The Pythagorean Theorem · 2019. 3. 19. · The Pythagorean Theorem . When you are looking for the...
Transcript of The Pythagorean Theorem · 2019. 3. 19. · The Pythagorean Theorem . When you are looking for the...

4.1 cm
5.2 cm
13.4 ft
14.8 ft
bc
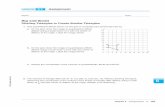
The Pythagorean Theorem When you are looking for the hypotenuse (longest side c), use the form 2 2 2c a b= + . When you are looking for one of the legs (shorter sides a or b), use the form 2 2 2a c b= − . In other words, when you are looking for the hypotenuse you will always be adding the squares of the other two sides. When you are looking for one of the legs you will always be subtracting. Examples: Find the missing side in each triangle below. Round to the nearest tenth.
a) b)

Your Turn Directions: Find the missing side in each triangle below. Round to the nearest tenth. a) b) 6 in. 3 cm 7 in. 5 cm c) d) 10.2 m 12.4 m 21.2 ft 26.1 ft e) f) 8.5 mm 6 m 6 m 9.2 mm

3 cm
5.6 in.
Squares and Square Roots Cubes and Cube Roots Power: a numerical expression that shows repeated multiplication; e.g., the power 32 is a shorter way of writing 2 2 2× × . It is read as ‘two to the third’ or ‘two cubed’. 2 is the base and 3 is the exponent. We say 2 has the exponent 3. Base: the number used as a factor in the power Exponent: the number used to express the number of factors in a power What does it mean when you are asked to ‘square’ a number? When would you be asked to do this? Squaring a number means multiplying by itself. We use this when finding area of a square. Example 1: Find the area of each of the following. a) b) Example 2: Write the first 10 perfect squares. What does it mean to find the ‘square root’ of a number? Taking the square root is the inverse of squaring. Example 3: Approximate each of the following to one decimal place then use your calculator to verify your answers.
a) 28 b) 61 c) 15 d) 39

4.1 cm
5.2 cm
13.4 ft
14.8 ft
bc
Example 4: Determine the square root of each of the following without using a calculator. Express each as a fraction in lowest terms.
a) 925
b) 1649
c) 1100
d) 169
Example 5: Determine the exact value of 1 36 1 000 0009 25× × without using a calculator.
Example 6: When is the square root of a number greater than the number? Give an example. Example 7: Find the missing side in each triangle below. Round to the nearest tenth.
b) b)
Example 8: A square wall tile has an area of 2100 cm . Determine the length of one of its sides. What is its perimeter?. What does it mean to cube a number? When would you be asked to do this? Multiply by itself 3 times such as when finding volume of a cube

4.5 cm
Example 9: Consider the following cube with side length 5 cm . Determine its volume. What do you think it means to find the cube root of a number? Find the number that can be multiplied by itself three times to give us the number Example 10: Use your calculator to calculate each of the following. Round to the nearest tenth.
a) 3 8 b) 3 67 c) 3 25 d) 3 100
Example 11: A softball comes in a cube-shaped box with a volume of 31728 cm . What is the length of one of its sides? What is its surface area? Squares and Square Roots: Cubes and Cube Roots Homework Directions: Complete each of the following in the spaces provided. 1. Find the area of the following square.

3.8 mm
4.2 mm
22.4 in.
25.8 in.
y
x
2. The area of a square is 264 cm . a) What is the length of one of its sides? b) What is its perimeter? 3. Approximate each of the following to one decimal place then use your calculator to verify your answers. a) 38 b) 57 c) 97 d) 139 4. Determine the square root of each of the following without using a calculator. Express each as a fraction in lowest terms.
a) 916
b) 2564
c) 49100
d) 12136
5. Determine the exact value of each of the following without using a calculator.
a) 100 36160 0009 49
× × b) 1 100 6425 36 121
× ×
c) 1 36 000 0009× d) 25 1 0.25
36 9+ −
6. Find the missing side in each triangle below. Round to the nearest tenth. a) b)

7. Consider the following cube with side length 8 m . Determine its volume. 8. The volume of a cube is 3125 mm . Determine the length of one of its sides. What is its surface area? 9. Use your calculator to calculate each of the following. Round to the nearest tenth. a) 3 27 b) 3 102 Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Exponent Laws Date: ______________________________ Introduction to Exponents Recall: Power: a numerical expression that shows repeated multiplication; e.g., the power 32 is a shorter way of writing 2 2 2× × . It is read as ‘two to the third’ or ‘two cubed’. 2 is the base and 3 is the exponent. We say 2 has the exponent 3.

