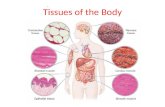
What are the four tissues of the body? Our body is made from these 4 tissues.
The human body: tissue types. The human body primary tissues: muscle nervous epithelial connective...
-
Upload
linette-hamilton -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of The human body: tissue types. The human body primary tissues: muscle nervous epithelial connective...
The human body
• primary tissues:musclenervousepithelialconnective
• organs:composed of at least two primary tissues
• systems:organs located in different regions of the body that perform related functions
Primary Tissues
• muscle– skeletal– cardiac– smooth
• nervous tissue– neurons– glial cells
• epithelial tissue– membranes– glands
Epithelial Tissue
• membranes - flat sheets of cells that cover and line body surfaces
• Functions: lines, covers, produces glands
• Cells are connected together• Have a basement layer of connective tissue
• Avascular• Layers:
– simple = 1 layer, regulates transport– stratified = many layers, acts as barrier
• shapes of cells in upper layer vary - squamous, cuboidal, columnar
Connective Tissue
• Connective tissue is found everywhere in the body
• Functions: binds (connects) body parts; supports organs and systems, provides protection from mechanical damage
• Has both living (cells) and matrix (nonliving) components
• Matrix: lots of extracellular material between cells that is not alive – fluid– proteins
Types of Connective Tissue
• Types of connective:- Adipose - Areolar- Cartilage - Reticular- Osseous- Blood
Osseous Tissue
• Function: support the body and protect body cavities; produces blood
• Composed of bones cells in cavities called osteocytes, have a very hard matrix, and collagen fibers
Dense Connective Tissue
• Composed of collagen fibers• Types:
– Tendons: attach muscle to muscle– Ligaments: connects bones to bone
Areolar Tissue
• Web-like matrix• Functions:
– Cushions, protects– Soaks up water to act like glue that holds other tissues together
Adipose Tissue
• Contains lipids• Cushions organs and stores nutrients
Reticular Tissue• Composed of delicate woven fibers• Forms stroma• Found in lymphatic organs
Blood
• Composed of fluid matrix called plasma
• Clotting fibers visible during clotting
• Cary nutrients, gases, and wastes through out the body
Muscle• Function: specialized to
contract or shorten to produce movement
• skeletal muscle“voluntary”striatedmultiple nuclei per cell
• cardiac musclefound only in heartspecialized striated muscle - not “voluntary”has intercalated discsuninuclei per cell
• smooth muscle
“involuntary”
not striated1 nucleus per cellattached to hollow organs like the stomach, intestines, esophagus
Nervous Tissue
• neurons (nerve cells)• Function: irritability and conduction of impulses- Dendrites - receive information- Cell body - contains nucleus, metabolic center, integrates input
- Axon - conducts nerve impulses
• glial cellsprovide support - enhance electrical activity of neurons