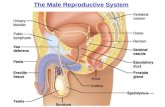
The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Epididymis.
The Reproductive System. The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system includes two...
-
Upload
marjorie-morris -
Category
Documents
-
view
220 -
download
1
Transcript of The Reproductive System. The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system includes two...

The Reproductive System

The Male Reproductive System• The male reproductive system
includes two testes, two epididymides, two vasa deferenta, the urethra, and the penis.
• The testes are contained in the scrotum, where the cooler temperature allows normal sperm development.
• Sperm form in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes in sperm to 23.
• A mature sperm consists of a head, which contains the nucleus and chromosomes; a midpiece, which contains mitochondria; and a tail, which consists of flagellum.
• Sperm take the following path to exit the body: seminiferous tubules of the testes epididymis vas deferens urethra.
• Fluids that are secreted by various exocrine glands are mixed with sperm to produce semen.

Male Reproductive Structures
•bladder- stores urine•pubis-protects area & supports muscles•testis- makes sperm•vas deferens- carries the sperm•seminiferous tubules- where meiosis occurs•epididymis- where sperm matures•seminal vesicle- creates a solution of sugars•anus- releases waste

The Formation of Sperm•Males begin to make sperm during puberty.•Two hormones released by the anterior pituitaries regulate the function of the testes:
•LH stimulates the secretion of testosterone, the main male sex hormone, or androgen, from cells located between the seminiferous tubules.•FSH + testosterone
sperm production in the seminiferous tubules.
•Sperm are haploid and are produced by meiosis.
•4 sperm cells result from each cell that begin meiosis.
•The structure of a mature sperm cell consists of 3 regions- a head, a midpiece, and a tail:
•head:•contains enzymes
•help sperm penetrate the protective layers surrounding an egg cell during fertilization
•contains 23 chromosomes which will be delivered to the egg
•midpiece:• contains mitochondria
•supply the energy that is required for a sperm cell to reach an egg
•tail-• consists of a single, powerful flagellum
• used to propel the sperm
stimulate

Path of Sperm Through the Body
•The path that sperm following leaving the body is: somniferous tubules testes epididymis vas deferens urethra seminal vesicles prostate glands bulbourethral gland penis. (see diagram)

The Female Reproductive System• The female reproductive structures
include two ovaries, two fallopian tubes, the uterus, the cervix, the vagina, the two labia, and the vulva.
• Eggs form in the ovaries. Meiosis reduces the chromosome number in eggs to 23. Eggs are about 75,000 times larger than sperm.
• Starting at puberty, the ovarian and menstrual cycles occur approximately every 28 days.
• The ovarian cycle consists of three phases: follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase.
• In follicular phase, FSH causes a follicle to grow. Estrogen produced by the follicle causes an egg to mature and the uterine lining to build up.
• Ovulation occurs midway through the ovarian cycle, when LH causes the follicle to rupture and release its egg.
• In the luteal phase, the follicle becomes a corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes progesterone, which stimulates further buildup of the uterine linning.
• Menstruation occurs at the end of the menstrual cycle, when a corpus luteum stops secreting hormones.

Female
Reproductive
Structures
•ovary- makes eggs•ovaduct/fallopian tubes- moves egg from ovary to uterus with the use of contractions and cillia; where fertilization occurs•uterus- where offspring develops

Formation of Eggs• A female is born with more that
400,000 eggs in her ovaries which are immature and cannot be fertilized.
• Most females release 300 to 400 mature eggs in their lifetime.
• Mature eggs are released about once every 28 days from puberty until about age 50.
• Egg formation occurs through meiosis.
• Each mature egg cell is haploid and contains 23 chromosomes.
• Egg formation results in one functional egg from each cell that begins meiosis (1 in 4).
• Sex hormones stimulate egg maturation during puberty.
• Meiosis II cannot occur in egg cells until they are fertilized.
• An egg is about 75,000 times larger than sperm and is visible to the unaided eye.

Preparation for Pregnancy• Each month the female reproductive
system prepares and releases an ovum in a series of events called the ovarian cycle, during which, the egg matures, enters the fallopian tube, and fuses with a sperm; if the egg does not fuse with a sperm it degenerates and is discarded with menstruation. During this period the menstruation cycle also prepares for possible pregnancy.
• An immature egg cell completes it’s first meiotic division during the follicular phase in which FSH stimulates cell division in a follicle, which provides nutrients for the egg. Estrogen is also secreted, stimulating mitotic divisions of cells in the lining of the uterus.

