SUMMER WORK - Coulsdoncoulsdon.ac.uk/sites/default/files/reigatecollege/downloads/... · Organelle...
Transcript of SUMMER WORK - Coulsdoncoulsdon.ac.uk/sites/default/files/reigatecollege/downloads/... · Organelle...

1
SUMMER WORK Before you return to classes in September you need to complete these two tasks
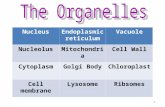
Task 2. Complete the labelling and filling in the blanks in the following tables on pages 7 to 8. You need to carry out research and find at least one function of the organelles found in the main types of cells - Eukaryotic and prokaryotic - as shown in the accompanying diagrams You need to prepare suitable notes for the organelles of the plant and animal cells so you can complete the diagrams of the two eukaryotic cells yourself. Note that some of the organelles are common to both types of cell. DO NOT USE CUT-AND PASTE FOR ANY PART OF THE ASSIGNMENT
EUKARYOTIC CELLS (PLANTS AND ANIMALS)

2

3
Task 3 Cell Organelles
Use your research to complete the following table by writing the name of the cell part or organelle
in the right hand column that matches the structure/function in the left hand column. A cell part may be used more than once.
Structure/Function Cell Part
Stores material within the cell
Closely stacked, flattened sacs (plants only)
The sites of protein synthesis
Transports materials within the cell
The region inside the cell except for the nucleus
Organelle that manages or controls all the cell functions in a eukaryotic cell
Contains chlorophyll, a green pigment that traps energy from sunlight and gives plants their green colour
Digests excess or worn-out cell parts, food particles and invading viruses or bacteria
Small bumps located on portions of the endoplasmic reticulum
Provides temporary storage of food, enzymes and waste products
Firm, protective structure that gives the cell its shape in plants, fungi, most bacteria and some protests
Produces a usable form of energy for the cell
Packages proteins for transport out of the cell
Everything inside the cell including the nucleus
Site where ribosomes are made
The membrane surrounding the cell
Name for the collection of DNA in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
Consist of hollow tubes which provide support for the cell
Small hair-like structures used for movement or sensing things
Composed of a phospholipid bilayer
Longer whip-like structures used for movement

4
Put a tick in the appropriate column(s) to indicate whether the following organelles are found in plant cells, animal cells or both.
Organelle Plant Cells
Animal Cells
Cell Wall
Vesicle
Chloroplast
Chromatin
Cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Lysosome
Mitochondria
Nucleolus
Nucleus
Plasma membrane
Central vacuole
Ribosome
Vacuole

5
Extension Activities If you want an extra challenge then complete the following Go to the Open Learning Initiative https://oli.cmu.edu/jcourse/lms/students/syllabus.do?section=df3e23850a000
1dc518491159056b43c Where you can complete the free introduction to Introduction to Biology course. You should aim to complete as much of units 1,3&4 as you can.
Here some sample exam questions Below is a list of cell types and their functions
Cell Type Function
Cardiac muscle cells Contraction of the heart
Alveolar macrophage cells To ingest and digest pathogens invading the lungs
Beta cells in islets of Langerhans To produce insulin (a protein)
Proximal tubule epithelial cells To reabsorb useful molecules filtered out of the blood by the kidneys.
Name one organelle you would expect to find a lot of in the cardiac muscle cells. Give a reason for your answer.
Suggest how alveolar macrophage cells are adapted to their function in terms of the organelles that they contain.
Name three organelles you would expect to find a lot of in beta cells in the islets of Langerhans
.
.
.
ALL this work will support your lessons and homework set in September.

