The Impact of ACA
-
Upload
athenista1 -
Category
Documents
-
view
34 -
download
1
Transcript of The Impact of ACA

Measuring the Impact of theACA and Health Care Reform
The information presented in this Webinar is current as of date of live airing – August 27, 2014
Dan HaleyVP, Gov’t and Regulatory Affairs
Josh GrayVP, athenaResearch

The BIG Question:Is the ACA
Working???

Depends on who you ask…

Evidence is mixed—and selectively invoked
• Increased access!
• Increased enrollment!
• Early bugs fixed!
• Premiums holding steady or falling!
• Rollout disaster!
• Key provisions delayed!
• Cost of care continuing to increase!
• Premiums increasing!

Our BIG Question:
How is the ACA impacting health IT policy, and our care
provider clients?
5

Again, the evidence is mixed

Again, the evidence is mixed
Increased access to insurance = increased access to care!
Lack of information fluidity and transparency means patients and providers cannot shop, so costs continue to rise.

Again, the evidence is mixed
Emphasis on accountable care = increased demand for modern information technology!
Government continues to subsidize closed platforms that do not interoperate.

Again, the evidence is mixed
Health IT standards and deadlines incentivize adoption and use!
Repeated deadline delays and reductions of standards create uncertainty and hamper innovation.

So the verdict is still out, but what do we
KNOW…?
A lot. Our platform and our data give us unparalleled insight
10

Josh Gray, Vice President, athenaResearch (JoshGray_hit)
Update on ACAView

Update onHealthcare
Reform

13
Health care reform rests on three pillars for expanding coverage and
controlling costs
Source: The Advisory Board Company
Fiscal Mechanisms
Slower Medicare cost increases
Disproportionate Share Hospital (DSH) reductions
Independent Payment Advisory Board empowered to reduce Medicare outlays above specified threshold
Delivery System Reform
Bundled payments expanding the episode of care
Shared Savings and ACOs creating total accountability for cost and outcomes
Pay-for-performance programs linking payments to care
Medical homes sharpening focus on high-risk patients
Coverage Expansion
Medicaid expansion broadens eligibility for low-income families• 26 states plus DC
have opted to expand Medicaid
Health insurance exchanges increase coverage options, offer subsidies for low- and middle-income families
Near-Universal Coverage, Sustainable Cost Growth

14
Bundled payments off to a solid start
Source: The Advisory Board Company; Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services.
Medicare Moving Quickly Private Sector Not Far Behind
Large Employers Exploring Bundling
Major Insurers in Pilot Stage
Partnering with Cleveland Clinic for select cardiac surgeries
Working with five major health systems for high-cost procedures
Offers employees cardiac and bundles at Johns Hopkins
BCBS North Carolina bundling orthopedic services at four sites
United bundling oncology services with Florida oncology clinics
Reimbursing bundled procedures at California orthopedic center
National initiative launched in 2011 by the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation (CMMI)
Offers 48 standardized bundles, including cardiac surgeries, orthopedics, diabetes, and CHF
Covers pre-admission, inpatient, and (in some cases) post-discharge care
350 participating providers
Bundled Payments for Care Improvement

0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
41 65 81
97
138
146
208
334356
458
479489
606 624
ACOs hitting their stride
15 Source: Leavitt Partners Center for Accountable Care Intelligence.
2010 2011 2012 2013
# o
f A
CO
s
Q4 Q1
Q2 Q3
Q4 Q1
Q2 Q3
Q4 Q1
Q2 Q3
Q4 Q1
• ACOs cover 18 million individuals
• > 50% of US population lives in markets served by ACOs
• 260 ACOs sponsored by medical groups
ACOs in Brief
2014

Two main drivers of coverage expansion
Expanded Medicaid Eligibility
Millions of Newly Eligible Individuals
Health Insurance Exchanges
More Options, with Generous Subsidies
Medicaid Eligibility, % Federal Poverty Level
47%Median State Eligibility, Pre-
ACA
133%States
ExpandingMedicaid
HIX
Primary mechanism for increasing coverage among low-income individuals
Expanded Medicaid eligibility covers individuals up to 133% of the federal poverty level (FPL)
Federal funding pays 100% of additional costs today, dropping to 90% in 2020
20 states have declined expansion, but allowed to participate in future years
National and state-run insurance exchanges link insurers and individuals
Plan tiers defined by actuarial value
Subsidies available to individuals with incomes up to 400% of the FPL
17 states operate own exchanges, 7 partner with federal government, 27 defer to federal exchange
Source: Kaiser Family Foundation, “State Decisions for Creating Health Insurance Marketplaces, 2014.”