…continued• The sharp LH level that occurs
midway through the ovarian cycle causes the follicle to rupture and release it’s egg which is know as ovulation.
• Following ovulation, an egg travels through the fallopian tube where it awaits fertilization on it’s way to the uterus.
• Once ovulation has begun, an egg must be fertilized within 24 hours (before the disintegration process begins).
• The luteal phase occurs when the cells of the ruptured follicle grow larger and fill the cavity of the follicle, forming a corpus luteum.
• The corpus luteum secretes progesterone and estrogen which causes the body to begin storing nutrients and preparing for possible pregnancy and decreases the amount of LH and FSH to prevent other eggs from being released.
• If an egg is fertilized, it attaches to the lining of the uterus and the chemicals of progesterone and estrogen are continually released; if the egg is not fertilized, the release of estrogen and progesterone stop, the thick lining of the uterus cannot be maintained and is expelled through the vagina during menstruation.
• Menstruation lasts from 5 to 7 days.• At around age 50, a woman no longer ovulates
due to the maturation, rupturing, or degeneration of her follicles causing the menstruation cycle to cease through a process known as menopause.

Gestation• Fertilization occurs in the
fallopian tube. Pregnancy begins when a blastocyst implants itself in the lining of the uterus.
• The three primary germ layers- the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm- form early in embryonic development. Four membranes- the amnion, yolk sac, allantois, and chorion- also form early in embryotic development.
• Nutrients, gases, and other substances pass through the placenta by diffusion from the mother to the fetus.
• For the first eight weeks of pregnancy, the developing human is called an embryo. From the eighth week until birth, a developing human is known as a fetus.
• Unnecessary drug use can negatively affect an embryo or fetus.
• During childbirth, contractions of the uterus initiated by prostaglandins and oxytocin push the baby from the mother’s body through the vagina.

•During fertilization an egg completes meiosis II (in which the nucleus of the egg & the nucleus of the sperm fuse) and form a zygote.•Fertilization mitotic division (cleavage) help create a ball of cells (morula) which divide and release fluid blastocyst.•Implantation- when the blastocyst burrows and imbeds itself into the lining of the uterus.•Implantation occurs about a week after fertilization and begin pregnancy.
fuse

Pregnancy
•first 2-3 weeks: human embryo resembles that of other animals
•embryo develops from cells on the inner part of the blastocyst
•cells reorganize into three distinct type of cells forming the 3 germ layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, & endoderm; different parts of the body result from each
•4 development-aiding membranes form•amnion-forms fluid filled amniotic
•surrounds the embryo (cushions embryo from injury & keeps embryo moist)
•yolk sac- does not contain a yolk; where first blood cells originate•allantois•chorion-surrounds all other membranes; forms chorionic villi
•chorionic villi + uterine lining = placenta•nutrients, gases, pathogens, and other substances pass to nourish the baby•attached to baby by umbilical chord
•grow to 2 in.
1st Trimester (1-3 months)
•For the first 8 weeks of pregnancy, the developing human is called an embryo.•Blood vessels that form in the chorionic villi originate in the allantois. •Blood from the mother/fetus never mixes; materials are exchanged across the placenta.•Embryo produces HCG which stimulates the corpus luteum and prevents menstruation.

…continued2nd Trimester (3-6 months)
• mother’s uterus enlarges• mother begins to feel movement • grows to 2lbs (34 in.)
3rd Trimester (6-9 months)• fetus grow quickly so that it is
prepared to survive outside its mother• fetus develops fat deposits under its
skin– insulate the body so it can
maintain a steady temperature
Fetal Development (by trimester)Fetal Development (by trimester)1. (1-3 months)
• brain/spinal cord/nervous system (3 weeks)• heart begins to beat (21 days)• arms/legs/eyes/ears/finger & toes (5 weeks)• brain activity (5 weeks)• embryo movement (5 weeks)
2. (3-6 months)• audible heartbeat• skeleton• layer of soft hair (lanugo)• begins to wake/sleep• swallows/sucks thumb/make a
fist/hiccup/kick/curl toes3. (6-9 months)
• can see light/dark• can react to music/loud noise• develops fat deposits (during 2nd half of 3rd
trimester)
•From 8 weeks until birth the developing human is called a fetus.

