The Binomial Theorem
11
The Binomial Theorem
description
The Binomial Theorem. Questions:. Put (x+y) 2 in standard form Put (x+y) 3 in standard form Put (x+y) 4 in standard form. Pascal’s Triangle. is a triangle of numbers, each new number being the sum of the two above it. - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Transcript of The Binomial Theorem

The Binomial Theorem

Questions: Put (x+y)2 in standard form
Put (x+y)3 in standard form
Put (x+y)4 in standard form

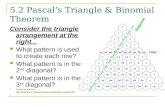
Pascal’s Triangle is a triangle of numbers, each new number
being the sum of the two above it. Each Row of Pascal’s triangle contains
coefficients for the expansion of (a+b)n
Let’s look at Pascal’s Triangle http://www.shodor.org/interactivate
/activities/pascal1/

Now
\

Use Pascal’s Triangle to expand (a+b)6
Use Pascal’s triangle to get the coefficients.
Then with the exponents a will decrease as b will increase.

Use Pascal Triangle to expand: (x-2)3

Review of Combinations

Another way to expand in called the Binomial
Theorem

Let’s look at (a+b)4

(x-2)5

Homework
P294
2,6,16,20,22