Table of Contents · A. Which angle measures 90 degrees? B. Which angle is greater than 90 degrees...
Transcript of Table of Contents · A. Which angle measures 90 degrees? B. Which angle is greater than 90 degrees...


Jumpstarters for Geometry
ii© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Table of Contents
Introduction to the Teacher .......................................................................................................1Lines, Rays, and Line Segments ..............................................................................................2Classifying Angles ....................................................................................................................3Measuring and Drawing Angles ................................................................................................4Classifying Pairs of Lines .........................................................................................................5Special Pairs of Angles .............................................................................................................6Identifying Polygons..................................................................................................................7Polygon Puzzles .......................................................................................................................8Congruent Figures ....................................................................................................................9Similar Figures ........................................................................................................................10Symmetrical Figures ...............................................................................................................11Two Types of Symmetry ..........................................................................................................12Transformations ......................................................................................................................13Geometric Patterns .................................................................................................................14Classifying Triangles ...............................................................................................................15Classifying Quadrilaterals .......................................................................................................16Classifying Parallelograms .....................................................................................................17Angle Measures of Triangles ..................................................................................................18Angle Measures of Quadrilaterals ..........................................................................................19Perimeter of Rectangles and Squares ....................................................................................20Perimeter of Polygons ............................................................................................................21Perimeter of Complex Figures ................................................................................................22Area of Rectangles and Squares ............................................................................................23Area of Triangles .....................................................................................................................24Area of Parallelograms ...........................................................................................................25Area of Complex Figures ........................................................................................................26Area of Irregular Regions .......................................................................................................27Circles .....................................................................................................................................28Circles and Central Angles .....................................................................................................29Circumference ........................................................................................................................30Area of Circles ........................................................................................................................31Solid Figures ...........................................................................................................................32Solid Figures and Nets ...........................................................................................................33Surface Area of Rectangular Prisms .....................................................................................34Volume of Rectangular Prisms ...............................................................................................35Volume of Cylinders ................................................................................................................36Volume of Triangular Prisms ...................................................................................................37Ordered Pairs .........................................................................................................................38Lengths on the Coordinate Plane ...........................................................................................39Answer Keys ...........................................................................................................................40
Table of Contents

Jumpstarters for Geometry
1© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Introduction to the Teacher
Introduction to the Teacher Just as physical warm-ups help athletes prepare for more strenuous types of activity, mental warm-ups help students prepare for the day’s lesson while reviewing what they have previously learned. The short warm-up activities presented in this book provide teachers andparents with activities to help students develop and reinforce geometry-related skills. Each page contains five warm-ups—one for each day of the school week. Used at the beginning of class, warm-ups help students focus on geometry-related concepts.
Geometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with the measurement, properties, and relationships of points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids. The warm-up activities in this book move from the most basic lines to more complex concepts such as angles, polygons, symmetry, transformations, perimeter, area, volume, circles, solid figures, and the coordinate plane.
Although the warm-ups have been arranged to present more basic topics up front, you do not need to give them to your class in sequential order. Choose the pages in the order that best fits your curriculum needs. In addition, the five warm-ups that are on the same page may be presented in any order, since they all relate to the same topic or skill.
Suggestions for use:
• Copy and cut apart one page each week. Give students one warm-up activity each day at the beginning of class.
• Give each student a copy of the entire page to complete day by day. Students can keep the completed pages in a three-ring binder or folder to use as a resource.
• Make transparencies of individual warm-ups and complete the activities as a group.
• Provide additional copies of warm-ups in your learning center for students to complete at random when they have a few extra minutes.
• Keep some warm-ups on hand to use as fill-ins when the class has a few extra minutes before lunch or dismissal.

Jumpstarters for Geometry
2© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Geometry Warm-ups:Lines, Rays, and Line Segments
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments 3Use letters and symbols to label each figure.
This line is AB or BA.
A. G H
B. R S
C. U V
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments 4Are the following statements true or false?
A. A line segment has only one endpoint.
B. A line has two endpoints.
C. A ray goes on without end in one direction.
D. A line goes on without end in two
directions.
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments 5
Look at the picture. Name the following figures.
A. two lines
B. five rays
C. two line segments that contain point Q
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments 2How many line segments are in the picture?
Name them.
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments 1Label each figure as a line, ray, or line segment.
A.
B.
C.
D.
T
P Q R
S
A B
P
O
R
Q
S
T
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments

