substrate system Comparison with experimental micrographs for Pb / Fe-Cr
diffusion couples
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy

Thank you for your attention!
MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, MATGEN-IV.3 summer school on “Materials for Generation IV reactors: Fundamentals, ongoing research and open questions”,ongoing research and open questions”, September 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), ItalySeptember 19-23, 2011, Lerici (SP), Italy