The Cell Membrane AP Chapter 7. Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane is the boundary that...
-
Upload
pamela-silva -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of The Cell Membrane AP Chapter 7. Overview: Life at the Edge The plasma membrane is the boundary that...

The Cell Membrane
• AP Chapter 7


Overview: Life at the Edge
• The plasma membrane is the boundary that separates the living cell from its surroundings
• The plasma membrane exhibits selective permeability, allowing some substances to cross it more easily than others
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings

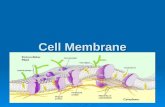
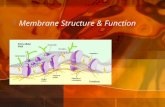
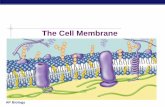
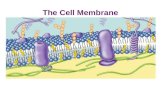
Composition of the cell membrane: lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol) and proteins
• Phospholipids are the most abundant lipid in the plasma membrane
- they are amphipathic molecules, contain hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions.• The fluid mosaic model states that a
membrane is a fluid structure with a “mosaic” of various proteins embedded in it
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings

Development of the Fluid Mosaic Model• In 1935, Hugh Davson and James Danielli proposed a
sandwich model in which the phospholipid bilayer lies between two layers of globular proteins
• In 1972, J. Singer and G. Nicolson proposed that the membrane is a mosaic of proteins dispersed within the bilayer, with only the hydrophilic regions exposed to water
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings

Sandwich model of the cell membrane
What is wrong with this model?
Proteins are mostly hydrophobic.All phospholipids are not alike.

Fluid Mosaic Model

Fig. 7-2
Hydrophilichead
WATER
Hydrophobictail
WATER
This slide shows how the hydrophobic andhydrophilic regions are set up.

Fig. 7-3
Phospholipidbilayer
Hydrophobic regionsof protein
Hydrophilicregions of protein

Double phospholipid layer

Different types of phospholipids

Different types of phospholipids making up the membrane

Fig. 7-4
TECHNIQUE
Extracellularlayer
KnifeProteins Inside of extracellular layer
RESULTS
Inside of cytoplasmic layer
Cytoplasmic layerPlasma membrane
Freeze-fracture studies of the plasma membrane supported the fluid mosaic model

The Fluidity of Membranes
• Phospholipids in the plasma membrane can move within the bilayer
• Most of the lipids, and some proteins, drift laterally (very rarely transverse flip-flops)
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
fluidity of membrane
fluidity of cell membrane

Fig. 7-5
Lateral movement(~107 times per second)
Flip-flop(~ once per month)
(a) Movement of phospholipids
(b) Membrane fluidity
Fluid Viscous
Unsaturated hydrocarbontails with kinks
Saturated hydro-carbon tails
(c) Cholesterol within the animal cell membrane
Cholesterol
Biology Animations

Fig. 7-6
RESULTS
Membrane proteins
Mouse cellHuman cell
Hybrid cell
Mixed proteinsafter 1 hour
This experiment shows how the proteins can move about the membrane.

The fluidity of the membrane depends on temperature and types of lipids making up the membrane.
• Membranes rich in unsaturated fatty acids are more fluid than those rich in saturated fatty acids
• Membranes must be fluid to work properly; they are usually about as fluid
as salad oil.
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings

Fig. 7-5b
(b) Membrane fluidity
Fluid
Unsaturated hydrocarbontails with kinks
Viscous
Saturated hydro-carbon tails

• Would you expect an amoeba that lives in a pond in a cold northern climate to have a higher or lower percentage of saturated fatty acids in its membranes during the summer as compared to the winter?

• The steroid cholesterol has different effects on membrane fluidity at different temperatures
• At warm temperatures (such as 37°C), cholesterol restrains movement of phospholipids
• At cool temperatures, it maintains fluidity by preventing tight packing
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings

Fig. 7-5c
Cholesterol
(c) Cholesterol within the animal cell membrane

Membrane Proteins and Their Functions
• A membrane is a collage of different proteins embedded in the fluid matrix of the lipid bilayer
• Proteins determine most of the membrane’s specific functions
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings

Fig. 7-7
Fibers ofextracellularmatrix (ECM)
Glyco-protein
Microfilamentsof cytoskeleton
Cholesterol
Peripheralproteins
Integralprotein
CYTOPLASMIC SIDEOF MEMBRANE
GlycolipidEXTRACELLULARSIDE OFMEMBRANE
Carbohydrate


• Peripheral proteins are bound to the surface of the membrane
• Integral proteins penetrate the hydrophobic core, are called transmembrane proteins
• The hydrophobic regions of an integral protein consist of one or more stretches of nonpolar amino acids, often coiled into alpha helices
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings

Fig. 7-8
N-terminus
C-terminus
HelixCYTOPLASMICSIDE
EXTRACELLULARSIDE

• Six major functions of membrane proteins:– Transport– Enzymatic activity– Signal transduction– Cell-cell recognition– Intercellular joining– Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular
matrix (ECM)
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings

Fig. 7-9
(a) Transport
ATP
(b) Enzymatic activity
Enzymes
(c) Signal transduction
Signal transduction
Signaling molecule
Receptor
(d) Cell-cell recognition
Glyco-protein
(e) Intercellular joining (f) Attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM)

Intercellular joiningE-selectin is a transmembrane protein expressed by endothelial cells
that binds to an oligosaccharide expressed on the surface of leukocytes

Construct a cell membraneTry this at home!
constructing a cell membrane

The Role of Membrane Carbohydrates in Cell-Cell Recognition
• Cells recognize each other by binding to surface molecules, usually carbohydrates
• Membrane carbohydrates may be covalently bonded to lipids (forming glycolipids) or more commonly to proteins (forming glycoproteins)
• Carbohydrates on the external side of the plasma membrane vary among species, individuals, and even cell types in an individual
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings

Membranes are bifacial• Carbohydrates (making glycoproteins and
glycolipids) on outer surface• Peripheral proteins generally on cytoplasmic
surface• Proteins have a distinct orientation, ie…
receptor proteins oriented at surface, enzyme proteins oriented toward cytoplasm


Synthesis and Sidedness of Membranes
• Membranes have distinct inside and outside faces – determined when the membrane is built by the ER and Golgi.
Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings

Fig. 7-10
ER1
Transmembraneglycoproteins
Secretoryprotein
Glycolipid
2Golgiapparatus
Vesicle
3
4
Secretedprotein
Transmembraneglycoprotein
Plasma membrane:
Cytoplasmic face
Extracellular face
Membrane glycolipid

Can you guess where you would find this cell?

This cell?
Notice how thin-walledthey are.

Need a hint?

These cells?