Base: the number used as a factor in the power Exponent: the number used to express the number of factors in a power Example 1: Represent each repeated multiplication as a power.
a) × × × ×3 3 3 3 3 b)
−
3 3 3 3 3 3 34 4 4 4 4 4 4
Example 2: Represent each power using repeated multiplication.
a) 65 b) − 36
Example 3: Is there is a difference between ( )−2
3 and − 23 ? Explain.
Example 4: Evaluate each of the following.
a) − 25 b) −
216
c) ( )−4
2 d) ( )−2
4
Example 5: Is there a difference between − 32 and ( )−3
2 ?
Example 6: Complete the table.
Power Base Exponent Repeated Multiplication
Value in Standard Form
65 3 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )3 3 3 3 3 3 3
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )− 2 2 2 2 2

=0base _____
Up until now all of your exponents have been natural numbers. Let’s investigate an exponent ‘0’. Evaluate each of the following:
=
=
=
=
=
5
4
3
2
1
2 _____2 _____2 _____2 _____2 _____
=
=
=
=
=
5
4
3
2
1
3 _____3 _____3 _____3 _____3 _____
If we follow the pattern what will 0 02 and 3 both equal? Can we develop a rule for any base raised to exponent 0?
Exponent Laws Introduction to Exponents Homework
1. Represent each repeated multiplication as a power.
a) 5 5 5 5 5 5 5× × × × × × b) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 c) 2 2 2 2 23 3 3 3 3
d) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )7 7 7 7 7 7− e) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2− − − − − − − − −
2. Represent each power using repeated multiplication.
a) 42 b) 42− c) ( )42− d) ( )4
2− −
3. Evaluate each of the following. a) 23 b) 23− c) ( )23− d) ( )23− −
e) 05 f) 05− g) ( )05− h) ( )05− −
4. Complete the table.
Power Base Exponent Repeated Multiplication
Value in Standard Form
52 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )5 5 5 5− − − −
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )4 4 4 4 4 4−

5. Multiple Choice: Which of the following does not represent -64? A. 62− B. ( )62− −
C. 34− D. ( )34− −
6. Multiple Choice: Which statement is false? A. 33.1 3.1 3.1 3.1= × × B. ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )43 3 3 3 3− = − − − −
C. ( )26 36− = D. 21 1− = −
7. If a power has a negative integer as its base, can you predict whether the power has a positive or negative value? Explain. 8. Arrange in order from least to greatest. ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )4 100 514 22 , 2 , 2 , 1 , 1− − − − − −
Exponent Laws Product, Quotient, and Power Laws Today we will develop and use three of the five exponent laws. Developing the Product Law for Exponents
1. Simplify 2 3x x⋅ by rewriting in expanded form. 2. Simplify 2 2 3b b b⋅ ⋅ by rewriting in expanded form. Is there an easier way to multiply expressions that have the same base without expanding? Developing the Quotient Law for Exponents
1. Simplify 6
2xx
by rewriting in expanded form.
2. Simplify 4aa
by rewriting in expanded form.
Is there an easier way to divide expressions that have the same base without expanding?