Jumpstarters for Geometry
3© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Classifying Angles 1Write three names for each angle. Use symbols and letters. (Examples: ∠PQR, ∠RQP, ∠Q )
A. B. C.
Classifying Angles 2A. What do you call the point that is common
to the two sides of an angle?
B. Can angle XYZ also be named angle
ZYX? Explain.
C. Can angle XYZ also be called angle YZX?
Explain.
Classifying Angles 3Write acute, obtuse, right, or straight to describe the angles.
A. B.
C. D.
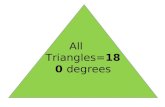
Classifying Angles 4Write acute, obtuse, right, or straight.A. Which angle measures 90 degrees? B. Which angle is greater than 90 degrees
but less than 180 degrees? C. Which angle is less than 90 degrees? D. Which angle equals 180 degrees?
Classifying Angles 5
Use the figure at right to answer these questions.
A. Name an acute angle.
B. Name a right angle.
C. Name a straight angle.
D. Name an obtuse angle.
Geometry Warm-ups:Classifying Angles
L
M N
GH
EX
V
Z
A
B
C
D
E
Classifying Angles

Jumpstarters for Geometry
4© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Geometry Warm-ups:Measuring and Drawing Angles
Measuring and Drawing Angles 5Use a protractor to measure angles A, B, C, and D. Write acute, obtuse, or right beside each measure.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Measuring and Drawing Angles 4
Draw the following angles on a separate sheet of paper. Then use a protractor to measure your angles.
A. an acute angle
B. an obtuse angle
C. a right angle
Measuring and Drawing Angles 3
Use a protractor to draw the angles with the following measures.
A. 30° B. 60° C. 135° D. 90°
Measuring and Drawing Angles 2
Use a protractor to measure the angles.
A. ° B. °
C. °
Measuring and Drawing Angles 1Write the missing numbers.
A. A straight angle measures degrees.
B. A right angle measures degrees.
C. An acute angle measures less than
degrees but greater than degrees.
D. An obtuse angle measures greater than
degrees but less than
degrees.
A B
CD
Measuring and Drawing Angles

Jumpstarters for Geometry
5© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Geometry Warm-ups:Classifying Pairs of Lines
Classifying Pairs of Lines 4Write “T” for true or “F” for false.
A. Parallel lines never intersect.
B. Some intersecting lines are perpen-
dicular.
C. Perpendicular lines rarely intersect.
D. If two lines are perpendicular, then
they are also parallel.
Classifying Pairs of Lines 5Write parallel, perpendicular, or intersecting for each pair of lines.
A. RU and TV
B. SQ and RU
C. RT and RU
D. UV and SQ
E. TV and QS
F. VT and TR
Classifying Pairs of Lines 3
A. Name two parallel lines.
B. Name two perpendicular
lines.
C. Name two intersecting lines
that are not perpendicular.
Classifying Pairs of Lines 2 Draw on a separate sheet of paper.
A. Draw a pair of parallel lines.
B. Draw a pair of perpendicular lines.
C. Draw a pair of intersecting lines that are not perpendicular.
Classifying Pairs of Lines 1Write parallel, perpendicular, or intersecting to describe each set of lines.
A. B.
C. D.
T
W
ZR
VS
UQ
R
T
S
Q
U
V
Classifying Pairs of Lines

Jumpstarters for Geometry
6© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Special Pairs of Angles 4A. Two angles are vertical. One angle measures
112 degrees. The other measures degrees.
B. Two angles are supplementary. One measures 97 degrees. The other measures degrees.
C. Two angles are complementary. One angle measures 36 degrees. The other measures
degrees.
Special Pairs of Angles 3The angles in each pair are supplementary. Write the missing angle measures.
A. ° B. ° C. °
Special Pairs of Angles 5A. Two complementary angles have the same measure. What is their angle measure? B. Two supplementary angles have the same measure. What is their angle measure? C. Two angles are complementary. One angle is twice the other. What are the angle measures? D. Two angles are supplementary. One angle measures 10 degrees more than the other. What are the angle measures?
Special Pairs of Angles 2The angles in each pair are complementary. Write the missing angle measures.
A. ° B. ° C. °
Special Pairs of Angles 1Write vertical, complementary, or supple-mentary to describe each pair of angles.
A. The sum of the measures of these two angles
is 180 degrees.
B. These angles are always congruent.
C. The sum of the measures of these two
angles is 90 degrees.
Geometry Warm-ups:Special Pairs of Angles
40°
? ?
45°
62°
?
135°?
57°
? 105°?
Special Pairs of Angles

