The Transatlantic Slave Trade and Colonial Slavery
description
Transcript of The Transatlantic Slave Trade and Colonial Slavery

The Transatlantic Slave Trade and Colonial Slavery
African-American History


3 Distinct Features of American Slavery:
Slaves not accepted into society & had no legal rightsSlave status inherent and passed on to childrenMostly unskilled, manual laborers

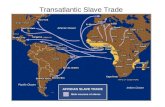
The Transatlantic Slave TradePortuguese controlled trade in 1500s, Dutch in 1600s, English in 1700s10-11 million slaves crossed the Atlantic
3.65 million to S. America3.32 million to Caribbean1.5 million to Mexico & Central America600,000 to N. America
Angola & Loango = biggest source overall
Slave Coast dominated after 1740East Africa not tapped until late 1700s
More men than women

A Typical Slave ShipDimensions: 80’ – 90’ by 25’Held 300 – 450 slavesVoyage lasted 90 – 100 days10 – 20% average mortality rateOutlawed by U.S. & U.K. in 1808
British abolition movement led by William WilberforceFrance 1831; Spain 1835Last known slave ship crossed Atlantic in 1867Cuba ended slavery in 1888

The Spanish EmpireViceroys ruled New Spain & Peru on King’s behalf
Each divided into provincesGovernors & audencias (courts) ruled provinces
Haciendas = large plantations growing cash crops (sugar, cotton, cocoa, tobacco, etc.)Mines were principle source of wealth for Spain
16 million kg. entered Spain between 1503-1650Crown kept 1/5 (quinto)Flowed primarily to Spanish Netherlands

Slave Labor in New Spain
Encomienda = grant of Indian labor to mine & hacienda ownersRepartimiento = requirement that Indians work so many days for SpanishModeled on feudalism, but no protection for workersWhen Indians died off, replaced by Africans

Why Africans Were EnslavedEric Williams argues slavery was based on economics, not racism
Indians enslaved first, then white indentured servants usedBlack slaves cheaper because held for life & less likely to escape
Winthrop Jordan argues slavery & racism developed dialectically
“black” associated with dirt, death & sin
David Brion Davis argues sugar/slave system moved from Mediterranean to Atlantic islands, & thence to Americas