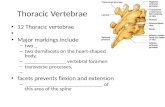
The typical vertebrae
-
Upload
garaka-rabel -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
772 -
download
6
Transcript of The typical vertebrae

1
Features Cervical (3-6) Thoracic (2-8) Lumbar (1-4)
Identification By the presence of foramina transversaria
By the presence of costal facets on lateral surfaces of the vertebral bodies (1 or 2 on each side)
1. By the absence of foramina transversaria and costal facets on body
2. By its large size
Body
Shape
Small (oval shaped), broader from side to side than anteroposteriorly
Heart-shaped with roughly same measurement from side to side & anteroposteriorly
1. Large (kidney shaped)
2. Wider from side to side than anteroposteriorly
3. Height of body is slightly greater anteriorly than posteriorly
Superior
1. Transversely concave
2. Has upward projecting lips on each side
3. Anterior border may be beveled
Inferior
1. Saddle-shaped (convex laterally & concave anteroposteriorly)
2. Lateral borders are beveled & form synovial joints with projecting lips of next lower vertebra
3. Anterior border projects downwards & may hide the intervertebral disc
Lateral
On each side, it bears 2 costal demifacets. Superior costal demifacet is larger, placed on upper border of body near pedicle, and articulates with numerically corresponding rib. Inferior costal demifacet is smaller, placed on lower border of body in front of inferior vertebral notch, and articulates with next lower rib.
Vertebral arch
Pedicles Directed backwards & laterally
Directed straight backwards
1. Short2. Strong3. Projected
backwards from upper part of body
Laminae 1. Relatively long & narrow
2. Thinner above than below
Overlap each other from above
1. Short, thick & broad
2. Directed backwards & medially
Garaka Rabel

2
3. Overlapping of adjoining vertebrae is minimum
Processes
Transverse Processes
1. Pierced by foramina transversaria
2. Each process has anterior & posterior roots which end in tubercles joined by costotransverse bar
Large, directed laterally & backwards. Anterior surface bears a facet near its tip, to articulate with tubercle of corresponding rib. In upper 6 vertebrae, these costal facets are concave & face forwards & laterally, while in lower 6 vertebrae, they are flat & face upwards, laterally & slightly forwards
1. Thin & tapering2. Directed laterally
& slightly backwards
3. Homologous with ribs in thoracic region
4. Accessory process is a small, rough elevation in posteroinferior aspect of the root of transverse process, which represents true transverse process of vertebra
5. Length increases from L1 to L3 & thereafter it decreases
Spinous Process (Spine)
1. Short2. Bifid3. Notch is filled by
ligamentum nuchae
Long, directed downwards & backwards. 5 to 9 spines are the longest, more vertical & overlap each other & lower spines are less oblique
1. Forms a vertical quadrilateral plate
2. Directed almost backwards & only slightly downwards
3. Thickened along its posterior & inferior borders
Superior Articular Processes
1. Form articular pillars, projected laterally
2. Articular facets are flat
3. Facets are directed backwards & upwards
Project upwards from the junction of pedicles and laminae.Articular facets are flat & directed backwards, little laterally & upwards.
1. Lie farther apart than inferior
2. Bear concave facets facing medially & backwards
3. Posterior border is marked by a rough elevation called mamillary process
Inferior Articular Processes
1. Form articular pillars, projected laterally
2. Articular facets are flat
3. Facets are directed forwards & downwards
Fused to the laminae.Articular facets are directed forwards, slightly downwards & medially.
1. Lie nearer to each other, than superior
2. Bear convex facets facing laterally & forwards
Vertebral Foramen
1. Larger than body2. Triangular in shape
(as pedicles are directed backwards & laterally)
Comparatively small & circular
1. Triangular in shape
2. Larger than in thoracic region, but smaller than in cervical region
Vertebral Superior Superior & inferior Shallow Inferior vertebral
Garaka Rabel

3
Notches
Vertebral Notch
vertebral notches are of equal size
notches are much deeper than the superior vertebral notches
Inferior Vertebral
NotchDeep & conspicuous
Attachments
Muscles
1. Vertical part of longus coli is attached to anterior surface (on each side of anterior longitudinal ligament)
2. Scalenus anterior3. Longus capitis4. Oblique part of
longus coli5. Scalenus medius6. Scalenus posterior
levator scapulae7. Splenius cervicis8. Longissimus
cervicis9. Iliocostalis cervicis10. Interspinales11. Semispinalis
thoracis & cervicis12. Spinalis
cervicis13. multifidus
In transverse process :1. Intertransverse
muscles – to upper & lower borders
2. Levator costae – on posterior surface
In spinous process :1. Trapezius2. Rhomboideus3. Latissimus dorsi4. Serratus posterior
superior5. Serratus posterior
inferior(and many deep muscles of back)
1. Right crus – upper 3 vertebrae
2. Left crus – upper 2 vertebrae
3. Psoas major – upper & lower borders of all lumber vertebrae (behind line of crura)
Ligament
In transverse process :1. Lateral
costotransverse ligament – at tip
2. Superior costotransverse ligament – along lower border
3. Inferior costotransverse ligament – along anterior surface
In spinous process :1. Supraspinous
ligament2. Infraspinous
ligament
Garaka Rabel