Introduction to A-level Chemistry Summer Homework
In preparation for the course we would like you to complete the following tasks:
Understanding the structure of atoms
The chemical properties of elements depend on their atomic structure and in particular on the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus. The arrangement of electrons in orbitals is also linked to the way in which elements are organised in the Periodic Table. Evidence for the way electrons are arranged in atoms (electron configuration) is gained from measuring ionisation energy. Chemists can measure the mass of atoms and molecules to a high degree of accuracy in a mass spectrometer. There are various different types of mass spectrometer. During the course, you will study the principles of operation of a modern Time of Flight (TOF) Mass Spectrometer. Tasks:
1. Define the terms relative atomic mass (Ar ) and relative molecular mass (Mr ). 2. Draw and write out the electron configuration of the first 20 elements in the Periodic
Table.
3. Outline the following points about the mass spectrometer:
a. The five main operation stages of the TOF mass spectrometer b. The main differences between a magnetic sector mass spectrometer and a
TOF mass spectrometer c. How to interpret simple mass spectra of elements d. How to use the data from a mass spectrometer to calculate relative atomic
mass from isotopic abundance.
3. Explain how first and successive ionisation energies in Period 3 (Na–Ar) and in
Group 2 (Be–Ba) give evidence for electron configuration and the arrangement of
electrons in energy levels (shells), sub-shells and orbitals.
There is a lot of information on the internet that will help you to answer these
questions.
A particularly useful website is Chemguide (http://www.chemguide.co.uk/).
Use diagrams when answering the questions.
This work is compulsory and must be submitted during the first lesson in September 2017.
Completing this work to high standards will enable you to get ahead in your studies.
Extension Activities
If you want an extra challenge then complete the following tasks:
1. Explain what isotopes are.
2. Make a table showing the number of fundamental particles in the atoms and
common ions of the first 20 elements in the Periodic Table.

3. Go to the following link and watch at least four Faces of Chemistry videos that you
think you might find interesting. http://www.rsc.org/learn-chemistry/resource/listing?searchtext=&reference=students&filter=all&fAudience=AUD00000002&fAudience=AUD00000001&MediaType=MED00000002&gclid=CJ3Om-Sf7dQCFaWw7QoduGoBGw Which videos did you decide to watch? What were the key themes of the video? What did you learn?
ALL this work will support yourlessons and homework set in September!

Unit 1 – Working as a Physicist
1 | P a g e
AS PHYSICS
Introductory Class Working as a Physicist &
Summer Tasks 16/17
STUDENT NAME: ………………………………………………….. TUTOR NAME: …………………………………………………..

Unit 1 – Working as a Physicist
2 | P a g e
S.I. units (systeme international d’unites) This is the system of “metric” units used in most scientific work. When a quantity such as length is measured the value is given a unit, in this case the unit being the metre. Remember that the value is meaningless unless the unit is shown. The name of each unit also has a standard symbol of no more than three letters, so for example the abbreviation for metre is m. Base units and derived units The S.I. system of units is based on seven base units, which are:
Quantity Unit
Name Symbol Name Symbol
mass m kilogram kg
length l metre m
time t second s
temperature T kelvin K
luminous intensity I candela cd
electric current I ampere A
Quantity of matter n mole mol
Luminous Intensity Iv candela cd
All other units are derived units and can be expressed as a combination of base units, even when the unit is given its own name. Examples of derived units are: metre2 (m2), the unit of area newton (N), the unit of force, where 1 newton = 1 kilogram metre / second2 Points to remember: 1. Symbols for units are always written in the singular. This is because s is the symbol for second e.g. 5 ms means 5 millisecond, not 5 metres. 2. You must be careful to distinguish between upper and lower case letters (i.e. capital and small letters) because the same letter can mean different things depending on whether it is upper or lower case. For example the prefix M, standing for mega, multiplies a unit by 1 000 000 whereas the prefix m, standing for milli, multiplies a unit by 0.001. 3. When the name of a unit is written in full it nearly always starts with a lower case letter, even if the unit is named after a person e.g. the newton which is named after Sir Isaac Newton. 4. Quantities also have symbols. To distinguish between the symbols for quantities and the units that they are measured in, it is normal in printed text to write the symbols for quantities in italic (sloping) print and the symbols for units

