Testing Overview
-
Upload
softwarecentral -
Category
Documents
-
view
188 -
download
3
Transcript of Testing Overview

Testing Overview
Overview of Software Testing
Test Plan Outline

Agenda
• Deliverables– Friday, May 31 @ 5 PM - Status Report #3– Friday, May 31 @ noon
• Requirements Document
• Project Plan
• Lecture: Testing Overview

Software Quality Factors
Revis
ion Transition
Operations
MaintainabilityFlexibilityTestability
PortabilityReusabilityInteroperabilty
Correctness, Reliablity, Efficiency, Integrity, Usability

Two Key Concepts
• Validation: Are we building the right thing? – Conformance to customer requirements and
quality attributes.
• Verification: Are we building the thing right? – Process conformance, quality activities.

Maturity of Testing Philosophy
PHASE O: Testing == DebuggingPHASE 1: Testing shows the software works
PHASE 2: Testing shows the software doesn’t work
PHASE 3: Testing doesn’t prove anything, it reduces risk of unacceptable software delivery.
PHASE 4: Testing is not an act, a mental discipline of quality.

Testing Ground Rules
– Objectives• Testing is the process of executing a program with
the intent of finding errors• A good test case is one that has a high probability of
finding an error• A successful test is one that uncovers an error
– Importance“The development of software systems involves a series of production
activities where opportunities for injection of human fallibilities are enormous…Because of human inability to perform and communicate with perfection, software development is accompanied by a quality assurance activity.” [Deutsch]

Ground Rules (continued)– Benefits
• Uncover errors in software• Demonstrates that software functions appear to be
working according to specification• Demonstrate performance requirements have been
met• Provide indication of software reliability and quality
– However, testing cannot show the absence of defects
– Minimal set of test cases needs to be developed because exhaustive testing not possible

Testing ParadoxEvery method you use to prevent or find bugs leaves a residue of subtler bugs against which those methods are ineffective.
Time
Errors Found
Cost

Testing Phases• Unit• Integration• Component• System• Usability• Regression• Validation• Alpha/Beta

Unit Testing Guidelines• Primary Goals
– Conformance to specifications• Determine extent to which processing logic satisfies
the functions assigned to the module• Logical and operational requirements taken from
specifications
– Processing accuracy• Input• Process• Output

Integration Testing Guidelines
• Primary goals– Compatibility
• Calling of modules in an operational environment• Verify that all modules are called correctly, do not
cause abnormal ends
– Inter-module processing accuracy• Check that data transfers between modules operate
as intended within constraints

Testing Strategies
• Dynamic Analysis– Black Box– White Box
• Static Analysis– Code Reviews– Walkthroughs– Inspections

Black Box Testing
• Used to demonstrate functions are operational
• Proper input produces correct output
• Focuses on the functional requirements
• Goal:– Set of inputs that fully
exercises all functional requirements
• Kinds of errors targeted:– Incorrect or missing
functions
– Interface errors
– Errors in data (structures or databases)
– Behavior or performance errors
– Initialization and termination errors

White Box Testing
• Uses structure of program to derive test cases
• Set of test cases case guarantee:– All independent paths have been executed at least once– Exercise all logical decisions, both T and F– Execute all loops at their boundaries and within bounds– Exercise internal data structures to ensure validity

Comparison of Test StrategiesTest Strategy Method Goal Disadvantages
White-Box Logic Proveprocessing
Functional flaws, datasensitive conditions, &errors across modulesdifficult to test
Black-Box Data Prove results Type 2 errors & logicproblems difficult to find
Top-Down Incremental Exercise criticalcode to improvereliability
Scaffolding takes timeConstant change mayintroduce new errors
Bottom-Up All ornothing
Perfect parts;If parts work,whole shouldwork
Functional flaws foundlate cause delaysErrors across modulesdifficult to trace and find

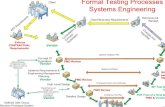
Test Plan Outline1. Introduction:
a. Purposeb. Program Description
2. Test Environment3. Test Case Descriptions:
a. Coverage Criteriab. Details
• Summary