The Muscular System
description
Transcript of The Muscular System
The Muscular System
Functions of Muscle: StabilityHold bones tightly together Stabilize joints
Small muscles hold vertebrae together Stabilize the spinal column
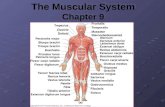
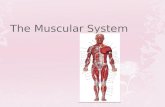
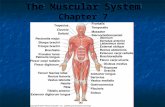
IntroductionThe human body has more than 600 individual muscles
Bones and joints do not produce movement
Muscles cause bones and supported structures to move by alternating between contraction and relaxationFunctions of muscleMuscle has the ability to contract, permitting muscles to perform various functionFunctions:MovementStabilityControl of body openings and passages Heat production
Microscopic Anatomy of Skeletal MuscleSarcomerecontractile unit of a muscle fiberOrganization of the sarcomereMyofilamentsThick filaments = myosin filamentsThin filaments = actin filaments
Microscopic Anatomy of Skeletal MuscleThick filaments = myosin filamentsComposed of the protein myosinHas ATPase enzymesMyosin filaments have heads (extensions, or cross bridges)Myosin and actin overlap somewhatThin filaments = actin filamentsComposed of the protein actinAnchored to the Z disc
Functions of Muscle: MovementSkeletal muscles Attached to bones by tendonsCross joints so when they contract, bones they attach to move
Smooth muscleFound on organ walls Contractions produce movement of organ contents
Cardiac muscle Produces atrial and ventricular contractions This pumps blood from the heart into the blood vesselsFunctions of Muscle: Control of Body Openings and PassagesSphincters Valve-like structures formed by muscles Control movement of substances in and out of passagesExample:A urethral sphincter prevents or allows urination
Functions of Muscle: Heat ProductionHeat is released with muscle contractionHelps the body maintain a normal temperatureMoving your body can make you warmer if you are cold
Apply Your Knowledge
True or False:___ Skeletal muscles are attached to bones by ligaments.__ Contractions of smooth muscle produce movement of organ contents.___ Cardiac muscle produces atrial and ventricular contractions.___ Sphincters control movement of substances out of passages.___ Heat is released as muscles relax.tendonsin and outcontractTTFFFANSWER:RIGHT!
Types of Muscle TissueMuscle cellsMyocytes called muscle fibers
Sarcolemma cell membrane
Sarcoplasm cytoplasm of cell
Myofibrils long structures in sarcoplasmArrangement of filaments in myofibrils produces striations
Muscle Group
Major Location
Major FunctionMode of Control
Skeletal Muscle
Attached to bones and skin of the face
Produces body movements and facial expressions
Voluntary
Smooth Muscle
Walls of hollow organs, blood vessels, and iris
Moves contents through organs; vasoconstriction
Involuntary
Cardiac MuscleWall of the heart
Pumps blood through heart
Involuntary
Types of Muscle Tissue: Skeletal MuscleMuscle fibers respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholineCauses skeletal muscle to contractFollowing contraction, muscles release the enzyme acetylcholinesteraseBreaks down acetylcholineAllows muscle to relaxMakes up about 90% of your musclesTypes of Muscle Tissue: Smooth MuscleMultiunit smooth muscleIn the iris of the eye and walls of blood vesselsResponds to neurotransmitters and hormonesVisceral smooth muscleIn walls of hollow organsResponds to neurotransmitters ANDStimulate each other to contract so that muscle fibers contract and relax together in a rhythmic motion peristalsis
Types of Muscle Tissue: Smooth Muscle (cont.) Peristalsis rhythmic contraction that pushes substances through tubes of the bodyNeurotransmitters for smooth muscle contraction AcetylcholineNorepinephrine Will cause or inhibit contractions, depending on smooth muscle type Makes up about 7% of your musclesTypes of Muscle Tissue: Cardiac MuscleIntercalated discsConnect groups of cardiac muscleAllow the fibers in the groups to contract and relax togetherAllows heart to work as a pump
Self-exciting does not need nerve stimulation to contractNerves speed up or slow down contraction
Type of Muscle Tissue: Cardiac Muscle (cont.)NeurotransmittersAcetylcholine slows heart rateNorepinephrine speeds up rateMakes up about 3% of your muscles
Apply Your Knowledge
Match the following:___ Self-excitingA. Skeletal muscle___ Contract in response toB. Smooth muscle acetylcholineC. Cardiac muscle ___ Stimulate each other to contract___ Peristalsis___ Slowed by acetylcholine___ Voluntary movementCAABBVery Good!CANSWER:
Production of Energy for Muscle ATP (adenosine triphosphate) A type of chemical energyNeeded for sustained or repeated muscle contractions Muscle cells must have three ways to store or make ATP Creatine phosphate Rapid production of energyAerobic respiration Uses bodys store of glucose Lactic acid production Small amounts of ATPATP = energyProduction of Energy: Oxygen DebtDevelops when skeletal muscles are used strenuously for several minutes and cells are low in oxygenPyruvic acidConverts toMuscle fatigueLactic acid which builds up
Oxygen debtTo liver for conversion to glucose, requiring more energy and oxygen to make ATPProduction of Energy: Muscle FatigueCondition in which a muscle has lost its ability to contract CausesAccumulation of lactic acid Interruption of the blood supply to a muscle A motor neuron loses its ability to release acetylcholine onto muscle fibers Apply Your KnowledgeMatch the following:___ Rapid production energyA. Lactic acid___ Needed for sustained orB. Pyruvic acid repeated muscle contractionsC. ATP___ Uses bodys store of glucoseD. Aerobic ___ Muscle fatigue respiration ___ With strenuous exercise,E. Creatineconverts to lactic acid phosphate
CADBEANSWER:Yippee!