Developing the Power Law for Exponents
1. Simplify ( )23x by rewriting in expanded form. 2. Simplify ( )34a by rewriting in expanded form.
Is there an easier way without expanding? Laws of Exponents
( )
m n m n
mm n
n
nm m n
Product Law : a a aaQuotient Law : aa
Power Law : a a
+
−
×
× =
=
=
Example: Simplify each of the following.
a) 3 7x x ______⋅ = b) 8
3d ______d
=
c) 5 84 4 ______⋅ = d) ( )( )
10
4
0.25______
0.25=
e) 13
7a ______a
= f) ( )23m ______=
g)
351 ______3
= h) ( ) ( ) ( )3 4
2 2 2 ______− − − =
i) 4 4 2d d d d ______⋅ ⋅ ⋅ = j) 3 2
4y y y ______
y⋅ ⋅
=
k) ( )35
4
b______
b= l)
( )( )
63
43
x______
x=
Your Turn
a) 3 4m m m ______⋅ ⋅ = b) 4 3
2x x ______
x⋅
= c) ( )63
10
a______
a=

Exponent Laws Product, Quotient, and Power Laws Homework Assignment Directions: Simplify each of the following.
a) 2 5a a ______⋅ = b) 6 8b b ______⋅ =
c) 6
4m ______m
= d) ( )53x ______=
e) 6 2 3y y y ______⋅ ⋅ = f) 12
9d ______d
=
g)
10
6
14 ______14
=
h) ( )82n ______=
i) ( )44a ______= j) 5 2 35 5 5 5 ______⋅ ⋅ ⋅ =
k) 7x ______
x= l)
5 4 3
2a a a ______
a⋅ ⋅
=
m) 2 3 3
4 2x x x ______
x x⋅ ⋅
=⋅
n) ( )25c ______=
o) ( )43
2
d______
d= p)
( )( )
45
32
m______
m=

Exponent Laws Power of a Product, Power of a Quotient Laws Today we will develop and use two other exponent laws. Developing the Power of a Product Law for Exponents
1. Simplify ( )245x by rewriting in expanded form. 2. Simplify ( )324a by rewriting in expanded form.
3. Simplify ( )423m by rewriting in expanded form. 4. Simplify ( )342y by rewriting in expanded form.
Is there an easier way without expanding? Developing the Power of a Quotient Law for Exponents
1. Simplify 32x
y
by rewriting in expanded form. 2. Simplify 2
a3
by rewriting in expanded form.
Is there an easier way without expanding?

Laws of Exponents
( )n n n
n n
n
Power of Product Law : ab a b
a aPower of Quotient Law :b b
=
=
Example: Simplify each of the following.
a) ( ) =42 3x y _________ b)
=
52m _________n
c) ( ) =243x _________ d) ( ) =
42 32x y _________
e)
=
32
35p _________q
f)
=
33
22x _________3y
g) ( ) =23 5 2 43a b c d _________ h)
=
23 2
5
d e _________4f
Your Turn
a) ( )22 34m n ______= b) 36 3
52x y ______
z
=

Exponent Laws Power of a Product, Power of a Quotient Laws Homework Assignment Directions: Simplify each of the following.
a) ( )24 5a b _________= b) 34
8x _________y
=
c) ( )32 55x y _________= d) ( )63 5m n _________=
e) 45
43c _________d
=
f)
24
23m _________2n p
=
g) ( )54 6 32x y z _________= h) 44 5
3
m n _________3p
=
i) ( )93 4g h _________= j) 75
6w _________u
=
k) ( )274xy _________= l) ( )36 73a b _________=

Exponent Laws Review Directions: Simplify each of the following.
a) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )5 9 4x x x x b) 7nn
c) 5 2
1 12 2
÷
d) 3 5
4 2
a a aa a⋅ ⋅⋅
e) ( ) ( )2 30.5 0.5⋅ f) ( )42d−
g) ( )432yx2 h) 35
3m
i) 2
34
2
nm5cb2
j)
7
2
45
cddc
k) 3
22
45234
yxyx
xyyx
⋅
l)
4 23 5 8 6
2 3 5 2
a b a ba b a b
⋅