Jumpstarters for Geometry
7© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Geometry Warm-ups:Identifying Polygons
Identifying Polygons 3Write the names of these polygons.
A. B. C. D.
Identifying Polygons 4
A. Can a polygon have only 2 vertices?
Explain.
B. Is a circle a polygon? Explain.
Identifying Polygons 5
A. Are all rectangles squares? Explain.
B. Are all squares rectangles? Explain.
Identifying Polygons 2How many sides, angles, and vertices do these polygons have?
Sides Angles Vertices
A. pentagon
B. quadrilateral
C. octagon
D. hexagon
Identifying Polygons 1Are these figures polygons?
A. D.
B. E.
C. F.
Identifying Polygons

Jumpstarters for Geometry
8© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Geometry Warm-ups:Polygon Puzzles
Polygon Puzzles 5A. Draw two lines to divide
the shape into three equal parts.
B. Connect the dots so that you get two squares.
Polygon Puzzles 4How many triangles are in this figure?
Polygon Puzzles 3Suppose you were going to cut this rectangle in half along the lines.
How many different ways could you cut it?
Draw your answers in the space below.
Polygon Puzzles 2A. Draw two triangles that are the same size
and shape using only four lines.
B. Draw two triangles that are the same size and shape using only five lines.
Polygon Puzzles 1A. Draw two squares using only five lines.
B. Draw two squares using only six lines.
Polygon Puzzles

Jumpstarters for Geometry
9© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Geometry Warm-ups:Congruent Figures
Congruent Figures 1Are the two figures in each set congruent?
A. B.
C. D.
Congruent Figures 2
Which two figures in each row are congruent? Write the numbers.
A.
B.
C.
Congruent Figures 5Use the square to do the following:A. Name the triangles that are congruent to triangle AXB. B. Name the segments that are congruent to
AC. C. Which triangles are congruent to triangle
ADC?
Congruent Figures 4Draw on a separate sheet of paper.
A. Draw a triangle that has exactly two
congruent sides.
B. Draw a triangle that has three congruent
sides.
C. Draw a figure that has four sides. Make all
the sides congruent. Do not make a square.
Congruent Figures 3
Triangle ABC is congruent to triangle DEF.
A. Which segment is congruent to AB?
B. Which segment is congruent to BC?
C. Which segment is congruent to AC?
D. Which angle is congruent to ∠ABC?
1. 2. 3.
4. 5. 6.
7. 8. 9.
A
B C F E
D
A B
CDX
Congruent Figures

Jumpstarters for Geometry
10© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Geometry Warm-ups:Similar Figures
Similar Figures 5The figures in each pair are similar. Find the missing lengths.
A. s = B. t = C. x = y =
Similar Figures 4Write “T” for true or “F” for false.
A. All squares are similar.
B. All rectangles are similar.
C. All triangles are similar.
D. All circles are similar.
E. All hexagons are similar.
Similar Figures 3Find the four pairs of similar figures. Write their numbers on the lines.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Similar Figures 2
Which two figures in each row are similar? Write the numbers.
A.
B.
C.
Similar Figures 1Are the two figures in each set similar?
A. B.
C. D.
1. 2. 3.
4. 5. 6.
7. 8. 9.
1. 2. 3.4.
5. 6. 7.
8.
3
4
5 6
8
s
12
6
t
2 2
3
4 4
4 4
y
8 x
Similar Figures

Jumpstarters for Geometry
11© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Name/Date
Geometry Warm-ups:Symmetrical Figures
Symmetrical Figures 5Complete the missing half of each design to find the missing words.
A. B.
C. D.
Symmetrical Figures 4Write how many lines of symmetry each figure has. Then draw them.
A. B. C.
Symmetrical Figures 3
Draw a line of symmetry through each figure.
A. B. C. D. E.
Symmetrical Figures 2Is the letter symmetrical? Write “yes” or “no.” If it is, draw the line of symmetry.
A. B. C.
D. E. F.
Symmetrical Figures 1Is the dashed line a line of symmetry?
A. B.
C. D. O F T
Z H V
OX HOE
DID ICE
Symmetrical Figures