Structure of Skeletal MusclesSkeletal muscles The major components of the muscular system
Composition Connective tissueSkeletal muscle tissue Blood vessels Nerves
Structure: Connective Tissue CoveringsFascia Covers entire skeletal muscles Separates them from each other
TendonA tough, cord-like structure made of fibrous connective tissueConnects muscles to bones
Aponeurosis A tough, sheet-like structure made of fibrous connective tissue Attaches muscles to other musclesStructure: Connective Tissue Coverings (cont.)Epimysium A thin covering that is just below the fascia of a muscle and surrounds the entire musclePerimysium Connective tissue that divides a muscle into sections called fasciclesEndomysium Covering of connective tissue that surrounds individual muscle cells
Apply Your Knowledge
Match the following:__Thin covering under the fascia that surrounds the muscle __Separates muscles from each other__Connects muscles to bones__Divides a muscle into sections called fascicles __Surrounds individual muscle cells__Attaches muscles to other musclesTendonPerimysium AponeurosisEpimysiumFasciaEndomysiumEABFCDANSWER:Excellent!
Attachments and Actions of Skeletal Muscles Actions depend largely on what the muscles are attached toAttachment sitesOrigin an attachment site for a less movable boneInsertion an attachment site for a more moveable bone
Attachments and Actions (cont.)Movement usually produced by a group of musclesPrime mover muscle responsible for most of the movementSynergists muscles that help the prime mover by stabilizing jointsAntagonist (agonist) produces movement opposite to prime moverRelaxes when prime mover contractsAttachments and Actions: Body Movements Flexion bending a body part
Extension straightening a body part
Hyperextension extending a body part past the normal anatomical position
Dorsiflexion pointing the toes up
Plantar flexion pointing the toes down
Abduction moving a body part away from the anatomical position
Adduction moving a body part toward the anatomical position
Attachments and Actions: Body Movements (cont.)Circumduction moving a body part in a circle
Pronation turning the palm of the hand down
Supination turning the palm of the hand up
Inversion turning the sole of the foot mediallyEversion turning the sole of the foot laterally
Retraction moving a body part posteriorly
Protraction moving a body part anteriorly
Attachments and Actions: Body Movements (cont.)Elevation lifting a body part; for example, elevating the shoulders as in a shrugging expression
Depression lowering a body part; for example, lowering the shoulders
Apply Your KnowledgeANSWER: Move the patients leg away from its position in the anatomical position. The doctor has asked you to abduct the patients leg so he can see the patients wound. In order to position the patient correctly, what will you have to do?
Correct!
Muscle Strains and SprainsStrains injuries due to over-stretched muscles or tendons
Sprains more serious injuries that result in tears to tendons, ligaments, and/or cartilage of joints
RICE is recommended treatment for eitherRestIceCompressionElevationMuscle Strains and Sprains (cont.)PreventionWarm up muscles A few minutes before an intense activity raises muscle temperature and makes muscle more pliableStretching Improves muscle performance and should always be done after the warm-up or after exercising Cooling down or slowing down Before completely stopping prevents pooling of blood in the legs and helps remove lactic acid from musclesAging and the Musculoskeletal SystemContractions become slower and not as strongDexterity and gripping ability decreaseMobility may decreaseAssistive devices helpfulRoutine exerciseSwimmingPhysical therapyIn SummarySkeletal musclesVoluntary controlProduce movement in conjunction with skeletal systemHelp stabilize jointsParticipate in heat productionSmooth musclesInvoluntary controlControl body openings and passages
Cardiac musclesInvoluntary controlResponsible for pumping action of the heartDiseases of the Muscular SystemMuscular DystrophyFibromyalgiaMyasthenia gravisBotulismTendonitis (lockjaw)TorticollisMyasthenic syndrome (Lambert-Eaton syndrome)PolymyositisAmyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)MyotoniaRhabdomyolysisFibrodysplasia ossificans progressivaMyoclonus (restless leg syndrome)Plantar fasciitis