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Polynomial Vocabulary Date: ______________________________ Today we will begin our work with polynomials. We will start with some basic vocabulary then move into operations on polynomials: adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing. Algebra: A branch of Mathematics that uses symbols to represent unknown numbers or quantities. Variable: A letter or a symbol representing unknown value(s). Algebraic Expression: The result of applying arithmetic operations to numbers and variables; for example: 3m 2+ is an algebraic expression. The variable ‘m’ has a coefficient of 3. The ‘2’ is a constant. Polynomial: An algebraic expression made up of terms connected by the operations of addition or subtraction; the variables can be multiplied by or divided by any numbers; for example: 23a 4ab 2+ +
and bh2
are polynomials. Note: 1a
is not a polynomial because it can be written as 1a− . You will learn
more about this in Math 10C. Term: An expression formed from the product of numbers and/or variables; for example: the polynomial 22m 4m 7− + has three terms and they are 22m , 4m− , and 7. It is possible for a polynomial to have only one term. For example, 35x is a polynomial. We have specific names for polynomials consisting of one, two, and three terms. Do you know the names? Polynomial consisting of 1 term: ______________________ Polynomial consisting of 2 terms: ______________________ Polynomial consisting of 3 terms: ______________________ Degree of a term: The sum of the exponents on the variables in a single term (monomial); e.g., first degree terms: 2a, b, 5m− , second degree terms: 2 2 24a , 3n , 7y− , third degree terms:
3 3 36b , 7m , x− − . The degree of 25x y is ‘3’ since the exponents are 2 and 1 and 2 1 3+ = . The degree of a constant term is 0. Degree of a polynomial: The degree of the highest-degree term in a polynomial; for example: first degree polynomials: 3a 1, 2 6b, 7x 2.5− + − , second degree polynomials: 2 2x 5x 8, 4ab 7a, 5m 9− + − + . Example 1: Create a polynomial to fit each description:
a) The degree is 3 and the constant is -5. _______________
b) The degree is 2 and the coefficient of ‘x’ is 3. _______________
c) The variables are ‘a’ and ‘b’, the degree is 1, and it is a binomial. _______________

Your Turn:
Create a trinomial that has a degree of 2, only one variable, and a constant of 6. Example 2: Complete the table.
Polynomial Degree Variable(s) Coefficient(s) Constant Term 23x 2x 7+ − 5m 9n+
2 38y 5x 2x− + Your Turn:
For the polynomial 3 26d 5d 7d 3− + − , identify the degree, the variable(s), the coefficient(s), and the constant term. Degree: _______________ Variable(s): _______________
Coefficient(s): _______________ Constant Term: _______________
Example 3: Consider the problem: Total possible points on a Math contest if questions from Part A are worth 2 points each and questions from Part B are worth 5 points each.
a) Create an algebraic expression to represent the statement above. Use the variable ‘a’ to represent the number of questions from part A and the variable ‘b’ to represent the number of questions from part B.
b) What mark will Sherry receive if she gets 12 questions right in Part A and 10 questions right in Part B? Show work.

2x 2x− x x−1−1
We often use a solid tile to represent the positive tiles and an empty tile to represent the negative tiles. In this chapter we will mostly just use the x-tiles. Example 4: Write a polynomial for the diagram below. We will only use the ‘x’ tiles. Example 5: Draw a diagram to represent the polynomials below. a) 23x 2x 4− + b) 2x 3x 2− + −

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Polynomial Vocabulary Date: ______________________________ Homework 1. Complete the table.
Polynomial Degree Variable(s) Coefficient(s) Constant Term 23 2k 4k− +
3 26x 2y−
m 2+ 2. Create a polynomial to fit each description:
a) The degree is 2 and the constant is -9. _______________
b) The degree is 1 and the coefficient of ‘p’ is 6. _______________
3. What is the value of 2 2x 2xy y− + when x 2= and y 3= − ? 4. Multiple Choice: Mark has saved $200. He earns $45 a week at a part-time job. He saves all the money he earns. Which of the following expressions represents Mark’s savings after working ‘n’ weeks? A. 200 45n+ B. 200 45n− C. 245n D. 45n 200−

