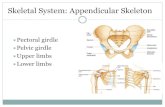
The Appendicular Skeleton - harcoboe.com · Shoulder Girdle •Only forms one joint with the axial...
Transcript of The Appendicular Skeleton - harcoboe.com · Shoulder Girdle •Only forms one joint with the axial...
The Upper Extremity
• Bones of the shoulder girdle – Clavicle and scapula
• Upper arm – Humerus
• Lower arm – Radius
– Ulna
• Wrist – Carpal bones
• Hand – Metacarpals
– Phalanges
Shoulder Girdle
• Only forms one joint with the axial skeleton
• Clavicle
– Sternoclavicular joint • Where the sternum
meets the clavicle
Shoulder Girdle
• Scapula – Shoulder blade – 3 borders
• Superior (top) • Vertebral (by the spine) • Axillary (side near the armpit)
– Spine • Ridge along the posterior portion of the bone
– Acromion process • Articulates with clavicle • Process that is located at the end of the spine
– Coracoid process • Projection on the anterior portion of the scapula • Only 2 major projections
Humerus
• Long bone that makes up the upper arm • Upper end (epiphysis)
– Head • Smooth rounded end that fits into glenoid fossa
– Anatomical neck • Groove immediately inferior to the head
– Greater and lesser tubercles • Greater is lateral to the head • Lesser is inferior (below) the greater
– Intertubercular groove • Groove b/t greater and lesser tubercles
– Surgical neck • Region below the tubercles that leads to the diaphysis • Common to fracture
Humerus
• Middle (diaphysis)
– Deltoid tuberosity • Protuberance midway
down shaft
• Deltoid attaches here
– Radial groove • Groove moving inferiorly
for radial nerve
Humerus • End (epiphysis)
– Eipicondyles • Medial and lateral projections
– Medial is larger of the two
– Capitulum • Rounded head below the lateral
epicondyle – Radius attaches
– Trochlea • Appears similar to a pully
• Deep depression in the epiphysis
• Articulates with the ulna
– Olecranon fossa • Depression on the posterior survace
• Olecranon process forms elbow here
– Coronoid fossa • Depression on the anterior portion
Forearm
• Radius – Thumb side
– Head • Proximal end
• Articulates with the capitulum
– Radial tuberosity • Projection just below the
head
– Styloid process • Located on the lateral,
distal end of the bone
Forearm
• Ulna – Pinky side – Longer than radius – Olecranon process
• Elbow
– Coronoid process • Opposite side of elbow
– Semilunar notch • Depression that articulates
with the trochlea
– Styloid process • Distal end
– Head • Distal end
Wrist
• 8 bones – 2 rows
– Proximal row • Pisiform
• Triquetrum
• Lunate
• Scapate
– Distal row • Hamate
• Capitate
• Trapezoid
• Trapezium
Hand
• Metacarpals
– “Middle” bones of the hand
– Distal end makes up the knuckles
– Numbered 1 – 5
• Phalanges
– Smaller bones that make up the fingers
– Separated into proximal, middle, and distal (finger tip)
• Hip – Coxal bones (pelvis)
• Thigh – femur
• Lower leg – Tibia – Fibula
• Foot – Tarsal bones – Metatarsals – Phalanges
The Lower Extremity
Coxal Bones
• Pelvic girdle – Combination of the sacrum and the coxal bones
bound together by ligaments
– Supports the trunk of the body and allows for leg attachment
• Coxal bones – Each bone is made up of 3 fused bones
• Illium
• Ischium
• Pubis
• Ilium
– Most superior
– Largest
– Palpable
• Ischium
– Strongest
– Most inferior
• Pubus
– Anterior to the ischium
Coxal Bones
• Horizontally divided into 2 parts – Pelvic inlet
• a.k.a. pelvic brim
• Above the inlet – False pelvis
• Runs from the tip of the ilium to the pelvic inlet
• Below the inlet – True pelvis
• Boundary of the pelvic outlet
• Pubic symphysis – Where the coxal bones
meet
Thigh Bones
• Femur
– Upper end (epiphysis) • Head
• Greater/lesser trochanter
– Middle portion (diaphysis) • Linea apera
• Supracondylar ridges
Thigh Bones
• Distal end (epiphysis)
– Lateral/medial condyles
– Lateral/medial epicondyles
– Adductor tubercle
– Trochlea
– Intercondyloid fossa • notch
Tibia
• Shin bone • Lateral/medial condyles
– Upper end of bone – Concave surface to articulate w/ femur
• Intercondylar eminence – Spine between condyles – Attachment for ACL and PCL
• Crest – Sharp ridge on the anterior – Part of the shin you can feel
Tibia
• Tibial tuberosity
– Protuberance just below condyles
– Palpable below the knee
• ½ “Ankle”
– Medial maleolus • Palpable on the inside of
the ankle
Fibula
• Smaller than tibia
• Deeper of the two bones – Always on the outside of
the lower leg
• Proximal end articulates with the tibia – @ lateral condyle
– Creates part of the knee joint
• Distal end (other ½ of the “ankle” – Articulates with the tibia
– Lateral malleolus
Foot
• Constructed similar to the hand
– Adapted to support weight
• Two way arch construction
– Longitudinal arch • Medial/lateral
longitudinal arches
– Transverse arch • Metatarsals & the distal
row of tarsals
Foot • Flat foot (fallen arches)
– Ligaments and muscles hold bones in place
– Keeps the arch intact
– Foot, knee, eventually back
• Very small number of individuals have a true “flat foot” – Usually over-pronation
• High arch – Charcot Marie Tooth
disorder (CMT)





































![The Human Body The Skeleton provides … Support/ShapeMovement Produces [White blood cells]Protects Bones Upper Body: Clavicle, Scapula, Sternum, Ribs, Humerus,](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/56649c755503460f9492861a/the-human-body-the-skeleton-provides-supportshapemovement-produces-white.jpg)