Unit 1 – Working as a Physicist
3 | P a g e
in normal upright print e.g. the symbol for the quantity time is t and the unit of time is the second with the symbol s,
so that time = 5 seconds is written as t = 5 s.
Obviously it is not possible to do this in hand written text, but it is usually obvious from its context. An equation relating several symbols together will usually involve quantities:
e.g. s = d meaning speed = distance t time
whereas a symbol following a number will be the unit of the number e.g. in 8 kg, kg is the symbol for the unit kilogram. The use of standard prefixes with S.I. units Larger and smaller units are (with a few exceptions) obtained by placing one of the standard prefixes given below before the unit (a fuller set of prefixes is given on a separate sheet). For example, the prefix kilo with the symbol k gives a unit 1000 times larger than the basic unit, no matter what the unit is e.g. 1 kilogram = 1,000 gram 1 kilometre = 1,000 metre.
Symbol Prefix Multiplies unit by or or
M (upper case) Mega 1 000 000 106
k kilo 1 000 103
d deci 1/10 0.1 10-1
c centi 1/100 0.01 10-2
m (lower case) milli 1/1 000 0.001 10-3
(Greek “mu”) micro 1/1 000 000 0.000001 10-6
n nano 1/1 000 000 000 0.000000001 10-9
The problems that follow use these common units:
Quantity Unit Symbol
mass kilogram kg
length metre m
time second s
volume litre l
energy joule J
power watt W
voltage volt V

Unit 1 – Working as a Physicist
4 | P a g e
Exercise 1 - Express: 1. 8 kilometre in metre Worked Example: 8 kilo metres, where kilo (k) multiplies by 1,000 8 × 1,000 metres = 8,000 m or 8 × 103
2. 2 millisecond in second 3. 3 megajoule in joule 4. 6 centimetre in metre 5. 5 decilitre in litre 6. 55 microvolt in volt 7. 800 nanosecond in second 8. 25 kilogram in gram 9. 0.75 MW in W 10. 482 cs in s
11. 40 g in g 12. 125 dm in m 13. 5.92 mJ in J 14. 9 640 nm in m Exercise 2 - Express: 1. 15 000 m in km
Worked Example: 15,000 metres, where kilo (k) multiplies by 1,000 15 × 1,000 metres = 15,000 m or 15 × 103 m 15 km k is substituted for × 1,000 or ,000 or × 103
2. 0.57 m in cm 3. 320 000 W in MW 4. 0.048 g in mg
5. 1.82 l in dl 6. 0.000 004 s in s 7. 0.000 000 004 m in nm 8. 64 000 000 J in MJ
9. 0.7 l in cl 10.. 0.000 08 m in m 11. 0.000 5 V in mV 12. 0.42 m in dm 13. 132 000 V in kV 14. 0.000 000 62 s in ns

Unit 1 – Working as a Physicist
5 | P a g e
Utilising online teaching tools: During the course, two online resources will prove to be particularly useful:
1. https://www.khanacademy.org
2. https://isaacphysics.org/
Watch the video on Khan Academy covering standard form:
https://www.khanacademy.org/math/pre-algebra/pre-algebra-exponents-
radicals/pre-algebra-scientific-notation/v/scientific-notation-old
Notice how it is referred to as scientific notation and not standard form as in the UK, if using Khan Academy and you can’t find additional courses please ask for advice. Create an account with Isaac Physics using the above link. When you return I will link your account to the College so I can view your responses.
On the homepage, you can click on the apple from any page to return to the home screen. Follow the link, for Isaac books as below.
Choose the, Physics Skills Mastery link. Select exercise A3, in the General Questions section. This should be completed for your return, please ensure you are logged in in order to save your responses and access them.

Unit 1 – Working as a Physicist
6 | P a g e
The Topic List for the AS Physics course is as follows: TOPIC 2: Mechanics
TOPIC 3: Electric Circuits
TOPIC 4: Materials
TOPIC 5: Waves and the Particle Nature of Light
For each of these topics, create a powerpoint slide (4 slides in total) on what
sub topics will be covered in each of these headingss.
You may use any format you believe appropriate (Spider diagram, bullet
points, flow chart, experiments list, famous names or breakthroughs in the field
of physics etc.) but you must include at least one image for each slide.
Outline which, you believe will be your strong area and your weak area and
which you are looking forward to the most and why.
Completion Checklist (Tick box when complete):
1. Exercise 1 & 2 on metric prefixes in pack
2. Watch Khan Academy video
3. Register with Isaac Physics
4. Complete exercise A3 on Issac Physics
5. 4 Powerpoint slides on AS Physics and your relation to the course

