1 The Plasma Membrane The Plasma Membrane - Gateway to the Cell copyright cmassengale.
The Plasma Membrane Honors Biology Chapter 6 History of the Plasma Membrane 1665: Robert Hooke ...
-
Upload
brandon-kory-gordon -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
0
Transcript of The Plasma Membrane Honors Biology Chapter 6 History of the Plasma Membrane 1665: Robert Hooke ...


The Plasma The Plasma MembraneMembrane
Honors BiologyHonors BiologyChapter 6Chapter 6

History of the Plasma History of the Plasma MembraneMembrane
1665: Robert Hooke 1665: Robert Hooke 1895: Charles Overton - composed of 1895: Charles Overton - composed of
lipids lipids 1900-1920’s: must be a phospholipid 1900-1920’s: must be a phospholipid 1925: E. Gorter and G. Grendel - 1925: E. Gorter and G. Grendel -
phospholipid phospholipid bilayerbilayer 1935: J.R. Danielli and H. Davson – 1935: J.R. Danielli and H. Davson –
proteins also part, proposed the proteins also part, proposed the Sandwich ModelSandwich Model
1950’s: J.D. Robertson – proposed the 1950’s: J.D. Robertson – proposed the Unit Membrane ModelUnit Membrane Model
1972: S.J. Singer and G.L. Nicolson – 1972: S.J. Singer and G.L. Nicolson – proposed proposed Fluid Mosaic ModelFluid Mosaic Model

Plasma Membrane is made of Plasma Membrane is made of PhospholipidsPhospholipids
Gorter + Grendel Gorter + Grendel – Red Blood Cells analyzedRed Blood Cells analyzed– Enough for Phospholipid bilayerEnough for Phospholipid bilayer– Polar heads face out and Polar heads face out and
Nonpolar tails face in Nonpolar tails face in– Does not explain why some Does not explain why some
nonlipids are permeable nonlipids are permeable

Plasma Membrane ModelsPlasma Membrane Models
Sandwich ModelSandwich Model(Danielli + Davson)(Danielli + Davson)2 layers of globular proteins with 2 layers of globular proteins with phospholipid inside to make a layer and phospholipid inside to make a layer and then join 2 layers together to make a then join 2 layers together to make a channel for molecules to passchannel for molecules to pass
Unit Membrane Model Unit Membrane Model (Robertson)(Robertson)Outer layer of protein with phospholipid Outer layer of protein with phospholipid bilayer inside, believed all cells same bilayer inside, believed all cells same composition, does not explain how some composition, does not explain how some molecules pass through or the use of molecules pass through or the use of proteins with nonpolar parts, used proteins with nonpolar parts, used transmission electron microscopytransmission electron microscopy
Fluid Mosaic Model Fluid Mosaic Model (Singer + Nicolson)(Singer + Nicolson)Phospholipid bilayer with proteins partially Phospholipid bilayer with proteins partially or fully imbedded, electron micrographs of or fully imbedded, electron micrographs of freeze-fractured membranefreeze-fractured membrane

Which membrane model is Which membrane model is correct?correct?
1) Rapidly freeze specimen1) Rapidly freeze specimen
2) Use special knife to cut membrane in half2) Use special knife to cut membrane in half
3) Apply a carbon + platinum coating to the surface3) Apply a carbon + platinum coating to the surface
4) Use scanning electron microscope to see the surface4) Use scanning electron microscope to see the surface
According to the electron micrograph which membrane model According to the electron micrograph which membrane model is correct?is correct?
Why?Why?
Fluid-Mosaic ModelFluid-Mosaic Model