BirthBirth1. hormones produced by fetus & mother initiate
birth2. high levels of estrogen, prostaglandins, &
oxytocin cause the uterus to contract3. Amniotic sac breaks (a.k.a. “breaking water”)4. muscles in the cervix & vagina relax enabling
them to enlarge so that the fetus can pass through them
5. contractions push the fetus through the vagina & cervix (childbirth)
6. placenta, amnion, & uterine lining are expelled (afterbirth)
7. baby begins breathing on it’s own8. umbilical chord is cut & tied9. umbilical arteries/veins close of (within 30 min
after birth)10. baby’s respiratory/excretory systems become
fully functional
(labor)
•occurs at about 270 days (after fertilization)
Processes in order

Key Vocabulary Terms• afterbirth- the remains of the placenta and the
membranes, which are expelled from the mother’s body following birth
• amniotic sac-a sac formed by the amnion
• blastocyst- the modified blastula stage of mammalian embryos
• bulbourethral gland- one of the two glands in the male reproductive system
• cervix- the neck of the uterus
• chorionic villius- fingerlike projections of the chorion that extend into the uterine lining
• corpus luteum- the structure that forms from the ruptured follicle in the ovary after ovulation; it releases hormones
• ejaculation- the expulsion of seminal fluids from the urethra of the penis during sexual intercourse
• embryo- an organism in an early stage of development of plants and animals; in humans, a developing individual is referred to as an embryo from the second through the eighth week of pregnancy
• epididymis- the long, coiled tube that is on the surface of a testis and in which sperm mature
• fallopian tube- a tube through which eggs move from the ovary to the uterus
• fetus-a developing human during the period from the eighth week after fertilization until birth
• follicle- a small, narrow cavity or sac in an organ or tissue, such as the ones in the ovaries that contain the developing eggs
• follicular phase- the stage in which an immature egg completes its first meiotic division
• gestation- in mammals, the process of carrying young from fertilization to birth
• human chorionic gonadotropin- a hormone that is secreted by the placenta and that stimulates ovulation and secretion of progesterone or testosterone
• implantation- the process by which the newly fertilized egg in the blastocyst stage embeds itself in the lining of the uterus
• labium- in some animals, one of a pair of lips around the mouth; also, in some female animals, one of two pairs of folds of skin and mucous membranes that cover and protect the openings of the vulva
• labor- the process by which the fetus and the placenta come out of the uterus

…Vocabulary• luteal phase- the menstrual stage in which the corpus
luteum develops• menopause- the termination of the menstrual cycle,
occurs between the ages of 45 and 55• menstrual cycle- the female reproductive cycle,
characterized by a monthly change in the lining of the uterus and the discharge of blood
• menstruation- the discharge of blood and discarded tissue from the uterus during the menstrual cycle
• ovarian cycle- a series of hormone-induced changes in which the ovaries prepare and release a mature ovum each month
• ovary- in the female reproductive system of animals, an organ that produces eggs
• ovulation- the release of an ovum from the follicle of an ovary
• ovum- a mature egg cell• penis- the male organ that transfers sperm to the
female reproductive tract during sexual intercourse and that carries urine out of the body
• placenta- the structure that attaches a developing fetus to the uterus and that enables the exchange of nutrients, wastes, and gasses between the mother and the fetus
• pregnancy- the period of time between implantation and birth
• prostate gland- a gland in males that contributes to the seminal fluid
• scrotum- the sac that contains the testes in most male mammals
• semen- the fluid that contains the sperm and various other secretions produced by the male reproductive organs
• seminal vesicle- one of two glandular structures in male vertebrates that hold and secrete seminal fluid
• seminiferous tubule- one of many tubules in the testes where sperm are produced
• testis- the primary male reproductive organs, which produce sperm cells and testosterone
• trimester- one of the three equal periods of about 12 weeks into which the human gestation period is divided
• umbilical cord- the structure that connects an embryo and then the fetus to the placenta and through which blood vessels pass
• uterus- in female mammals, the hollow, muscular organ in which a fertilized egg is embedded and in which the embryo and fetus develop
• vagina- the female reproductive organ that connects the outside of the body to the uterus and that receives sperm during reproduction
• vas deferens- a duct from which sperm move from the epididymis to the ejactory duct at the base of the penis
• vulva- the external part of the female reproductive organs