Supplemental Figure Legends: Supplemental Figure 1...
Transcript of Supplemental Figure Legends: Supplemental Figure 1...

31
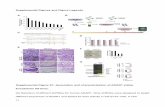
Supplemental Figure Legends: Supplemental Figure 1. Caerulein treatment had similar acute effects. Caerulein (50 µg/kg) was
injected intraperitoneally at the time points shown (a). Histologic examination showed that within
24 hours after caerulein treatments, acute pancreatitis as indicated by edema and acinar cell
vacuolization developed in both control (b) and Acinar-Ras mice (c, 100X, inset 400X).
Measurements of pancreatitis parameters such as edema (d) and serum amylase (e) also indicated a
similar extent of acute inflammation after initial caerulein treatments.
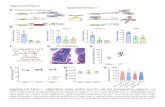
Supplemental Figure 2. Inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrosis were evident in caerulein-
induced chronic pancreatitis in Acinar-Ras mice. 4 weeks after caerulein treatment pancreata of
Acinar-Ras mice showed strong infiltration of leukocytes (a, 100X, inset 400X), mainly
macrophages (b, 100X, inset 400X). Stroma replacement with positive collagen trichrome staining
(c, 100X) and abundant smooth muscle actin expression (d, 100X, inset 400X) was observed in
these animals. Total Ras was increased in acinar-Ras mice as compared with controls 4 weeks after
caerulein treatment (e).
Supplemental Figure 3. Caerulein treatments resulted in prolonged elevation of Ras downstream
signaling in the presence of mutant K-Ras. Phospho-Erk immunostaining indicated that increased
Erk activity was localized in acinar derived cells of pancreata from Acinar-Ras mice (a) compared
with control animals (b) at week 4 (100X, inset 400X). Caerulein caused prolonged elevation of
phosphor-Erk in Acinar-Ras mice as detected by western blot (c).
Supplemental Figure 4. LPS treatments led to chronic inflammation and precancerous lesions in
Acinar-Ras but not control mice. LPS (10 mg/kg) was injected intraperitoneally once per week for 4
consecutive weeks (a). Pancreata of control mice were histologically normal after LPS treatments
(b, 100X). In contrast, pancreata of Acinar-Ras mice developed chronic pancreatitis and PanINs

32
within 4 weeks (c, 100X). Ras activity was strongly increased in pancreata of Acinar-Ras mice
after 4 weeks of LPS treatments (d) (*p<0.05 versus non-treated Acinar-Ras mice).
Supplemental Figure 5. NF-B inhibitory subunit IB- was phosphorylated after caerulein
induction in Acinar-Ras mice. After 2 series of caerulein treatments (week 4) increased
phosphorylation of IB- was detected by phosphor-specific antibody against IB- in pancreata of
Acinar-Ras mice (a, 200X) but not in controls (b, 200X).
Supplemental Figure 6. Cox-2 expression in pancreatic acinar cells led to chronic pancreatitis and
cancer in Acinar-Ras but not control mice. Pancreata of mice expressing Cox-2 alone were 2.5
times bigger than those of control littermates (a) (*p<0.05 compared to control mice, n=7 animals).
Cox-2 alone induced development of acinar cell vacuolization and cyst formation which was
observed after 8-months (b, 100X, inset 400X).
Supplemental Figure 7. Levels of active phospho-Erk increased in pancreata expressing both Cox-
2 and mutant K-Ras. Phospho-Erk was examined by immunohistochemical staining in the pancreata
expressing Cox-2. Cox-2 expression alone increased the level of phospho-Erk in many acinar cells
(a, 100X). The expression of oncogenic K-Ras alone increased phospo-Erk levels only in the rare
PanINs (b, 100X). The combination of expression of both Cox-2 and mutant K-Ras generated
much higher levels of phospho-Erk in acinar derived cells of 2-month-old mice (c,100X).
Supplemental Figure 8. Ras, Cox-2 and NF-B pathways examination in normal human pancreatic
tissues. p-Erk (a), Cox-2 (b), p65 translocation(c) and p-IB-(d) staining were not evident in
normal pancreas as compared with the strong staining of these signaling molecules in human
pancreatic cancer tissues shown in Figure 8.

Supplemental Figure 1
CaeruleinInjections Analysis5x 1x 1x 1x 1x
Days
5x 1x 1x 1x 1x
1 2 3 4 5 14 15 16 17 18 28a
b c
WTCer 24h
Acinar-RasCer 24h
1.5
ControlAcinar-Ras
gh
t)
d
150
200
ControlAcinar-Ras
(%)
e
0.5
1.0
Pan
crea
s(%
of
Bo
dy
Wei
g
50
100
150
Am
yla
se
ac
tivit
y
0.0Cearulein - + - +
0Cearulein - + - +
A

b
Supplemental Figure 2
a
c d
Acinar-Ras 4 weeks post CerLeukocytes
Acinar-Ras 4 weeks post CerMacrophages
c d
Acinar-Ras 4 weeks post CerCollagen
Acinar-Ras 4 weeks post CerSmooth muscle actin
e
Acinar-RasControl
Collagen Smooth muscle actin
Total Ras
GAPDH

Supplemental Figure 3
ba
Control Acinar-Rasc
Acinar-Ras 4 weeks post Cerp-Erk (Brown)
WT 4 weeks post Cerp-Erk
400 C t l
p-ERK
t-ERK
0 2 4 0 2 4 Time (Week)
*
200
300
400 ControlAcinar-Ras
o-E
RK
/To
tal-
ER
K%
of
co
ntr
ol
*
WEEK 0 WEEK 2 WEEK 40
100
Ph
os
ph %

Supplemental Figure 4
LPS
Days 1 14 28217a
LPSinjections Analysis1x 1x 1x 1x
b cb c
WT 4 weeks post LPS Acinar-Ras 4 weeks post LPS
- - - + + + Ras-GTP
GAPDH
LPSd
400
600
Ras
/ G
AP
DH
of c
ontr
ol
*
0
200
LPS - +
Act
ive
R%
o

Supplemental Figure 5
ba
Acinar-Ras 4 weeks post Cerp-IKB- (Brown)
WT 4 weeks post Cerp-IKB-

Supplemental Figure 6
2.5
a
*
1.0
1.5
2.0
Pa
nc
rea
s%
of
Bo
dy
We
igh
t)
Control0.0
0.5(%
b
Cox-2Tg
Cox-2Tg

Supplemental Figure 7
ba
p-Erk p-Erk
Cox-2Tg Acinar-Ras
c
A i R C 2
p-Erk
Acinar-Ras-Cox-2

Supplemental Figure 8
a b
c d
Normal human pancreasIHC: p-Erk
Normal human pancreasIHC: Cox-2
Normal human pancreasIHC: p-IKB-
Normal human pancreasIHC: p65