Fluid-Mosaic ModelFluid-Mosaic Model FluidFluid – the plasma membrane is the consistency of olive oil – the plasma membrane is the consistency of olive oil
at body temperature, due to unsaturated phospholipids. (cells at body temperature, due to unsaturated phospholipids. (cells differ in the amount of unsaturated to saturated fatty acid differ in the amount of unsaturated to saturated fatty acid tails) tails)
Most of the lipids and some proteins drift laterally on either Most of the lipids and some proteins drift laterally on either side. Phospholipids do not switch from one layer to the next.side. Phospholipids do not switch from one layer to the next.
Cholesterol affects fluidity: at body temperature it lessens Cholesterol affects fluidity: at body temperature it lessens fluidity by restraining the movement of phospholipids, at fluidity by restraining the movement of phospholipids, at colder temperatures it adds fluidity by not allowing colder temperatures it adds fluidity by not allowing phospholipids to pack close together.phospholipids to pack close together.
MosaicMosaic – membrane proteins form a collage that differs on – membrane proteins form a collage that differs on either side of the membrane and from cell to cell (greater either side of the membrane and from cell to cell (greater than 50 types of proteins), proteins span the membrane with than 50 types of proteins), proteins span the membrane with hydrophilic portions facing out and hydrophobic portions hydrophilic portions facing out and hydrophobic portions facing in. Provides the functions of the membranefacing in. Provides the functions of the membrane

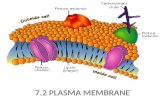
Structure of the Plasma Structure of the Plasma MembraneMembrane

Structure of the Plasma Structure of the Plasma MembraneMembrane
Phospholipid bilayerPhospholipid bilayer
PhospholipidPhospholipid– Hydrophilic headHydrophilic head– Hydrophobic tailsHydrophobic tails
CholesterolCholesterol
ProteinsProteins– Transmembrane/Transmembrane/
Intrinsic/Intrinsic/IntegralIntegral
– Peripheral/ExtrinsicPeripheral/Extrinsic
Cytoskeletal filamentsCytoskeletal filaments
Carbohydrate chainCarbohydrate chain
GlycoproteinsGlycoproteins
GlycolipidsGlycolipids

Label the Blank Diagram of the Label the Blank Diagram of the Plasma MembranePlasma Membrane
Phospholipid bilayerPhospholipid bilayer
PhospholipidPhospholipid– Hydrophilic headHydrophilic head– Hydrophobic tailsHydrophobic tails
CholesterolCholesterol
ProteinsProteins– Transmembrane/Transmembrane/
Intrinsic/IntegralIntrinsic/Integral– Peripheral/ExtrinsicPeripheral/Extrinsic
Cytoskeletal filamentsCytoskeletal filaments
Carbohydrate chainCarbohydrate chain
GlycoproteinsGlycoproteins
GlycolipidsGlycolipids

Proteins of the Plasma Proteins of the Plasma Membrane Provide 6 Membrane Provide 6 Membrane Functions:Membrane Functions:
1) 1) Transport ProteinsTransport Proteins
2) 2) Receptor ProteinsReceptor Proteins
3) 3) Enzymatic ProteinsEnzymatic Proteins
4) 4) Cell Recognition Cell Recognition ProteinsProteins
5) 5) Attachment ProteinsAttachment Proteins
6) 6) Intercellular Junction Intercellular Junction
ProteinsProteins

1)1) Transport ProteinsTransport Proteins
Channel ProteinsChannel Proteins – – channel for lipid channel for lipid insoluble molecules insoluble molecules and ions to pass and ions to pass freely throughfreely through
Carrier ProteinsCarrier Proteins – – bind to a substance bind to a substance and carry it across and carry it across membrane, change membrane, change shape in processshape in process

2)2) Receptor ProteinsReceptor Proteins
– – Bind to chemical Bind to chemical messengers (Ex. messengers (Ex. hormones) which hormones) which sends a message sends a message into the cell causing into the cell causing cellular reactioncellular reaction

3)3) Enzymatic ProteinsEnzymatic Proteins
– – Carry out enzymatic Carry out enzymatic reactions right at reactions right at the membrane the membrane when a substrate when a substrate binds to the active binds to the active sitesite

4)4) Cell Recognition Cell Recognition ProteinsProteins
– – Glycoproteins (and Glycoproteins (and glycolipids) on glycolipids) on extracellular surface extracellular surface serve as ID tags serve as ID tags (which species, type (which species, type of cell, individual). of cell, individual). Carbohydrates are Carbohydrates are short branched short branched chains of less than chains of less than 15 sugars15 sugars

