The Muscular System
description
Transcript of The Muscular System

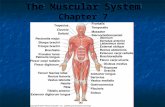
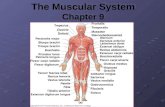
The Muscular System
The Skeletal Muscles

Types of Muscle Smooth - lines blood vessels and other
organs (ex. Stomach) (involuntary) Cardiac - found in heart (involuntary) Skeletal - attached to skeleton to create
movement (voluntary)

Functions of skeletal muscle Movement Posture Stabilize joints Generate heat

Insertion* - point ofattachment to moveable bone
Origin* - Attachment to less moveablebone
Origin andInsertion
*Muscles areattached to bones bytendons

Flexors and Extensors Flexor - decreases
angle between bones at a joint (ex.curling forearm towards upper arm)
Extensor - increases angle between bones at a joint (ex. straightening arm)

Prime mover/Agonist vs. Antagonist Prime movers are
muscles that produce the most force for a give movement
Antagonists oppose the force of the prime mover, but are not activated during the movement

Types of Muscle Contractions
Isometric - muscle contracts, but does not shorten or lengthen
Isotonic - muscle contracts, and either shortens or lengthens Concentric - muscle contracts as it shortens Eccentric - muscle contracts as it lengthens

Muscle Contraction Muscle contraction is stimulated by motor
neurons Motor neurons are nerve cells that
stimulate skeletal muscle Each muscle is innervated by at least one
motor nerve A motor neuron and the muscle fibers it
controls are called a motor unit

Motor Units Motor units are
activated during contraction
To exert more force (i.e. moving a heavy weight or moving very quickly) more motor units must be recruited
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.

Parts of a Muscle Fiber (a.k.a. muscle cell)
• Sarcolemma - cell membrane of muscle fiber• Sarcoplasm - cytoplasm of muscle fiber• Sarcoplasmic reticulum - endoplasmic
reticulum of muscle fiber (stores Ca2+ ions)• T-tubules - folding in of the sarcolemma
(allows nerve impulses to reach into the interior of a fiber)

Muscle Contraction (cellular level) Motor neuron sends nerve impulse to muscle fibers Impulse travels along sarcolemma of fiber and down T-
tubules Calcium ions are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ allow myosin heads to attach to actin binding sites
forming a cross-bridge Using the energy of ATP, myosin pulls on actin, causing the
muscle to shorten along its length

Sarcomere - smallest contractile unit of skeletal muscle
A Band - area occupied by myosin filaments (dark)
H zone - area between actin filaments
Z disk - proteins marking the beginning and end of the sarcomere
I band - area where there is no mysoin (light)
QuickTime™ and aTIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor
are needed to see this picture.