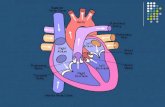
The Heart
-
Upload
francesca-roberts -
Category
Documents
-
view
21 -
download
0
description
Transcript of The Heart

The HeartYouTube - Heart Anatomy.webloc

• Label your heart diagram with septum, L & R atria, L & R ventricles, two atrioventricular valves, pulmonary valve and aorta valve.
• Add blue and red arrows to show flow of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.

Heart Check
1. Why do the ventricles have thick walls?
2. Why do the atria have thin walls?
3. Why is the left ventricle thicker than the right?
4. How do the valves prevent backflow when the ventricle contracts?

Circulation and blood vessels
• Veins towardsheart
• Arteries away
• Label your diagram with the vena cava, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein and aorta.

Circulation check1. Which 2 vessels carry blood to the heart?
2. Which vessel carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs?
3. Which vessel carries oxygenated blood back to the heart?
4. Which vessel carries blood to the rest of the body?
1. “ Arteries carry oxygenated blood and veins carry deoxygenated blood ” True or False? Explain.

The Cardiac Cycle
1 2 33 phases:1. Atrial systole (contracts)2. Ventricular systole (contracts)3. Diastole (relaxes)Concept II Practice- Rep#129DBC

Pressure changes in heart
1. What are phasesa, b and c called?
2. Describe what is happening in the heartat points 1 – 10 on the graph.
(c)

Cardiac Cycle check
• What are the 3 phases of the cardiac cycle called?
• Match them with phases 1,2 and 3 above. • Match ABC with phases 1,2 and 3 of cycle.
Concept II Practice- Rep#129DBC

Coordinating the heartbeat
• myogenic
• SAN (sinoatrial node)the ’pacemaker’
• AVN (atrioventricular node)after slight delay
• Bundle of Hiscontraction from base of heart

Coronary Heart Disease• Coronary arteries provide heart muscle with blood carrying oxygen and glucose for respiration.
• If these arteries become blocked (atheroma) problems arise.
e.g. myocardial infarction

Atheroma• Fatty deposits build up under the endothelium of the artery when it becomes damaged.(damage can be caused by uneven blood flow, high blood pressure, chemicals or viral infection.)
• White blood cells collect under the endothelium and absorb fatty materials e.g. LDLs ( contain cholesterol).

Atheroma
• Lumen reduced.

Thrombosis• As a result of atheroma a lumpy area, called a
plaque, forms on the artery wall. • This can lead to a blood clot forming
(thrombosis). Can completely block the lumen.

Aneurysm• The artery wall can bulge in weakened areas.
• This is an aneurysm.
• It can burst.
• Aneurysms and thrombosis can form in other parts of body too.

Heart Attack

• Atheroma can reduce blood supply to the heart muscle.
• Angina is chest pain caused by exercise.

Myocardial Infarction• Muscle can die
(infarction).

Symptoms of Myocardial Infarction
• Severe pain in chest • Sick, breathless• Rapid but weak pulse
• The affected area of muscle will stop working and the heartbeat can be disrupted which leads to uncoordinated contractions : fibrillation.
• No pulse detected as not enough force to pump blood into aorta.
• Emergency defibrillation is necessary.• 1/3 victims die within an hour : need heart compressions
and artificial respiration until defibrillater available.

CHD worldwide
• What are the risk factors?

Risk Factors
• Age and Sex• Genetic factors• Smoking• High blood pressure• High concentration of LDLs (diet high in
saturated fats)