5)5) Attachment ProteinsAttachment Proteins- Attach to cytoskeleton (to Attach to cytoskeleton (to
maintain cell shape and maintain cell shape and stabilize proteins) and/or stabilize proteins) and/or the extracellular matrix the extracellular matrix (integrins connect to both).(integrins connect to both).
- Extracellular Matrix – Extracellular Matrix – protein fibers and protein fibers and carbohydrates secreted by carbohydrates secreted by cells and fills the spaces cells and fills the spaces between cells and supports between cells and supports cells in a tissue. cells in a tissue.
- Extracellular matrix can Extracellular matrix can influence activity inside the influence activity inside the cell and coordinate the cell and coordinate the behavior of all the cells in a behavior of all the cells in a tissue.tissue.

6)6) Intercellular Junction Intercellular Junction ProteinsProteins
– – Bind cells togetherBind cells together– Tight junctionsTight junctions– Gap junctionsGap junctions

• Materials must Materials must move in and out of move in and out of the cell through the cell through the plasma the plasma membrane.membrane.
• Some materials Some materials move between the move between the phospholipids.phospholipids.
• Some materials Some materials move through the move through the proteins.proteins.
How do materials move into How do materials move into and out of the cell?and out of the cell?

Plasma Membrane TransportPlasma Membrane Transport
• Molecules move across the plasma Molecules move across the plasma membrane by:membrane by:

What are three types of What are three types of passive transport?passive transport?
1)1) DiffusionDiffusion
2)2) Facilitated Facilitated DiffusionDiffusion
3)3) OsmosisOsmosis ATP energy is ATP energy is notnot needed to move the needed to move the molecules through.molecules through.

Passive Transport 1: Passive Transport 1: DiffusionDiffusion
• Molecules can move directly Molecules can move directly through the phospholipids of through the phospholipids of the plasma membranethe plasma membrane
This is called …This is called …

What is Diffusion?What is Diffusion?
• Diffusion is the net Diffusion is the net movement of movement of molecules from a high molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration to a low concentration until concentration until equally distributed.equally distributed.
• Diffusion rate is Diffusion rate is related to related to temperature, temperature, pressure, state of pressure, state of matter, size of matter, size of concentration concentration gradient, and surface gradient, and surface area of membrane.area of membrane.
http://www.biologycorner.com/resources/diffusion-animated.gif

What molecules pass through What molecules pass through the plasma membrane by the plasma membrane by
diffusion?diffusion?• Gases (oxygen, carbon Gases (oxygen, carbon
dioxide)dioxide)
• Water molecules (rate Water molecules (rate slow due to polarity)slow due to polarity)
• Lipids (steroid Lipids (steroid hormones)hormones)
• Lipid soluble molecules Lipid soluble molecules (hydrocarbons, (hydrocarbons, alcohols, some alcohols, some vitamins)vitamins)
• Small noncharged Small noncharged molecules (NHmolecules (NH33))

Why is diffusion important to Why is diffusion important to cells and humans?cells and humans?
• Cell respirationCell respiration• Alveoli of lungsAlveoli of lungs• CapillariesCapillaries• Red Blood CellsRed Blood Cells• Medications: Medications:
time-release time-release capsulescapsules

Passive Transport 2: Facilitated Passive Transport 2: Facilitated DiffusionDiffusion
• Molecules can move through Molecules can move through the plasma membrane with the the plasma membrane with the aid of transport proteinsaid of transport proteins
This is called …This is called …

What is Facilitated Diffusion?What is Facilitated Diffusion?
• Facilitated Facilitated diffusion is the diffusion is the net movement of net movement of molecules from a molecules from a high high concentration to a concentration to a low concentration low concentration with the aid of with the aid of channel or carrier channel or carrier proteinsproteins..