17
Enrollment surged in the last few weeks
Source: Kaiser Family Foundation, “Total Monthly Marketplace Enrollment,” whitehouse.gov.
Oct 2013 Nov 2013 Dec 2013 Jan 2014 Feb 2014 Mar 2014 Apr 2014
106k365k
2.15M
3.30M
4.24M
8.02M3 Million+
Exchange Enrollment in Final Month
Jeffrey ZientsDirector of the National Economic Council
Former Director of the OMB, Chief Performance Officer of the United States, and head of HealthCare.gov “tech surge”
Todd ParkChief Technology Officer of the United States
Former CTO of the Department of Health and Human Services, co-founder of Athenahealth
7 MillionOriginal Enrollment
Target

Many states not expanding Medicaid
18
Expanding Medicaid
26 States plus DC
ConsideringExpansion
4States
Not Expanding Medicaid
20States
Source: The Advisory Board Company.

19
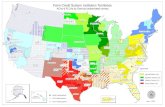
Coverage expansion exerting an uneven affect on states
South Dakota
Texas
Virginia
Pennsylvania
North Dakota
Maine
Wyoming
Tennessee
Utah
Wisconsin
Minnesota
North Carolina
New York
Ohio
Connecticut
Rhode Island
Colorado
Arizona
West Virginia
Washington
Significant Variation in the Newly InsuredNewly Insured Individuals per 1,000 Residents
Insured via Exchanges
Enrolled in Medicaid
Source: Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, “Medicaid & CHIP: April 2014 Monthly Applications,
Eligibility Determinations, and Enrollment Report,” Charles Gaba, ACASignups.net (various sources).
94
9286
83
6967
6560
5855
2018
1413
119
865
5
8.4 Million
Insured via Exchanges
5.3 Million
Newly Enrolled in Medicaid
Most
New
ly I
nsu
red
Few
est
New
ly I
nsu
red

Introducing ACAView

Overview
21
athenahealth today:
• Businesses: Billing, EHR, Patient Portal, Referral Coordination, Business Intelligence
• Architecture: Single-instance, multi-tenant cloud based application
• Billing: 36K MDs, 14K midlevels, 51M patients
• EHR: 12K MDs, 4K midlevels, 22M Lives
• 50 states and 92 medical specialties
• 2013 (clinicals): 12M patients, 40 M visits
• 2013 (claims): 30M patients, 80 M visits

Office Visit Characteristics: Physician DemographicsAthenahealth ACAView Practices vs NAMCS
Practice Size (Physicians)
12
3-56-10
11+
Census Region
Northeast
MidwestSouthWest
MSA Status Metro
32%12%
25%18%
14%
20%22%
38%21%
89%
18%14%
27%19%22%
22%22%
46%10%
88%
ACAView 20131 NAMCS2
Source: athenaResearch1: 30 million visits to practices active on the athenahealth network before 20112. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/ahcd/namcs_summary/2010_namcs_web_tables.pdf
A robust sample: physician demographics

Office Visit Characteristics: Patient DemographicsAthenahealth ACAView Practices vs NAMCS
Age
< 1515-2425-4445-6465-74
75+
Insurance
CommercialMedicare
Medicaid or CHIPMedicare and
MedicaidUninsured
Workers' Compensation
Other
Gender Female
16%8%
20%31%
13%12%
63%25%
14%2%4%1%6%
60%
13%8%
19%30%
15%15%
58%21%
10%5%3%2%2%
59%
ACAView 20131 NAMCS2
Source: athenaResearch1: 30 million visits to practices active on the athenahealth network before 20112. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/ahcd/namcs_summary/2010_namcs_web_tables.pdf
A robust sample: patient demographics

ACA View: Measuring the impact of health care reform
+24
Metrics include…
• Percent of total visits from new patients
• Percent of new patients with chronic disease
• Patient copays
• Bad debt
• Provider reimbursement levels
• Appointment wait time
• Work RVUs per visit

Partnering with RWJF to track the impact of coverage expansion
25
ACCESS PHYSICIAN VOLUMES DELEGATION
▶ New patient visits as % of total visits for PCPs
▶ Days to schedule an appointment
▶ Visits per week for PCPs
▶ Schedule density
▶ Percent of visits where rendering provider is a PA or NP for PCP practices
ACUITY/HEALTH STATUS REIMBURSEMENTPATIENT FINANCIAL
OBLIGATIONS
▶ Distribution of E&M visits by level
▶ Number of dx per visit
▶ % of patients w diabetes dx
▶ % of patients w HBP dx
▶ % of w hyperlipidemia
▶ Referrals per visit
▶ Scripts per visit
▶ Obesity rate
▶ HbA1C values
▶ BP values
▶ LDL values
▶ wRVU per visit
▶ % change in allowables per RVU
▶ Denials
▶ First pass rate
▶ Patient financial obligation ($/visit)
▶ Patient out-of-pocket payments ($/visit)
▶ % of patient obligations paid at 90 and 180 days
▶ Proportion of charges going to collections.

