The Polks Tax Calculation
Transcript of The Polks Tax Calculation

Huy Xuan Trinh
ACCT 3350.001
Professor Steven Solcher
April 10, 2014
Individual Tax Return Project

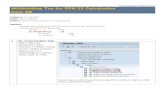
Tax Computation OverviewGross Income (minus exclusions) Reference
Robert 105,000$ Gross Income and bonus received W-2 (Form 1040)8,000$ Employer Reimbursement W-2 (Form 1040)
Lisa 100,000$ Consulting Income Schedule-C9,000$ Ford Motor Bonds Schedule B
200,000$ Cash Received from Like Kind Exchange Form 8824(75,000)$ Loss from worthless stock Schedule-D311,111$ Gain Recognized from Installment Sales Form 6252
7,000$ Income generated from gamblings 1040Gross Income 665,111$
Deductions for AGIRobert 8,000$ Reimbursed Employee Expenses Schedule ALisa 24,640$ Deductible Business Expense Schedule C
2,700$ Deductible Home Office Expenses Form 88296,000$ Bad Debt Expenses Schedule C4,215$ Self Employment Tax Deduction Schedule SE7,000$ State and local sales taxes
52,555$
Adjusted Gross Income 612,556$ Deduction from AGI Itemized Schedule-A
6,000$ Robert's contribution of medical coverage14,000$ The Polks' Medical and Dental Expenses 20,000$
61,255.60$ 10% AGINo medical deduction allowed
6,300$ Advalorem Tax13,500$ Qualified mortgage Interest
500$ Qualified Charitable Contribution
1,150$ Unreimberused employee business expenses12,251.12$ 2 % of AGI
No miscellaneous deduction allowedTotal Itemized Deduction 20,300$
9,377$ Reduction to Itemized Deduction because of filing status Standard Deduction10,923$ Allowable Itemized Deductions 12,200$
Personal and Dependency Exemptions11,700$ 2 personal exemption and 1 dependent exemption
612,556$ AGI422,500$ The threshold for exemptions phase-out
No Exemptions AllowedTaxable Income 600,356$

1. Taxpayer Biographical InformationThe Polk filed a joint return and use cash basis for tax purposes.
The Polks qualifies for 2 personal exemptions ($3,900*2 = $ 7,800).
The Polks may also claim the following as dependent ($3900):
Tyler Polk. All dependency tests have been met for a qualifying child. He is under 19, provides none of his support, is the Polk’s son, lives with his family and is the U.S. citizen.
The Polks may not claim the following as dependent:
Anne Marie Polk. She is neither a qualifying child nor a qualifying relative. She fails the Age Test to be a qualifying child (she is above 19 and does not attend college) and the Gross Income Test to be a qualifying relative (her gross income is $ 17,000 > $ 3,900). Anna Marie Polk will file a tax return for her own as a single taxpayer. Anna Marie qualifies for one personal exemption ($3,900).
However, since the family AGI is higher than the threshold for exemptions phase-out, the Polks is not allowed to take any personal and dependency exemptions.
2. Taxpayer Gross Income
2.1 Robert PolkRobert’s gross incomes include his yearly salary and his previous year bonus (received in 2012):
$90,000 + $15,000 = $105,000
Assume that Robert’s employer, MGM, has an accountable reimbursement plan, Robert’s gross incomes include the $8,000 reimbursement.
2.2 Lisa PolkLisa’s gross incomes include:
- Consulting Income: $100,000- Ford Motor Company bonds: $9,000
Not include:
- Cash gifts from Lisa’s parents: - The money billed but not paid until 2013 (cash basis tax payer is only taxed when received)- The interest income from City of Dallas bonds (tax-exempt income)- Assume Sarah Duval is Lisa’s friends and the loan Lisa made to Sarah is an interest-free loan.
Under administrative convenience; the $3,000 loan is exempted from the imputed interest rules. Therefore, the $3,000 repayment is excluded from gross income (as it was not deductible in the year the loan was made).
- Federal Income Tax refund (2010 return) $9,000

Like-kind Exchange
Amount realized ( 500,000 + 200,000) 700,000$ Adjusted basis 400,000$ Realized gain 300,000$ Recognized gain (Cash Boot Received) (200,000)$ Defereed Gain 100,000$
Basis in the tract in Dixie County (500,000 - 100000) 400,000$
Installment Sales
Amount Realized (400,000 + 125,000*4) 900,000$ Basis in land 200,000$ Recognized Gain 700,000$ Interest Income (125,000 * 4 * 8%) 40,000$
Recognized gain in Interest Income2012 400,000*(700,000/900,000) 311,111$ 311,111$ 2013 125,000*(700,000/900,000) 97,222$ 10,000$ 107,222$ 2014 125,000*(700,000/900,000) 97,222$ 10,000$ 107,222$ 2015 125,000*(700,000/900,000) 97,222$ 10,000$ 107,222$ 2016 125,000*(700,000/900,000) 97,222$ 10,000$ 107,222$
700,000$ 40,000
2.3 Anna Marie Polk
Anna Marie’s gross income is $ 17,200, derived from performing at various events.
2.4 Other Polks’ Joint Income
The Polks include $8,200 from gambling winnings in their gross income. However, the amount of taxable income is only $ 7,000 ($ 8,200 - $ 1,200) because of the $ 1,200 losses.

