The Human Body. Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues –Epithelial, connective,...
-
Upload
frederica-marianna-daniels -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of The Human Body. Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues –Epithelial, connective,...

The Human Body

Levels of Organization in the Body
• Cells
• Tissues– Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous
• Organs– Examples include stomach, liver, heart
• Organ Systems– Examples include digestive and circulatory
systems

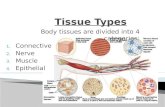
Tissues in the Human Body
• Epithelial– Covering or lining tissue
• Connective– Joins, stores and supports
• Muscle– Internal and external movement
• Nerve– Conducts electrical signals
Blood
Muscle
Nerve

Human Organ Systems
• Skeletal
• Muscular
• Circulatory
• Immune
• Respiratory
• Digestive
• Excretory
• Reproductive
• Nervous
• Endocrine
• Integumentary

Cranium (skull)
Mandible (jaw)

Clavicle (collarbone)Sternum (breastbone)
Humerus (upper arm)
Rib
Vertebra (backbone)

PelvisRadius
Ulna
Carpals (wrist)
Phalanges (fingers)
Metacarpals (hand)
(forearm)

Femur (thigh)
Patella (knee cap)
Tibia
Fibula
Tarsals (ankle)
Phalanges (toes)
Metatarsals (foot)
(lower leg)

What are the main functions of the skeletal system?
– Framework and support of body• Where muscles attach
– Protects internal organs
– Storage of vitamins and minerals (calcium), and bone marrow (produces blood cells)

What types of tissues make up the skeletal system?
• Connective tissue– Cartilage made of protein fibers
– Bone is formed during “ossification” when cartilage hardens

What are bones?
• A solid network of LIVING cells and protein fibers that are surrounded by deposits of calcium salts.

What is the advantage of spongy bone tissue in the ends of long bones?
• The ends of the bone is where force is applied
• Spongy bone adds strength without adding mass

Which cells are produced in red bone marrow?
• Red blood cells – carry oxygen
• Some white blood cells– Killer T cells – B cells (produce antibodies)
• Platelets – help with blood clotting

Compact bone (dense bone)
Spongy bone(adds strengthwithout mass)
Periosteum (tough layer of connective tissue surrounding bone)
Haversian Canal (contains blood vessels)

Joints
• Place where one bone attaches to another– Immovable joints (fixed)
• Example: bones of skull
– Slightly moveable joints• Example: joints between vertebrae
– Freely moveable joints• Examples: Shoulder, Knee, Elbow, Hand

Freely Moveable Joints

Freely Moveable Joints