Introductory Day and Choices Day 2017
Psychology: Summer Preparation Assignment
Research three psychologists and summarise their famous work. Some
examples of psychologists you might like to research are:
Sigmund Freud
Stanley Milgram
Phillip Zimbardo
Roger Sperry
Elizabeth Loftus
Simon Baron-Cohen
Solomon Asch
John Bowlby
Harry Harlow
Ivan Pavlov
Albert Bandura
… any others you wish to research
Some examples of websites you might like to use are:
www.bps.org.uk www.psychology.about.com
http://famouspsychologists.net/
http://www.psychnet-uk.com/x_new_site/student_information/psychologists.html NO WIKIPEDIA print-outs
NO Plagiarism (copy and paste)
What to include in this assignment
- Picture of the psychologist
- Title of their research
- Summary of the findings of their research
- Why you find the study interesting
- Why you think the study is of interest to psychologists and everyday life
Deadline: First Psychology lesson in September

Coulsdon College BTEC Engineering
Introduction to BTEC Engineering Summer Homework
In preparation for the course we would like you to complete the following tasks:
Using Breadboards
Scenario: In engineering, a prototype is a first example of a product that can be tested and
used as a demonstration tool of the finished product. A College has requested your
engineering education company to create an introduction powerpoint they can utilise as an
introduction to what a breadboard is for their engineering department.
You task:
Create a powerpoint detailing how an electronics breadboard works.
You should include:
i) Description of the function of a resistor in a circuit
ii) Description of the function of an LED in a circuit
iii) Description of the function of a capacitor in a circuit
iv) Diagrams/Images
v) Explanations of what your chosen diagrams/images show
vi) An example on a breadboard of how to connect a resistor and LED in series
vii) An example on a breadboard of how to connect a resistor and capacitor in
series
viii) References for all resources used
(A website reference should include the website name, full URL address, the
date you accessed it and a clear link to which section of work it relates to)
ix) A justification for the quality and reliability of the web resource
(i.e. is it Dave’s blog on completing homework, a University, a College or an
individual with stated Engineering qualifications and experience)
In electronic engineering (Units 6 & 35), a key piece of prototyping equipment is called a
‘breadboard’ which you will be using extensively for your own circuit builds.
In Communications for Engineering (Unit 2), you will be studying methods engineers use
for effective communication and the digital methods available in the modern engineering
environment.

Introduction to BTEC Science Summer Homework
In preparation for the course we would like you to complete the following tasks:
Understanding the use of Titrations
It is often necessary in chemistry to find the concentration of a substance in solution, for example the amount of chlorine in drinking water or the amount of an additive added to food. Such analysis is carried out by chemists using a technique known as titration. During a titration a solution of known concentration is reacted with a solution of unknown concentration (the analyte). The endpoint is determined, usually by a colour change, and the unknown concentration is found through a series of calculations. Tasks:
1. Research and find four uses of titrations, describe each one briefly. 2. Explain the main stages in carrying out a titration.
3. Research pH curves (titration curves) and answer the following questions:
a. What is meant by equivalence point in a titration? b. Sketch a pH curve for the reaction of a strong acid with a strong Alkali and
label the equivalence point. c. Describe, as fully as possible, an experimental method that could be used to
generate a pH curve d. Define the terms strong acid, weak acid, strong base, and weak base e. Explain as fully as possible why it is not usually possible to titrate a weak acid
against a weak base.
There is a lot of information on the internet that will help you to answer these
questions.
A particularly useful website is Chemguide (http://www.chemguide.co.uk/).
Use diagrams when answering the questions.
This work is compulsory and must be submitted during the first lesson in September 2017.
Completing this work to high standards will enable you to get ahead in your studies.
Extension Activity
If you want an extra challenge then complete the following tasks:
There are many errors that can occur in titration analysis. Describe as many of these errors as possible and explain how they can be minimised.
ALL this work will support your lessons and homework set in September.