The mad scramble for africa
-
Upload
heidi-sager -
Category
Business
-
view
1.855 -
download
4
description
Transcript of The mad scramble for africa

The Scramble for Africa


Guiding Questions
• Why did mother countries lose most of
their colonies?
• Why do the mother countries want to
colonize Africa?
• Who organized the colonization process?
• What were the rules?
• How did they govern the colonies?

Mother Countries Lose Colonies
• In the early 1800’s, Europe’s mother
countries had lost most of their colonies.
– England had lost the American colonies in
the American Revolution
– Spain had lost most of their holdings in
North, Central, and South America due to
uprisings and revolts.

– The Portuguese had lost most of their
colonies to the Dutch
– The Dutch managed to hold on to their
colonies, but with great difficulty

Reasons for the Scramble
• Late 1800’s, Europe decides
to colonize Africa
• Europe wants to colonize
Africa to ensure trade
• England wants to control the
Suez Canal to ensure a
shorter route to India
• Gold and diamonds found all
over Africa!!

• Palm oil and lots of timber for export
• Greediness! They want to get land
just so the others won’t get it first!
• Nationalism is on the rise in Europe.
Citizens feel a sense of pride about
their countries worldwide assets.


Treaty of Berlin
• European and American leaders met in Berlin to
discuss the colonization of Africa
• King Leopold of Belgium wanted to exploit the
Congo River Valley.
• However, the other participants wanted to
regulate the new colonies to be made and make
sure they had access to important trade routes.

Treaty Rules
• Colonized areas must be occupied, not just
claimed
• Mother countries must defend their claims
and set up a colonial government
• They agreed not to import any more
firearms into Africa (giving them a military
advantage)
• Agreed to ban Inter-African slave trade

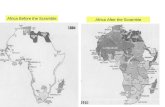
Effects of Treaty of Berlin
• Over 90% of Africa was now under
European Control
• The new borders ignored the traditional
boundaries. It separated peoples who had
gotten along, as well as joining groups
together who were traditional enemies.
• Even language groups were separated
from each other


Types of Colonial Rule
1. Company Charter: The mother country
gives permission for the company to go in
and exploit the natural resources of the area.
2. Direct Rule: The mother country divides up
the local areas and rules over them
individually (so they can’t join together for
revolt)

3. Indirect Rule: the mother country
allowed local chiefs to rule, but really
they were just “puppets” of the
mother country
4. Settler’s Rule: Mother country
sends colonists over and they take
charge of governing the colony
(Example: South Africa)

Follow up questions
• Why did mother countries lose most of
their colonies?
• Why do the mother countries want to
colonize Africa?
• Who organized the colonization process?
• What were the rules?
• How did they govern the colonies?