5. Marian gives French lessons in the evening. She charges $20 for adults and $15 for children. The expression 20a 15c+ represents her earnings. How much does Marian make if she gives lessons to four adults and nine children? Show work. 6. Write a polynomial for the diagram below. We will only use the ‘x’ tiles. The polynomial is ____________________. 7. Draw a diagram to represent the polynomials below. a) 22x 5x 1− − b) 24x x 3− + +

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Equivalent Expressions Date: ______________________________ Today we will look at simplifying algebraic expressions by gathering like terms. Like Terms: Terms that differ only by the numerical coefficients. Examples of like terms are
• 3x and 2x− • 2 26y and y− • 5ab and 2ba • 2 24m n and m n− • 18 and 3−
Example 1: Identify the like terms in each group. a) 25b 3cb 2b 7c 6b−
b) 2 2 2 13x 4xy 2x 7x y2
−
c) 23pq 12 4pq 3 qp− − Example 2: Simplify each of the following expressions by combining like terms. a) 4x 2x 3 6− + − b) 5b 6 3b 4 4b 3+ − − − + c) 2 2 2 22x 3xy y x 4xy 2y+ − + − − d) 2 2 2 2a 5ab 10b 3a 2ab 6b− − − + − +

2b 5+
Your Turn Simplify 2 2 2 2 2 23b bc 2c 2b 4b 3bc 5c 7bc c− + − − + − − + . Example 3: Find an expression for the perimeter of the quadrilateral below.
Your Turn Find an expression for the perimeter of the triangle below. Example 4: A heating company charges $60 per hour plus $54 for a service call. Use the variable ‘n’ to represent the number of hours the technician works in your house. a) What expression represents the total cost of the job? b) What is the cost for a job requiring 2 hours?
2b 3−
2b 4+3b 1+
5m 4+
4m 3+

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Equivalent Expressions Date: ______________________________ Homework 1. Identify the like terms in each group. a) 24m 5mn n 6m 6nm 4n−
b) 2 2 2 2 1 15x y 3xy x 3x x y5 5
− − −
c) 3 2 35a 4a 6a 1 a 2a− − − 2. Simplify each of the following. a) 2 22d 3d d 5d− + − b) 2 2y 2y 2y y+ − + c) 2 2p 4p 3 3p 5 2p− + + − − + d) m 4 6 3m− + + e) 2 2a 3a 2a a− + − f) 2 2 2 22m n 3mn mn 4mn 4mn 7m n− + − − − g) 3 2 3 2 3 2 2x y 2x y xy 2x y 3x y 5x y− + − + − 3. Which expressions are equivalent to 23x x 4− + − ? There is more than one answer. 24 3x x− + + 2x 4 3x− − 2 2x 2 4x 3x 6 2x+ − + − − 2 23 5x x 1 2x− − + + + 2 22x 2 x x 4x 2− + − − − 2 2 24 3x 3x 0 5x 4x 6x− − − − + + − 4. Consider the polynomial 23x 5x 6− − . Write an equivalent expression with 6 terms.

5. Write a simplified expression for the perimeter of each figure below. a) b) 6. The diagram below represents a piece of string. Write a simplified expression for its total length. 7. A publisher makes books for a number of distributors. For one book, the charge to the distributor is represented by a fixed cost of $3000 plus $16 per book. a) Write an expression for the cost that a distributor is charged for ‘b’ copies of this book. b) How much do 600 books cost?

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Date: ______________________________ Today we will focus on adding and subtracting polynomials. Recall: you may want to add the opposite when required to subtract like we did with integers. Example 1: Simplify each of the following.
a) ( ) ( )5x 2 3x 7− + + b) ( ) ( )5a 4b c 12a 6b 7c+ − + − −
c) ( ) ( )6m 4 8m 1− − − d) ( ) ( )2 24a 2a 5 a 6a 7− − − − +
Example 2: Add 2 23a 2ab b− + and 2 25a 3ab 6b− − − . Simplify your answer. Example 3: Subtract 5m 8− from 22m 3m 4− + . Simplify your answer.