What molecules move through the What molecules move through the plasma membrane by facilitated plasma membrane by facilitated
diffusion?diffusion?• IonsIons (Na(Na++, K, K++, Cl, Cl--))
• Sugars Sugars (Glucose)(Glucose)
• Amino AcidsAmino Acids
• Small water soluble Small water soluble moleculesmolecules
• Water (faster rate)Water (faster rate)

How do molecules move through How do molecules move through the plasma membrane by facilitated the plasma membrane by facilitated
diffusion?diffusion?
• Channel and Carrier proteins are specific:Channel and Carrier proteins are specific:• Channel Proteins allow ions, small solutes, and Channel Proteins allow ions, small solutes, and
water to passwater to pass• Carrier Proteins move glucose and amino acidsCarrier Proteins move glucose and amino acids• Facilitated diffusion is rate limited, by the number Facilitated diffusion is rate limited, by the number
of proteins channels/carriers present in the of proteins channels/carriers present in the membrane.membrane.

Specific Types of Facilitated Specific Types of Facilitated DiffusionDiffusion
Counter TransportCounter Transport – the – the transport of two substances at transport of two substances at the same time in opposite the same time in opposite directions, without ATP. Protein directions, without ATP. Protein carriers are called carriers are called AntiportsAntiports..
Co-transport Co-transport – the transport of – the transport of two substances at the same time two substances at the same time in the same direction, without in the same direction, without ATP. Protein carriers are called ATP. Protein carriers are called SymportsSymports..
Gated ChannelsGated Channels – receptors – receptors combined with channel proteins. combined with channel proteins. When a chemical messenger When a chemical messenger binds to a receptor, a gate opens binds to a receptor, a gate opens to allow ions to flow through the to allow ions to flow through the channel. channel.

Why is facilitated diffusion Why is facilitated diffusion important to cells and humans?important to cells and humans?
• Cells obtain food Cells obtain food for cell respirationfor cell respiration
• Neurons Neurons communicatecommunicate
• Small intestine Small intestine cells transport food cells transport food to bloodstreamto bloodstream
• Muscle cells Muscle cells contractcontract

Passive Transport 3: Passive Transport 3: OsmosisOsmosis
• Water Molecules can move Water Molecules can move directly through the directly through the phospholipids of the plasma phospholipids of the plasma membranemembrane
This is called …This is called …

What is Osmosis?What is Osmosis?
• Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a Osmosis is the diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane. Water molecules semipermeable membrane. Water molecules bound to solutes cannot pass due to size, only bound to solutes cannot pass due to size, only unbound molecules. Free water molecules unbound molecules. Free water molecules collide, bump into the membrane, and pass collide, bump into the membrane, and pass through.through.

Osmosis in actionOsmosis in action• What will happen in the What will happen in the
U-tube if water freely U-tube if water freely moves through the moves through the membrane but glucose membrane but glucose can not pass?can not pass?
• Water moves from side with Water moves from side with high concentration of water high concentration of water to side with lower to side with lower concentration of water. concentration of water. Movement stops when Movement stops when osmotic pressure equals osmotic pressure equals hydrostatic pressure.hydrostatic pressure.

Why is osmosis important to Why is osmosis important to cells and humans?cells and humans?
• Cells remove Cells remove water produced water produced by cell by cell respiration.respiration.
• Large intestine Large intestine cells transport cells transport water to water to bloodstreambloodstream
• Kidney cells form Kidney cells form urineurine

Osmosis and TonicityOsmosis and Tonicity
Tonicity refers to the total solute Tonicity refers to the total solute concentration of the solution outside concentration of the solution outside the cell.the cell.
What are the three types of tonicity?What are the three types of tonicity?1)1) IsotonicIsotonic
2)2) HypotonicHypotonic
3)3) HypertonicHypertonic

IsotonicIsotonic Solutions that have the Solutions that have the samesame concentration concentration
of solutes as the suspended cell.of solutes as the suspended cell.
What will happen to a cell placed in an What will happen to a cell placed in an Isotonic solution?Isotonic solution?
The cell will have no net movement of water The cell will have no net movement of water and will stay the same size.and will stay the same size.
Ex. Blood plasma has high concentration of Ex. Blood plasma has high concentration of albumin molecules to make it isotonic to albumin molecules to make it isotonic to tissues.tissues.