Jumpstarters for Geometry
40© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments 1 (p. 2)A. line segment B. lineC. ray D. ray
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments 2 (p. 2)
A. 6: PQ, SQ, QR, QT, PR, ST (or reverse order)
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments 3 (p. 2)
A. GH or HG B. RS C. VU
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments 4 (p. 2)A. false B. false C. true D. true
Lines, Rays, and Line Segments 5 (p. 2)
A. PQ, TR (or QP, RT ) B. SQ, SR, ST, SP, SO
C. QS, QP
Classifying Angles 1 (p. 3) A. ∠LMN, ∠NML, ∠M B. ∠GEH, ∠HEG, ∠EC. ∠XVZ, ∠ZVX, ∠V
Classifying Angles 2 (p. 3)A. vertexB. Yes. Y is the vertex for both angles. C. No. Angle YZX has point Z for a vertex rather than
point Y.
Classifying Angles 3 (p. 3)A. acute B. right C. straight D. obtuse
Classifying Angles 4 (p. 3)A. right B. obtuse C. acute D. straight
Classifying Angles 5 (p. 3)A. ∠ABD or ∠DBE B. ∠ABE or ∠EBCC. ∠ABC D. ∠DBC
Measuring and Drawing Angles 1 (p. 4)A. 180 B. 90 C. 90, 0 D. 90, 180
Measuring and Drawing Angles 2 (p. 4)A. 45° B. 100° C. 120°
Measuring and Drawing Angles 3 (p. 4)A. B.
C. D.
Measuring and Drawing Angles 4 (p. 4)Angles and answers will vary.
Measuring and Drawing Angles 5 (p. 4)A. 90°, right B. 135°, obtuseC. 45°, acute D. 90°, right
Classifying Pairs of Lines 1 (p. 5)A. intersecting B. perpendicularC. perpendicular D. parallel
Classifying Pairs of Lines 2 (p. 5)Drawings should be made according to the directions. Examples:
A. B.
C.
Classifying Pairs of Lines 3 (p. 5)
A. RS, TU B. TU, WZ C. RS, VQ or TU, VQ
Classifying Pairs of Lines 4 (p. 5)A. T B. T C. F D. F
Classifying Pairs of Lines 5 (p. 5)A. parallel B. intersectingC. perpendicular D. parallelE. intersecting F. perpendicular
Special Pairs of Angles 1 (p. 6)A. supplementary B. vertical C. complementary
Special Pairs of Angles 2 (p. 6)A. 50° B. 45° C. 28°
Special Pairs of Angles 3 (p. 6)A. 45° B. 123° C. 75°
Special Pairs of Angles 4 (p. 6)A. 112 B. 83 C. 54
Geometry Warm-ups:Answer Keys
30°60°
135° 90°
Answer Keys

Jumpstarters for Geometry
41© Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers
Special Pairs of Angles 5 (p. 6)A. 45° B. 90° C. 60°, 30° D. 95°, 85°
Identifying Polygons 1 (p. 7)A. yes B. no C. yes D. yesE. yes F. no
Identifying Polygons 2 (p. 7)A. 5, 5, 5 B. 4, 4, 4 C. 8, 8, 8 D. 6, 6, 6
Identifying Polygons 3 (p. 7)A. pentagon B. quadrilateral C. hexagon D. octagon
Identifying Polygons 4 (p. 7)A. No. A polygon needs at least 3 vertices to be a
closed shape.B. No. A circle is not made up of line segments.
Identifying Polygons 5 (p. 7)A. No. A rectangle may have two pairs of sides that
are different lengths. B. Yes. A square is a special type of rectangle. All four
sides are equal.
Polygon Puzzles 1 (p. 8)A. B.
Polygon Puzzles 2 (p. 8)A. B. or or
Polygon Puzzles 3 (p. 8)There are 4 different ways to cut the rectangle in half.
Polygon Puzzles 4 (p. 8)There are 13 triangles: 9 small, one-cell triangles; 3 medium, four-cell triangles; and 1 large, nine-cell triangle.
Polygon Puzzles 5 (p. 8)A. B.
Congruent Figures 1 (p. 9)A. no B. no C. yes D. yes
Congruent Figures 2 (p. 9)A. 1, 3 B. 5, 6 C. 7, 8
Congruent Figures 3 (p. 9)
A. DE B. EF C. DF D. ∠DEF
Congruent Figures 4 (p. 9)Examples of drawings:A. B. C.
Congruent Figures 5 (p. 9)A. Triangles BXC, CXD, DXA B. BD onlyC. Triangles DCB, CBA, BAD
Similar Figures 1 (p. 10)A. no B. yes C. yes D. no
Similar Figures 2 (p. 10)A. 1, 2 B. 4, 6 C. 7, 8
Similar Figures 3 (p. 10)Pairs may be listed in any order.A. 1, 7 B. 2, 6 C. 3, 8 D. 4, 5
Similar Figures 4 (p. 10) A. T B. F C. F D. T E. F
Similar Figures 5 (p. 10)A. s = 10 B. t = 3 C. x = 8, y = 6
Symmetrical Figures 1 (p. 11)A. yes B. no C. yes D. no
Symmetrical Figures 2 (p. 11)A. yes B. no C. yes
D. no E. yes F. yes
O O T
H H V
Answer Keys