3x 4y 2+ −
23x 2x+
24x 9x+
5y 7+
Your Turn Simplify each of the following.
a) ( ) ( )4m 2n p 5m 6n 4p− − + − + b) ( ) ( )2 22b b 3 5b 8b 2+ − − − −
Example 4: Find the perimeter of the rectangle below.
Your Turn The perimeter of the triangle shown is 210x 7x+ . Find an expression for the missing side.

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Date: ______________________________ Homework 1. Simplify each of the following.
a) ( ) ( )3m 6 8m 9− + + b) ( ) ( )3x 8y 10 5y 6x 9− + + − −
c) ( ) ( )4x 6 9x 5− − − d) ( ) ( )2 22y y 3 6y 5y 8− − − − +
e) ( ) ( )2 2 2 27m n 3mn mn 5m n mn 2mn− + − − + f) ( ) ( ) ( )5ab a b 3a 2b 4ab 4a b− + + − − − −
2. Subtract 2x 2x 8− + from the sum of 22x 5x 4− − and 2x 2x 6+ + . 3. Subtract 12m 8n− from the sum of 4m 2n− , 6m n+ , and m n− . 4. Which addition statement does the diagram below model? Circle one.

5. Find a simplified expression for the perimeter of the rectangle below. 6. The perimeter of the trapezoid below is 8x 4+ . Find an expression for the missing side. 7. Complete the addition pyramid. Find the value in any box by adding the expressions in the two boxes immediately below it.

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Multiplying and Dividing Monomials Date: ______________________________ Before we multiply monomials let’s look at what it means to multiply. Multiplication Using an Area Model The diagram below represents 3 4× and 4 3× . Draw an area model to represent 24 35× . 4 units
Now let’s look at a product using algebra tiles to model multiplication. Let’s model ( ) ( )4x 3x .
Example 1: Model the product ( ) ( )3x 2x using algebra tiles.
3 un
its

4x
10.5x
Example 2: Write a simplified expression for the area of the rectangle below. Example 3: Find each product.
a) ( ) ( )2x 5x− b) ( ) ( )43m 2m c) ( ) ( ) ( )2y 3x 2y− − d) ( ) ( )2 4 52m n 8m−
Your Turn Simplify each of the following. a) ( ) ( )3y 7y− b) ( ) ( )49m 2m
Example 4: Find each quotient.
a) 212x
3x b)
325m5m
c) 3 5
2
42a b6ab
d) 8 4 3
3 4
24x y z2x y z−
Your Turn Find the quotient for each.
a)6
2
81a9a
b) 2 9
6
40x y25xy−

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Multiplying and Dividing Monomials Date: ______________________________ Homework 1. Simplify each of the following.
a) ( ) ( )39x 2x− b) ( ) ( )2 412a 2a− c) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( )2 33m 2m n 4n− − d) ( ) ( )3 6 5 23x y z x z−
2. A rectangle has a width of 2.7x and a length of 1.3x . Find an expression to represent the area of the rectangle. 3. A square has side length represents by 3.5x . Find an expression to represent the area of the square. 4. Simplify each of the following.
a) 7
3
22x2x
b) 9
7
16a8a− c)
6 12
10
90m n10mn
−−
d) 5 6 7
2 5
32a b c4a b−
5. Find an expression for the length of the rectangle below with the given information.
2A 15 x= w 2.5x=

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Multiplying Polynomials by Monomials Date: ______________________________ Today we will multiply polynomials by monomials. We will explore products using an area model as well as use algebra tiles. Finding the product ( ) ( )3x 2x 3+ Using An Area Model
Now let’s look at the product using algebra tiles to model multiplication. Let’s model ( ) ( )3x 2x 3+ .
How about using the distributive property? The distributive property allows you to expand algebraic expressions. Multiply the monomial by each term in the polynomial.
( )a b c ab ac+ = +
Now try ( ) ( )3x 2x 3+ using distribution.
1A 2A3x
2x 3+2x 3

4x
6x 7+
Example 1: Expand each expression. a) ( )2m 3m 8− b) ( )22x 3x 5x 4− + −
c) ( )26 3a 2a 4− − − d) ( ) ( )2 22x y 6xy 3xy 4xy− +
Your Turn Find the product for each expression. a) ( )22a 5a a 4− + b) ( ) ( )22c 3c 4 3c− −
Example 2: A pool table has a width of 4x and a length of 6x 7+ . Write a simplified expression for the area of the pool table.

