THE ATOM · PDF file · 2013-06-10THE ATOM HISTORY AND STRUCTURE . ... J.J....
Transcript of THE ATOM · PDF file · 2013-06-10THE ATOM HISTORY AND STRUCTURE . ... J.J....

THE ATOM
HISTORY AND STRUCTURE

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Atom-
The smallest unit of an element that maintains the
properties of that element.
Originated from the Greek word Atomos - meaning
indivisible particle.

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Ancient views of the atom
Aristotle
Earth, air, fire, water
everything was made from
these four basic “elements”
Democritus Model
Made of small indivisible
particles
Different atom for every
substance

ATOMIC STRUCTURE Dalton Model - John Dalton’s
atomic theory, developed in the early 1800’s.
All elements are composed of atoms.
All atoms of the same element have the
same mass, and atoms of different
elements have different masses.
Compounds contain atoms of more than
one element.
In a particular compound, atoms of
different elements always combine in the
same way. Atoms still small indivisible spheres

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
J.J. Thomson’s model
Early 1900’s
Discovered particles in the
atom with a negative
charge and called them
electrons
Since atoms are neutral,
there must also be positive
charges
His model described the
atom as a positively
charged sphere with
negative particles
scattered throughout.
Like raisins in plum pudding
DISCOVERY OF
ELECTRONS
ELECTRON
CHARGE
ELECTRON
MASS

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Discovery of the proton

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
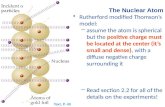
Ernest Rutherford’s model
1911
Gold Foil Experiment.
Shot alpha particles at gold foil.
Most went through, but some bounced back
Like throwing marbles at a chain link fence.
The atom has a tiny positive core called a
nucleus
Electrons are whirling around the nucleus
The atom is mostly empty space

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Rutherford’s gold foil experiment

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Neils Bohr model
1913
Modified Rutherford’s model to explain energy release and absorption
Electrons move in paths called energy levels
Electrons in each level have a definite amount of energy
Adding energy moves an electron further from the nucleus
When electrons return to a lower level they give off energy. (light)

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Schrodinger
Electron cloud model
Same as Bohr model but instead of paths for the
electrons there are regions of space called
electron clouds.

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Atomic Number –
The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus
In a neutral atom this also equals the number of
electrons
Mass Number-
The number of protons plus neutrons
Not all atoms of an element contain the same
number of neutrons (isotopes)
Isotopes are identified by their mass number
Hydrogen-1, Hydrogen-2, Hydrogen-3

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Parts of the atom
Nucleus
The part of the atom that
has most of the mass
Has a positive charge
Contains protons and
neutrons

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Discovery of the Neutron

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Electron orbital-
A region in an atom where there is a high probability of finding electrons
Electrons exist in energy levels
Each level holds a certain number of electrons
Level 1 2e-
Level 2 8e-
Level 3 18e-
Level 4 32e- , higher levels also hold 32e-
Valence electrons
Outer level electrons
Determine an atom’s chemical properties
No element has more than eight valence electrons (OCTET rule)
Neutral atoms have equal numbers of protons and electrons

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Drawing Bohr Models
Determine the number
of Protons, neutrons,
and electrons.
Determine the number
of energy levels
available for electrons
(period)
Place electrons
according to the
periodic table map
Bohr model of Oxygen
Protons?
Atomic # 8 – 8 protons
Also means 8 electrons
Neutrons
Mass # - Atomic #
16 – 8 = 8 neutrons
Energy levels?
Period 2 – 2 energy
levels

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Bohr model of Oxygen
8 – protons
8 – neutrons
8 – electrons / 2 levels
8p
8n
2e-
6e-

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Bohr model of Tin (Sn)
Protons
Atomic number 50 so 50 p
Electrons
50e-
Neutrons
119 – 50 = 69 n
Energy levels
5th period – 5 levels
50p
69n
2e-
8e-
18e-
18e-
4e-

ATOMIC STRUCTURE
Bohr model of Uranium (U)
Protons
Atomic number 92 – 92 p
Electrons
Also 92 e-
Neutrons
Mass # - Atomic #
238 – 92 = 146 n
Energy Levels
Period 7 – 7 energy levels
92p
146n
2e-
8e-
18e-
32e-
21e-
9e-
2e-