HypotonicHypotonic Solutions that have a Solutions that have a lowerlower solute solute
concentration than the suspended cell.concentration than the suspended cell.
What will happen to a cell placed in a What will happen to a cell placed in a Hypotonic solution?Hypotonic solution?
The cell will gain water and swell.The cell will gain water and swell. If the cell bursts, then we call this lysis. If the cell bursts, then we call this lysis.
(Red blood cells = hemolysis)(Red blood cells = hemolysis) In plant cells with rigid cell walls, this In plant cells with rigid cell walls, this
creates turgor pressure.creates turgor pressure.

HypertonicHypertonic Solutions that have a Solutions that have a higherhigher solute solute
concentration than a suspended cell.concentration than a suspended cell.
What will happen to a cell placed in a What will happen to a cell placed in a Hypertonic solution?Hypertonic solution?
The cell will lose water and shrink. (Red The cell will lose water and shrink. (Red blood cells = crenation)blood cells = crenation)
In plant cells, the central vacuole will In plant cells, the central vacuole will shrink and the plasma membrane will pull shrink and the plasma membrane will pull away from the cell wall causing the away from the cell wall causing the cytoplasm to shrink called plasmolysis.cytoplasm to shrink called plasmolysis.

Review: Passive TransportReview: Passive Transport
• DiffusionDiffusion – O – O22 moves in and CO moves in and CO22 moves out moves out during cell respirationduring cell respiration
• Facilitated DiffusionFacilitated Diffusion – glucose and – glucose and amino acids enter cell for cell respirationamino acids enter cell for cell respiration
• OsmosisOsmosis – cell removal or addition of water – cell removal or addition of water

Review TonicityReview Tonicity What will happen to a red blood cell in What will happen to a red blood cell in
a hypertonic solution?a hypertonic solution? What will happen to a red blood cell in What will happen to a red blood cell in
an isotonic solution?an isotonic solution? What will happen to a red blood cell in What will happen to a red blood cell in
a hypotonic solution?a hypotonic solution?

1) Active Transport1) Active Transport2) Exocytosis2) Exocytosis3) Endocytosis3) Endocytosis
– PhagocytosisPhagocytosis– PinocytosisPinocytosis– Receptor-Mediated Receptor-Mediated
endocytosisendocytosis
What are three types of What are three types of Active transport?Active transport?
ATP energy is ATP energy is requiredrequired to move the to move the molecules through.molecules through.

Active TransportActive Transport Molecules move from areas of low Molecules move from areas of low
concentration to areas of high concentration to areas of high concentration with the aid of ATP concentration with the aid of ATP energy.energy.
Requires protein carriers called Requires protein carriers called Pumps.Pumps.

The Importance of Active The Importance of Active TransportTransport
Bring in essential molecules: ions, Bring in essential molecules: ions, amino acids, glucose, nucleotidesamino acids, glucose, nucleotides
Rid cell of unwanted molecules Rid cell of unwanted molecules (Ex. sodium from urine in kidneys)(Ex. sodium from urine in kidneys)
Maintain internal conditions Maintain internal conditions different from the environmentdifferent from the environment
Regulate the volume of cells by Regulate the volume of cells by controlling osmotic potentialcontrolling osmotic potential
Control cellular pHControl cellular pH Re-establish concentration Re-establish concentration
gradients to run facilitated gradients to run facilitated diffusion. (Ex. Sodium-Potassium diffusion. (Ex. Sodium-Potassium pump and Proton pumps)pump and Proton pumps)

The Sodium-Potassium PumpThe Sodium-Potassium Pump 3 Sodium ions move out 3 Sodium ions move out
of the cell and then 2 of the cell and then 2 Potassium ions move Potassium ions move into the cell.into the cell.
Driven by the splitting of Driven by the splitting of ATP to provide energy ATP to provide energy and conformational and conformational change to proteins by change to proteins by adding and then taking adding and then taking away a phosphate group.away a phosphate group.
Used to establish an Used to establish an electrochemical gradient electrochemical gradient across neuron cell across neuron cell membranes.membranes. http://www.biologie.uni-hamburg.de/b-online/library/biology107/bi107vc/fa99/terry/images/ATPpumA.gif

