The human brain … … tricks us whenever it can!. Sensation and Perception Sensation: what occurs...
-
Upload
miya-lamison -
Category
Documents
-
view
222 -
download
0
Transcript of The human brain … … tricks us whenever it can!. Sensation and Perception Sensation: what occurs...

The human brain …
… tricks us whenever it can!

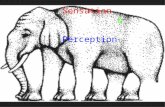
Sensation and Perception
Sensation: what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor
Perception: the organization of sensory information into meaningful experiences

Gestalt Psychology
• The brain is always trying to build a complete image or experience out of the confusion of all the stimuli it is receiving from all of the senses.
• The process of “filling in the blanks” is known as Gestalt.• The brain wants to find a meaning to everything, image,
feeling, or shape it is sensing.• Gestalt is a German word meaning patterns or
configurations.• Look at the images, shapes, and patterns in the next
slides. What do you see? What are you really seeing?

The phenomenal power of the human mind I cdnuolt blveiee taht I cluod aulaclty uesdnatnrd waht I was rdanieg
The phaonmneal pweor of the hmuan mnid! Aoccdrnig to a rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn't mttaer inwaht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoatnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be in the rghit
pclae. The rset can be a taotl mses and you can sitll raed it wouthit a porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by
istlef, but the wrod as a wlohe. Amzanig huh? Yaeh, and I awlyas thought slpeling was ipmorantt.

Sensory Thresholds
• Absolute threshold– The minimum amount of energy that can be
detected 50% of the time

Absolute Thresholds
• Taste: 1 gram (.0356 ounce) of table salt in 500 liters (529 quarts) of water
• Smell: 1 drop of perfume diffused throughout a three-room apartment
• Touch: the wing of a bee falling on your cheek from a height of 1cm (.39 inch)
• Hearing: the tick of a watch from 6 meters (20 feet) in very quiet conditions
• Vision: a candle flame seen from 50km (30 miles) on a clear, dark night

Sensory Thresholds
• Sensory adaptation– An adjustment of the senses to the level of
stimulation they are receiving
• Difference threshold– The smallest change in stimulation that can
be detected 50% of the time– Also called the just noticeable difference

Sensory Thresholds
• Weber’s Law– States that the difference threshold is a
constant proportion of the specific stimulus– Senses vary in their sensitivity to changes in
stimulation

Subliminal Perception
• The notion that we may respond to stimuli that are below our level of awareness
• Research shows that the effect only occurs in controlled laboratory studies
• Research outside the laboratory shows no significant effect of subliminal information

Vision

Receptor CellsCells in the retina that are sensitive to light
Visual receptors are called rods and cones
• Rods– About 120 million rods– Respond to light and
dark– Very sensitive to light– Provide our night
vision
• Cones– About 8 million cones– Respond to color as
well as light and dark– Work best in bright
light– Found mainly in the
fovea

Theories of Color Vision
• Trichromatic theory– Three different types of cones
• Red• Green• Blue-violet
– Experience of color is the result of mixing of the signals from these receptors
– Can account for some types of colorblindness

Forms of Colorblindness
• Approximately 10% of men and 1% of women have some form of colorblindness
• Dichromats– People who are blind to
either red-green or blue-yellow
• Monochromats– People who see no color at
all, only shades of light and dark


Theories of Color Vision
• Trichromatic theory cannot explain all aspects of color vision– People with normal vision cannot see
“reddish-green” or “yellowish-blue”– Color afterimages



If something‘s rotating – go home, you need a break!

Take a look at the picture.

Optical Illusions and Visual Phenomena Want to confuse your eyes and brain a bit?
Yes? Then you might want to have a look at the following pics ..

It ...

… doesn‘t move!

... parallel or not?

Coil or circle?

Concentrate on the cross in the middle, after a while you will notice that this
moving purple dot will turn green!
Look at the cross a bit longer and you‘ll notice that all dots except the green one will disappear.

Do you see gray areas in between the squares?
Now where did they come from?

How many faces do you see?

Do you see one man in this picture...or several people?If you look very carefully, you'll find 9 different faces in the picture;the 9th belongs to a dog.

• You may not see it at first, but the white spaces create the word OPTICAL,while the blue landscape spells out ILLUSION.

The Man in the Coffee BeansThe "illusion" is that this is just a picture of coffee beans; but it is not. Can you find a man's face among the beans? Some say that if you find the man in 3 seconds or less, the right half of your brain may be more well developed than most.PS: This is not a trick. A man's face is really hidden among the beans.

Which of the figures in the picture do you think would measure the tallest with a ruler?
Don't measure -- just guess!

You should see a man's face and also a word...
Hint: Try tilting your head to the right, the world begins with 'L'

Impossible Planes
In this category you'll find images where different planes are in contradiction (the dimensional kind, not the flying ones). Have a look at this drawing. The left drawing is the normal situation : the upper and lower side are nicely in 1 plane. The right drawing is different however : the upper side is still nice and possible, but the right column has moved. The lower side now has a completely different orientation. By the way, if you imagine the right column has only become shorter and is floating mid-air, it can be possible.

Impossible figures can be drawn on paper but can't exist in real life. Take "The Pool" for example : a beautifully made image of a swimming pool. The man on the ladder won't get into the pool however ... although it's taking him horizontally, the ladder is connecting the two sides of the
pool.

The upper side of the wall is on one straight line, but the three pillars it's standing on are one three different planes. There's even enough room for seating.

Best things last ...

* Follow the instruction below.
* 1) Stare at the 4 little dots on the middle of the picture for 30 seconds * 2) then look at a wall near you * 3) a bright spot will appear * 4) twinkle a few times and you‘ll see a figure * 5) What do you see? Or even who do you see?