3. Taxpayer Business Expenses & Deduction for AGI
3.1 Robert PolkAssume the expense from lodging- not at a MGM does not have business purpose and the $500 fines are not deductible because it is against the public policy, the total business-related expenses Robert incurred is as follows:
Airfare $5,100Lodging: value of stays at a MGM $3,300Meals(50%) $400Entertainment(50%) $175Car rentals, limos, taxis $750
$9,725
Since reimbursement ($8,000) is less than actual expenses ($ 9,725), Robert may deduct the $8,000 for AGI. The rest, $1,725 ($9,725 - $8,000) is treated as itemized deductions with 50% rule applies for meals and entertainment and the 2% limit for overall miscellaneous deductions.
Worthless Stock
The Groupon stock that Robert held for more than a year (qualified as long-term investments) became worthless as the company went bankrupt in 2012. Assuming that Groupon had not paid any dividends to Robert, Robert is allowed to deduct the total amount of his investments in the stock: 5000 shares * $15 = $ 75,000.
Since the Polks filed jointly, the $ 75,000 loss will be netted against other gains to get the total gain from long-term investments.
3.2 Lisa PolkFollowing are Lisa’s expenses associated with her consulting business:
Deductible Business Expenses
Supplies 4,000$ Legal 8,000$ CPA license fee 1,500$ Subscription to professional journals 7,500$ Bad Debt Expense 6,000$ State and Local Sales Tax 7,000$ Dues to professional organizations 250$ Auto Expenses (6000 miles*0.565) 3,390$
37,640$
All the expenses above are deductible because they have the business purposes and meet the five negativity test.

Home Office
Following are the amount of deductions that Lisa is allowed to take to her home office. Since she used 200 sq. feet of her 2,000 sq. foot house, she is allowed to deduct 10% (200/2000) of all her real estate expenses:
Advalorem Taxes 7,000$ Mortgage Interest 15,000$ Repairs to roof 2,000$ Uitilities 3,000$
27,000$ *10%$2,700
Bad Debt Expense
Lisa is also to deduct $ 6,000 as a bad debt because the person who owed her were convicted of arson in 2012 and is serving time in prison.
State and Local Sales Tax
Assume the Polks’ state and local sales taxes are expenses associated with Lisa’s consulting business, therefore, they are allowed to deduct $ 7,000 as business expenses.
Self-Employment Tax
Lisa is self-employed. Therefore, she is subjected to the 15.3% self-employment tax, with half of them are deductible for AGI (see Schedule SE).
4. Taxpayer Losses & Deduction from AGI
4.1 Robert PolkRobert’s allowable itemized deductions include:
The excess of 10% of AGI from his contributions $6,000 to his employer’s group health insurance plan.
The excess of 2% of AGI from the total miscellaneous deductions. Since $2,300 is smaller than 2% of the Polks’ AGI ($13,775). None of the amount is deductible.
4.2 Joint Allowable Itemized Deductions
Advalorem Taxes on Residence (90%) 6,300$ Interest on Home Mortgage (90%) 13,500$ Contributions to Salvation Army 500$

Life insurance premiums are not allowed to deduct. Ad Valorem Taxes and Mortgage Interest are deductible on the amount of personal use (90%). Medical expense 10% AGI limit. The total amount of the family medical expenses was $ 20,000
($6,000 from Robert’s contribution to his employer’s medical coverage and $14,000 family medical expenses. However, since $20,000 is smaller than 10% of AGI limit ($688,771), none of the amount is deductible.
Contribution to Texas governor’s election campaign fund is not deductible
5. Calculation of Tax Due 5.1 The Polks- MFJ
Tax Amount from Tax Computation Worksheet 106,387$ Self-employment Tax 8,429$ Medicare Taxes on Unearned Income 13,758$ Amount of Tax on Taxable Income 128,575$
Tax Paid 71,000$ Tax Due 57,575$
The Polks taxable income is separated into two parts: earned income and unearned income. Tax on Earned income is derived by looking at the tax table provided by the IRS. The tax on unearned income is taxed at two levels: 15% and 20% because part of Polk’s taxable income is in the 39.6% marginal tax rate bracket. Following is an illustration of the computation:
Taxable Income 600,356$ Tax on Earned IncomeEarned Income 164,245$ 33,453$
Long-term Capital Gain 436,111$ Tax Treatment AmountAmount (450,000-164,245) 285,755$ 15% 42,863.25$ Amount in 39.6% marginal tax rate 150,356$ 20% 30,071.20$
72,934.45$
Lisa is the owner of her consulting business. This year she had net operating gain. Therefore, she is also subjected to self-employment tax at 15.3% of her profit.
The Polks unearned income this year is higher than the 250,000 threshold. Therefore, they are subjected to additional 3.8% Medicare tax.

5.2 Anna Marie Polk- Single
Gross Income 17,200$ Deduction for AGIDedudction from AGI
Standard Deduction 6,100$ Personal Exemption 3,900$
Taxable Income 7,200$
Tax Due 718$