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Multiplying Polynomials by Monomials Date: ______________________________ Homework 1. Find the product for each expression. a) ( )3 a 4− b) ( )5x 3x 2y+
c) ( )24m 2m 3m 4− + d) ( ) ( )2 26y 2y 1 3y− −
e) ( )22x 2x 5x 4− − + f) ( ) ( )24 2a 3a 5− − +
g) ( )2 24cd 7c d 5cd− h) ( ) ( )2x 4x 6 3x− −

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Dividing Polynomials by Monomials Date: ______________________________ Yesterday we multiplied polynomials by monomials. Today we will divide polynomials by monomials. Recall: When dividing a monomial by a monomial you divide coefficients and subtract exponents on like bases.
For example: 5 3
3 22
32x y 4x y8x y
= since 5 2 3 3 232 8 4, x x x , and y y y÷ = ÷ = ÷ = .
What do you think you would do to simplify 2x 4y 82
− + ? Write 2x 4y 82
− + as three separate
expressions. Example 1: Find the quotient for each expression.
a) 26x 3x 9
3− + b) 15x 5y
5−−
c) ( ) ( )4 3 218a 27a 9a 3a− − + ÷
d) 2 245x y 25xy 40xy
5xy− − e)
5 3 24m 4m 8m 2m2m
− + + f) 3 4 4 2 5
2
14b c 35b c 21b c7b c
+ −
Your Turn Simplify each of the following.
a) 7 5 3
2
24x 36x 30x6x
− − b) ( ) ( )4 4 3 3 2 3 2 25a b 15a b 25a b 20ab 5ab− − + − ÷

Example 2: The area of the rectangle given below can be represented by the expression 3 2A 6x 12x 18x= − + . If the width is ‘ 6x ’, find an expression for the length.
Your Turn: The area of the rectangle given below can be represented by the expression 2A 10x 16x 12= − + . If the width is ‘2 ’, find an expression for the length.
3 2A 6x 12x 18x= − +6x
2 2A 10x 16x 12= − +

Mathematics 9 Name: ______________________________ Dividing Polynomials by Monomials Date: ______________________________ Homework 1. Find the quotient for each expression.
a) 16x 18y2− b)
6 4 2
2
7a 21a 28a7a
− +
c) 3 29m 36m 18m
9m+ − d)
4 3 225d 20d 15d 10d5d
− − +−
e) ( ) ( )2 2 2 236a b 24a b 12ab 6ab− − ÷ f) 4 3 3 4 3 3
3
8m n 24m n 16m n8mn
− +
g) 8 9 7 7 7 5 6 5 4
6 4 4
30x y z 40x y z 50x y z10x y z
− + h) ( ) ( )5 4 4 3 3 226b c 28b c 32b c 2b c+ − ÷ −
2. The area of the rectangle given below can be represented by the expression 4 3 2A 8x 24x 16x= + − . If the width is ‘ 28x ’, find an expression for the length.
4 3 2A 8x 24x 16x= + −28x

15 cm11 cm
18 cm
Mathematics 9 Name: ________________________ Applications of Polynomials Date: _________________________ Perimeter vs Area Directions: Determine the perimeter and area of each of the following composite shapes. 1.
Perimeter Area

2x
8x 7+
3x
2.
Perimeter Area

4x 9+
2x
3x 5+
x
3.
Perimeter Area

6x 8+
2x
7x
4.
Perimeter Area