Introduction to Interstitial Lung Disease(ILD) or Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease (DPLD)
Suppurative Lung DIsease
-
Upload
nur-liyana-ahmad-zaki -
Category
Documents
-
view
223 -
download
0
Transcript of Suppurative Lung DIsease
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
1/33
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
2/33
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
3/33
By
Dr. Eman Arram
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
4/33
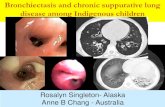
Bronchiectasis is an abnormal
permanent dilatation of the mediumsized cartilagenous bronchi,
accompanied by variable destruction of
muscular and elastic components of
the bronchial walls. It may be
congenital or acquired. It may be focalor diffuse.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
5/33
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
6/33
It is a syndrome & characterized by
cough and expectoration that is
usually copious and related to
posture and time
It includes:
Bronchiectasis
Lung abscess
Empyema with bronchopleural fistula
Infected cystic lung
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
7/33
Dilatation of medium sized
subsegmental bronchi from about the
4th to 9th generations and filling with
purulent secretions or mucus plugs.
Bronchial wall inflammation and
destruction and replacement of the all
components of the wall by fibrous
tissue.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
8/33
Pathogenesis:
Initiating factors for bronchiectasis:
Infection
Bronchial obstruction
Fibrosis
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
9/33
Site: Bilateral in 30% of patients.
Left lower lobe > Rt lower lobe (>3 times). Left LL posterior basal segments is almost
always affected then lingula then Rt LL thenmiddle lobe.
The particular lobes affected may sometimesbear a relationship to underlyingpredisposition:
Upper lobe bronchiectasis is often 2ry to TB,lung abscess or cystic fibrosis.
Middle lobe bronchiectasis in TB.
Central bronchiectasis in ABPA.
Bronchiectasis due to FB aspiration is more inthe Rt LL or in post segment of UL.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
10/33
Classification (Reids classification) Cylindrical (tubular)
Cystic (saccular)
Varicose
Fusiform
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
11/33
A) Congenital and hereditary disorders: Primary ciliary dyskinesia syndromes (PCD).
Cystic fibrosis
Alpha1 anti-trypsin deficiency
Tracheomalacia
Tracheobronchomegally Intralobar bronchopulmonary sequestration
Immunodeficiency syndromes
Yellow nail syndrome
Aetiology of Bronchiectasis
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
12/33
Kartagners syndrome:
Bronchiectasis. Sinusitis or absent frontal air
sinuses
Situs inversus
Youngs syndrome:
Recurrent pulmonary infections
predisposing to bronchiectasis
Sinusitis
Infertility (obstructive azospermia)
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
13/33
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
14/33
B) Acquired bronchiectasis:
1- Post-infection:
Bacterial: klebsiela pneumonia, S.
aureus, B. pertussis.
Mycobacteria.
Mycoplasma.
Viruses as infleunza, adenoviruses,
herpes simplex, measless and HIV.
Fungi eg histoplasmosis.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
15/33
2- Bronchial obstruction:
Endobronchial: FB, tumor, mucoid impaction.
Extrabronchial compression: LN, tumor, aneurysm.
Bronchial stenosis.
3- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
4- Inhalation / Aspiration injury:
Inhalation of irritants such as ammonia, NO2, smoke
and toxic fumes.
Heroin use. Aspiration of gastric contents.
Recurrent aspiration pneumonias, alcoholism,
neurologic disorders, lipoid pneumonia.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
16/33
5- Autoimmune diseases:
Inflammatory bowel disease. Coeliac disease.
SLE.
Rheumatoid arthritis. Cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis.
Primary biliary cirrhosis.
Thyroiditis.
Pernicious anemia.
.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
17/33
Clinical presentation of
bronchiectasis: Chronic cough with copious amount
of foul-smelling sputum more in the
morning and on leaning forwards with
characteristic winter exacerbations.
Dyspnea.
Chest pain.