Proportion of Visits from New Patients, By Specialty Category
January through July
30%
20%
10%
0%
PCP Pediatrics OB/GYN Surgery Other
20.5%
18.3%
26.6%
44.0%
34.6%
20.4%19.0%
26.1%
44.4%
33.8%
40.6%2013 2014
Sample: Over 35 million visits to practices active on the athenahealth network before 2011Source: athenaResearch
40.6%
Physicians are so far not seeing more new patients

Work Intensity Metrics for New Patients to PCPs2013 vs 2014, January through July
Work RVUper Visit
Diagnoses per Visit
% of Visits with High
Complexity E&M Code*
2013 2.0 2.4 8.9%
2014 2.0 2.4 8.3%
* E&M code level 4 or 5.Sample: Over 35 million visits to practices active on the athenahealth network before 2011Source: athenaResearch
Complexity of new patients holding steady

2013 2014 % Change
EstablishedPatients
Diabetes 9.5% 9.4% -1%
High Blood Pressure
19.4%
19.6%
1%
High Cholesterol 15.8% 15.2% -4%
NewPatients
Diabetes 5.5% 5.6% 2%
High Blood Pressure
12.7% 12.9% 2%
High Cholesterol 7.2% 7.1% -2%
*% of encounters with diagnosisSample: 430K visits/month, to locations active before 2011Source: athenaResearch
Chronic Disease Rates*, Jan-JulyPCP Visits for Commercially Insured (18-64)
New patients this year have similar rates of chronic
diseases…

Figure 6: Chronic Disease Rates (18-64)*, Jan-MayPCP Visits for Privately Insured, Small Practices, South
Census Region
2013 2014 % Change
EstablishedPatients
Diabetes 10.0% 9.8% -2%
High Blood Pressure 1 22.4% 22.9% 2%
High Cholesterol 17.1% 16.6% -3%
NewPatients
Diabetes 5.1% 5.7% 12%
High Blood Pressure 14.5% 1 15.5% 7%
High Cholesterol 8.6% 8.7% 2%
*% of encounters with diagnosisSample: 50K visits/month, to locations active before 2011Source: athenaResearch
…except for patients receiving care at small practices in the
South

Payer Mix for Adult (18-64) PCP Visits, January through May Medicaid Expansion States vs Non-Expansion States
Sample: 5,000 primary care providers active on athenahealth prior to 2011Source: athenaResearch
Different payer mix shifts depending on Medicaid
expansion status
8.3%
7.3%
10.8%
10.3%
7.7%
7.1%
4.2%
3.8%
69.0%
71.5%
13.8%
15.8%
9.8% 9.8%
4.7%
3.2%
3.6%
3.2%
68.1%
68.0%
2.5%
-1.0%
-0.6%
-0.6%
-0.3%
-0.2%
2.0%
0.1%
-1.5%
-0.4%

16%
12%
8%
4%
0%
Sample: 5,000 primary care providers active on athenahealth prior to 2011Source: athenaResearch
Medicaid is spiking in expansion states, flat elsewhere
Non-Expansion State: UninsuredExpansion State: Medicaid
Non-Expansion State: Medicaid
Expansion State: Uninsured
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 101112 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 101112 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
2012 2013 2014
Adult (18-64) PCP Visits from Medicaid and Uninsured Patients Medicaid Expansion States vs Non-Expansion States
3.1%4.3%
5.7%
6.1%
6.2%
6.8%
16.0%12.4
%

Confidential – do not distribute. Copyright © 2011 epocrates, inc. All rights reserved.
▶ Patient obligations ▶ Patient out of pocket payments
▶ Referrals per visit
▶ Schedule density ▶ Patient payments as percent of obligations – 90 and 180 days
▶ Scripts per visit
▶ Appointment lag time ▶ Denials – new and exiting patients
▶ Obesity rate
▶ Allowables per RVU ▶ First pass rate ▶ HbA1c, BP, LDL values outside threshold
▶ Proportion of charges going to collections
▶ Percent of visits performed by MDs, NPs, PAs
Just scratching the surface: timeline for future metrics
9/15/14 12/15/14 3/15/14

For more information
SLIDE 33 CONFIDENTIAL – DO NOT DISTRIBUTE. Copyright © 2011 Epocrates, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Source: http://www.rwjf.org/content/dam/farm/reports/issue_briefs/2014/rwjf414550