The Human Cardiovascular System
description
Transcript of The Human Cardiovascular System

The HumanCardiovascular System
*In preparation for a pig’s heart dissection
Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D.,Human Anatomy

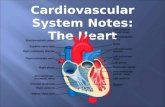
Cardiovascular/Circulatory System:
• Principles• Structures• Two circuits
• Pulmonary• Systemic
• Heart Details• Other Details

CV System Function:Circulate blood through entire body for
• Transport of oxygen to cells• Transport of CO2 away from cells• Transport of nutrients (glucose) to cells• Movement of immune system components
(cells, antibodies)• Transport of hormones

How?• Heart is pump• Diffusion in capillaries
Arteries = AwayVeins = Return

• Heart/Great Vessels--1 Route• Smaller arteries & veins --many routes
-collateral circulation
Overall Organization

Walls of Arteries and Veins• Tunica externa
– Outermost layer– Strengthens, Anchors
• Tunica media– Middle layer– Vaso-constriction/dilation
• Tunica intima– Innermost layer– Minimize friction
• Lumen

Artery/Vein DifferencesArteries Veins
Direction of flow
Blood Away from Heart
Blood to Heart
Pressure Higher Lower
Walls THICKER: Tunica media thicker than tunica externa
THINNER: Tunica externa thicker than tunica media
Lumen Smaller Larger
Valves No valves Valves (see next)



Capillaries• Microscopic: 1 cell thick• Network • Entire goal of C-V system is
to get blood into capillaries where diffusion takes place

GREAT VESSELS•Aorta• IVC, SVC•Pulmonary Trunk•Pulmonary Veins

2 Circulatory Paths
Pulmonary
Systemic
heartarteries arterioles veinsvenules capillaries



Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D.,Human Anatomy
Heart Chambers and Valves

Right Heart Chambers: Pulmonary Circuit• Right Atrium (forms most of posterior of heart)
– Receives O2-poor blood from body via IVC, SVC, Coronary sinus
• Right Ventricle– Receives O2-poor blood from right atrium
through tricuspid valve– Pumps blood to lungs via Pulmonary Semilunar
Valve in pulmonary trunk
– Septum

Left Heart Chambers: Systemic Circuit• Left Atrium
– Receives O2-rich blood from 4 Pulmonary Veins
• Left Ventricle (forms apex of heart)– Receives blood from Left Atrium via bicuspid valve– Pumps blood into aorta via Aortic Semilunar
Valve to body



Heart Valves: Lub*-Dub**• *Tricuspid Valve: Right AV valve
– 3 Cusps (flaps) made of endocardium and CT– Cusps anchored in Rt. Ventricle by Chordae Tendinae– Chordae Tendinae prevent inversion of cusps into atrium– Flow of blood pushes cusps open– When ventricle in diastole (relaxed), cusps hang limp in ventricle– Ventricular contraction increases pressure and forces cusps closed
• *Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve: Left AV valve– 2 cusps anchored in Lft. Ventricle by chordae tendinae– Functions same as Rt. AV valve
• **Semilunar valves: prevents backflow in large arteries– Pulmonary Semilunar Valve: Rt Ventricle and Pulmonary Trunk– Aortic Semilunar Valve: Left Ventricle and Aorta– 3 cusps: blood rushes past they’re flattened, as it settles they’re pushed
down (valve closed)

Location of Heart in Thorax

Heart Wall • Epicardium (most superficial)
– Visceral pleura• Myocardium (middle layer)
– Cardiac muscle– Contracts
• Endocardium (inner)– Lines the heart

Blood supply to heart wall• Rt and Lft Coronary Arteries
– Branch from Ascending Aorta– Have multiple branches along heart– Coronary Heart Disease
• Cardiac Veins– Coronary Sinus (largest)– Many branches feed into sinus

http://www.rmgh.net/wiki/images/4/4b/Coronary_arteries_and_cardiac_veins.gif

Chamber contraction/relaxation