Haemoptysis.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
18/33
Wheezy chest.
Concomitant sinusitis in some cases.
General manifestations: fever, weight
loss, growth retardation, GIT troubles.
Clubbing of the fingers and may be
HPOA.
Oedema LL.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
19/33
Complications of bronchiectasis:
Recurrent haemoptysis, pneumoniaand pleurisy are common.
Lung abscess and metastatic brain
abscess.
Amyloidosis.
Cor pulmonale and respiratoryfailure.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
20/33
1) Chest radiography:
Investigations
Tooth past or gloved finger
appearance.
Tramlines appearance. Honeycoomb or soap bubble
appearance in cystic bronchiectasis.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
21/33
2) Bronchography:
It was the investigation of choice.
3) HRCT chest:
Is now the favored investigation of
establishing the diagnosis ofbronchiectasis.
Cylindrical bronchiectasis appears as
uniformly dilated airways.
Signet ring sign: dilated bronchi appear
as ring structures with internal diameters
greater than those of their accompanying
pulmonary artery branches.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
22/33
Bronchogram showing cystic
bronchiectasis
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
23/33
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
24/33
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
25/33
4) Fiberoptic bronchoscopy:
Evaluation of patients with recurrenthaemoptysis.
Perform more selective segmental
bronchography.
5) Sputum culture and sensitivity:
H.influenza, S.pneumoniae, moraxella
catarrhalis, staphyloccocus aureus,
klebsiella pneumonia, pseudomonas
aeruginosa, adenovirus and anaerobes.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
26/33
6) Pulmonary function tests:
Obstructive ventilatory defect is the
predominant defect usually mild.
Preoperative evaluation of patients.
7) Other investigations: Sweat chloride test in CF.
Serum immunoglobulins.
ECG evidence of cor pulmonale inadvanced disease.
CBC anaemia and leucocytosis.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
27/33
A) Medical treatment:
1) Postural drainage:
Gravitational drainage of accumulated sputum in
the bronchiectatic area facilitated by directpercussion, mechanical percussors and vibrators.
Treatment
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
28/33
2) Antimicrobial therapy:
Amoxycelline 250mg TDS for 2 weeks may be
increased to 3 gm twice daily in severe cases.
Ofloxacin 200 mg twice daily for 10-15 days.
Clarithramycin 250 mg twice daily for 10 days.
Tetracyclines.
B lactam antibiotics e.g. amoxycelline
clavulinic acid.
Antistaph, antipseudomonal antibiotics.
Nebulized antibiotics for pseudomonas
aeruginosa.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
29/33
3) Expectorants and mucolytics.
4) Bronchodilators.
5) Corticosteroids: when there is failure
to obtain an adequate response to
bronchodilators.6) Human gamma globulin: IM 25 mg/kg
weekly or 2 weekly intervals in patients
with immunodeficiency syndromes.7) Vaccination: by influenza and
pneumoccocal vaccine specially in
children.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
30/33
B) Surgical treatment:
Indications: The diagnosis has been confirmed with
bilateral bronchogram or HRCT.
Localized disease to one lung or part ofthe lung.
Significantly disturbed patient by
recurrent infective exacerbation orhaemoptysis despite medical treatment
over a period of at least 12 months.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
31/33
Good pulmonary function. No systemic causal factor.
Patient is less than 40 years.
Surgical maneuvers include either
segmentectomy, lobectomy or even
pneumonectomy.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
32/33
C) Embolotherapy:
Bronchial artery embolization to control
massive or recurrent haemoptysis for
patient not candidates for surgery.
-
8/13/2019 Suppurative Lung DIsease
33/33
Thank you forattention






![Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease … · 2018-10-28 · Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD),[[1] is a group](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5e7d31d2ec5074254471c7d0/interstitial-lung-disease-ild-or-diffuse-parenchymal-lung-disease-2018-10-28.jpg)