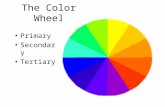
The COLOR wheel helps to organize the colors in the spectrum. Not all colors may be found on the...
-
Upload
norman-lyons -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of The COLOR wheel helps to organize the colors in the spectrum. Not all colors may be found on the...

TheCOLOR wheel
helps to organize the colors in the spectrum.
• Not all colors may be found on the color wheel (ex. black, gray, white, browns, {neutrals} and other specialty colors; ex. neons and metallics).

Colors are organized into 4 major groups:
• 1. Primary Colors
• 2. Secondary Colors
• 3. Intermediate Colors
• 4. Neutral Colors

1. Primary Colors
• Primary colors cannot be produced by mixing other colors together. They can only be made from nature or from chemicals.
• Primary colors make all the other colors.
• The primary colors are RED, BLUE, and YELLOW

2. Secondary Colors• Secondary colors are produced by mixing primary
colors• Primary color+primary color=secondary Color
• + Violet
• + Orange
• + Green

3. Intermediate Colors• Intermediate (in-between) colors are produced by mixing a
primary and secondary color that are side-by-side on the color wheel
• Primary color+Secondary color=Intermediate Color
• blue-green, blue-violet,
• red-violet, red-orange
• yellow-orange, yellow-green

4. Neutrals
white,
black,
gray, {values}
and browns

COLOR SCHEMES

• Monochromatic• Analogous• Complementary
Split complementTriadic

• Monochromatic Color SchemeMono = one, single,. . . as in monorailChroma = colorthus monochromatic = One color.
• This color scheme can be achieved by using tints and shades of one hue.

Color schemes
Analogous
• Colors that are next to each other on the color wheel. Colors with a family resemblance.
• Analogous colors will have some of the same primary color; ex. yellow, yellow-orange, and orange, or blue, blue-green, and green etc.
• Analogous will always mix well.

Color schemes
Complementary• Colors that are opposite each other on the
color wheel; ex. red and green, violet and yellow, yellow-green and red-violet etc.
• If mixed together in near equal amounts, complements make a neutral color.
• If a little of a hue’s complement is mixed in with it, the result will be a dulling or neutralizing of that hues intensity.

Split complement:
• Three colors that are opposite each other on the color wheel, but to either side of the exact opposite (complement); ex. red, blue-green, and yellow-green

Triadic:
• Colors that are equally spaced. The most famous of these is the primary triad . . . red, yellow, and blue.
• Triadic harmonies are most effective if only one color is allowed to dominate.

Assignment
• Create a color strip for each of the following and label each:
1. Monochromatic color scheme (5)
2. Analogous color scheme (3)
3. Complementary color scheme (5)

Criteria:
• Correct colors for scheme
• Correct mixing
• Craftsmanship