Active Transport 2: Active Transport 2: ExocytosisExocytosis
Movement of large Movement of large molecules bound in molecules bound in vesicles vesicles out ofout of the cell the cell with the aid of ATP with the aid of ATP energy. Vesicle fuses energy. Vesicle fuses with the plasma with the plasma membrane to eject membrane to eject macromolecules.macromolecules.
Ex. Proteins, Ex. Proteins, polysaccharides, polysaccharides, polynucleotides, whole polynucleotides, whole cells, hormones, mucus, cells, hormones, mucus, neurotransmitters, neurotransmitters, wastewaste

Active Transport 3: Active Transport 3: EndocytosisEndocytosis
Movement of large molecules Movement of large molecules intointo the the cell by engulfing them in vesicles, cell by engulfing them in vesicles, using ATP energy.using ATP energy.
Three types of Endocytosis:Three types of Endocytosis:– PhagocytosisPhagocytosis– PinocytosisPinocytosis– Receptor-mediated endocytosisReceptor-mediated endocytosis

PhagocytosisPhagocytosis ““Cellular Eating” – engulfing large Cellular Eating” – engulfing large
molecules, whole cells, bacteria molecules, whole cells, bacteria Ex. Macrophages ingesting bacteria Ex. Macrophages ingesting bacteria
or worn out red blood cells.or worn out red blood cells. Ex. Unicellular organisms engulfing Ex. Unicellular organisms engulfing
food particles.food particles.

PinocytosisPinocytosis ““Cellular Drinking” – engulfing liquids Cellular Drinking” – engulfing liquids
and small molecules dissolved in and small molecules dissolved in liquids; unspecific what enters.liquids; unspecific what enters.
Ex. Intestinal cells, Kidney cells, Plant Ex. Intestinal cells, Kidney cells, Plant root cellsroot cells

Receptor-Mediated Receptor-Mediated EndocytosisEndocytosis
Movement of very specific Movement of very specific molecules into the cell with molecules into the cell with the use of vesicles coated the use of vesicles coated with the protein clathrin. with the protein clathrin.
Coated pits are specific Coated pits are specific locations coated with clathrin locations coated with clathrin and receptors. When specific and receptors. When specific molecules (ligands) bind to molecules (ligands) bind to the receptors, then this the receptors, then this stimulates the molecules to stimulates the molecules to be engulfed into a coated be engulfed into a coated vesicle.vesicle.
Ex. Uptake of cholesterol Ex. Uptake of cholesterol (LDL) by animal cells(LDL) by animal cells

Review Types of EndocytosisReview Types of Endocytosis
What is What is phagocytosis?phagocytosis?
What is pinocytosis?What is pinocytosis?
What is receptor-What is receptor-mediated mediated endocytosis?endocytosis?

Types of Cell JunctionsTypes of Cell Junctions
In Animal Cells:In Animal Cells:
Tight JunctionsTight Junctions
DesmosomesDesmosomes
Gap JunctionsGap Junctions
In Plant Cells:In Plant Cells:
PlasmodesmataPlasmodesmata

Tight JunctionsTight Junctions Transmembrane Proteins of opposite Transmembrane Proteins of opposite
cells attach in a tight zipper-like cells attach in a tight zipper-like fashionfashion
No leakageNo leakage Ex. Intestine, Kidneys, Epithelium of Ex. Intestine, Kidneys, Epithelium of
skinskin

DesmosomesDesmosomes Cytoplasmic plaques of two cells bind Cytoplasmic plaques of two cells bind
with the aid of intermediate filaments with the aid of intermediate filaments of keratin of keratin
Allows for stretchingAllows for stretching Ex. Stomach, Bladder, HeartEx. Stomach, Bladder, Heart

Gap JunctionsGap Junctions Channel proteins of opposite cells join Channel proteins of opposite cells join
together providing channels for ions, together providing channels for ions, sugars, amino acids, and other small sugars, amino acids, and other small molecules to pass.molecules to pass.
Allows communication between cells.Allows communication between cells. Ex. Heart muscle, animal embryosEx. Heart muscle, animal embryos

PlasmodesmataPlasmodesmata Channels between the cell walls of plant Channels between the cell walls of plant
cells that are lined with the plasma cells that are lined with the plasma membranes of adjacent cells and smooth membranes of adjacent cells and smooth ER runs through.ER runs through.
Allows for the exchange of cytosol Allows for the exchange of cytosol between adjacent cells; moving water, between adjacent cells; moving water, small solutes, sugar, and amino acids.small solutes, sugar, and amino acids.
Ex. Xylem and Phloem in PlantsEx. Xylem and Phloem in Plants

Review Types of Cell Review Types of Cell JunctionsJunctions
What is the difference between a What is the difference between a plasmodesmata, tight junction, gap plasmodesmata, tight junction, gap junction, and desmosome?junction, and desmosome?

ReferencesReferences
Campbell, Neil A., Jane B. Reece, and Lawrence G. Campbell, Neil A., Jane B. Reece, and Lawrence G. Mitchell. (1999). Mitchell. (1999). BiologyBiology. Reading: Addison . Reading: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.Wesley Longman, Inc.
Mader, Sylvia S. (1996). Mader, Sylvia S. (1996). BiologyBiology. Boston: Times . Boston: Times Mirror Higher Education Group, Inc.Mirror Higher Education Group, Inc.
Raven, Peter H. and Johnson, George B. (1989). Raven, Peter H. and Johnson, George B. (1989). BiologyBiology. Boston: TimesMirror/Mosby College . Boston: TimesMirror/Mosby College Publishing.Publishing.

MitochondriaMitochondria

What is a Mitochondrion?What is a Mitochondrion?
A cellular organelle probably of endosymbiotic A cellular organelle probably of endosymbiotic origin that resides in the cytosol of most nucleated origin that resides in the cytosol of most nucleated (eurkaryotic) cells.(eurkaryotic) cells.
This organelle produces energy by oxidising This organelle produces energy by oxidising organic acids and fats with oxygen by the process organic acids and fats with oxygen by the process of of oxidative phosphorylationoxidative phosphorylation and generates and generates oxygen radicals (reactive oxygen species oxygen radicals (reactive oxygen species ROS )as a toxic by-productROS )as a toxic by-product

Mitochondrial Mitochondrial Structure (cont.)Structure (cont.)

Mitochondrial GeneticsMitochondrial Genetics
Each cell contains many mitochondria, Each cell contains many mitochondria, each of which contains multiple copies each of which contains multiple copies of 16.5-k-b circular DNA moleculeof 16.5-k-b circular DNA molecule
The mitochondrial genome is subject to The mitochondrial genome is subject to a number of peculiarities of inheritancea number of peculiarities of inheritance

Number of Mitochondria per cellNumber of Mitochondria per cell
Most somatic cells Most somatic cells 100-10,000100-10,000 LymphocyteLymphocyte 10001000 Oocytes Oocytes 100,000100,000 Sperm Sperm few hundredfew hundred
No mitochondria in red cells and some terminally No mitochondria in red cells and some terminally differentiated skin cellsdifferentiated skin cells

Mitochondrial GeneticsMitochondrial Genetics
Interest in mitochondrial genetics Interest in mitochondrial genetics comes mostly from:comes mostly from:
interest in diseases caused by interest in diseases caused by mutations in mDNAmutations in mDNA
interest in human historyinterest in human history


Mitochondrial Mitochondrial StructureStructure

4 4444 44

Oxidative phosphorylation



Endoplasmic ReticulumEndoplasmic Reticulum




A. Functions of A. Functions of the rER the rER Proteins Proteins
synthesized on synthesized on ribosomes of ribosomes of rER include: rER include:
sec secretory retory
proteins,proteins, inte integral membrane gral membrane
proteins,proteins, solu soluble proteins of ble proteins of
organelles. organelles.

A. Functions of the rER Proteins synthesized on ribosomes of rER include: secretory proteins, integral membrane proteins, soluble proteins of organelles

Golgi apparatus


Golgi complex and cell’s secretion




Acrosomal, Cortical ReactionsAcrosomal, Cortical Reactions


ribosomesribosomes











![Plasma Membrane [7.2] Goals: Understand the concept of homeostasis in relation to the plasma membrane Demonstrate and understand how the plasma membrane.](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5697c01d1a28abf838cd0a9a/plasma-membrane-72-goals-understand-the-concept-of-homeostasis-in-relation.jpg)