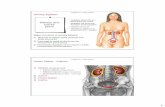
Summary of the Urinary System - homeschool.ie
Transcript of Summary of the Urinary System - homeschool.ie

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
1
Summary of the Urinary System
Definitions of Urinary System
Excretion: removal of waste products of metabolism
Metabolism: sum of all chemical reactions in a living organism
Homeostasis: maintaing a constant internal environment in a living organism
Osmoregulation: maintaing a constant water level in a living organism. Detected by the
hypothalamus
Filtration: removal of materials from the blood
Reabsorbtion: returning of filtered material to the blood
Glomerular filtrate: content of the blood that has passed through the glomerulus
Diffusion: movement of molecules from an area of high molecule concentration to an area of
low molecule concentration across a semi permeable membrane. Passive process; doesnt
require energy (ATP)
Osmosis: movement of water molecules from an area of high water concentration to an area of
low water concentration across a semi permeable membrane. Passive process; doesnt require
energy (ATP)
Osmotic gradient: difference in water concentration between two areas
Semi permeable/ selectively permeable: controls water enters an area based on size of molecule
Active transport: movement of molecules that requires energy (ATP)
Exocrine gland: a gland that has a duct (tube) coming out of it
Endocrine gland: a gland that does not have a duct (tube) coming out of it
ADH: anti- diuretic hormone
Hormone: proteins produced by endocrine glands (ductless glands) that transport chemical
messages around the human body dissolved in blood
Homework Questions
2008 Q13
2006 Q13
DEB 2005
DEB 2015

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
2
Part of the excretory system and is involved in Homeostasis
Urinary System and the kidney have a role to play in homeostasis
Homeostasis: maintaining a constant and balanced internal environment in a living organism
Kidneys role in homeostasis
Excretion: removal of waste products of metabolism from a living organism (not to be confused
with egestion)
Osmoregulation: maintaining a constant water balance in a living organism
Excretion:
Excretory Product Source Site of Excretion How
Urea Protein Kidneys Via filtration in the
nephron
CO2 Carbohydrates/
proteins/ Lipids
Lungs Breathing
H20 Cellular Respiration,
food
Lungs, Skin, kidney Breathing, Sweating
Salts Skin, lungs, kidney Breathing, Sweating

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
3
Kidney
Exocrine gland (has a duct-ureter)
Located in the pelvic cavity
Renal Artery (comes from Aorta/ linked to afferent arteriole): carries O2 and food to the kidney
Renal Vein (goes to the vena cava/ linked to efferent arteriole): carries CO2 and waste products
away from the kidney
Part of kidney Role Part of Nephron structure
Cortex Filtration Glomerulus/ bowman’s
capsule/ distal convuluted
tubule
Medulla Reabsorption Proximal convuluted tubule/
loop of henle/ collecting duct
Pelvis Excretion Collecting duct
Filtration: removal of materials from the plasma part of the blood
Reabsorption: returning of filtered materials to the blood

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
4
Nephron
Kidney is made up of millions of nephron which increase the surface area for filtration
and reabsorption
Aid the filtration and reabsorption process by:
o Having a large surface area (many of them)
o Walls of nephron are one cell thick
o Surrounded by a good blood supply
Structure of the Nephron
Afferent Arteriole (cortex): blood enters the kidney via the afferent arteriole. This
blood comes from the renal artery which is linked to the Aorta. The afferent
arteriole is larger than the efferent arteriole so that it creates pressure and forces
the blood out of the arteriole to enter the glomerulus
Glomerulus (cortex): the content of the blood containing water, salts, amino acids,
triglycerides, glucose is passed through the glomerulus and becomes known as the
glomerulus filtrate. (blood and filtrate will contain the same amount of glucose,
amino acids etc for this reason).Red Blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and
large undigested proteins are not passed through the glomerulus as they are too
large and continue straight on the the efferent arteriole

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
5
Bowman’s Capsule (cortex): glomerulus filtrate collected by the Bowman’s capsule
and passed to the proximal convuluted tuble. The Bowman’s capsule is the part of
the nephron involved in filtration. The glomerulus is not the part of the nephron
involved in filtration. The glomerulus is part of the circulatory system
Proximal Convuluted Tubule (medulla): Majority of reabsorption of all food groups
occurs here as well as some water. Food and salt molecules are reabsorbed by
diffusion. Water molecules are reabsorbed by osmosis
Loop of Henle: For the remainder of the nephron water and salts are reabsorbed
along the loop of henle.
Distal Convuluted Tubule: this is the site of action of Anti- Diuretic Hormone (ADH)
which affects the permeability of the nephron wall and will determine the amount
of water that is reabsorbed at this stage
ADH (after intense/vigorous excercise, after eating salty foods or on a warm day)
o Water level in the blood is low detected by the hypothalamus of the brains
o sends a message to the pituitary gland (endocrine gland-ductless gland that
produces hormones) in the brain to produce a large amount of ADH
o Travels in the blood to the distal convuluted tubule/ collecting duct of the
nephron in the blood
o ADH increases the permeability of the nephron wall
o Large volume of water is reabsorbed by the nephron back into the blood
o Volume of urine is low
o Has a high salt concentration
o Dark yellow/ brown in appearance
Collecting Duct: any water which is not reabsorbed back into the blood is
transported via the collecting duct to the ureter and transported to the bladder.
ADH can also act in the collecting duct
Functions of water (following reabsorbtion): solvent, medium for chemical
reactions, transport, temperature regulation, formation of plasma

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
6
Urinary System
Revision Diagram of Nephron

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
7

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
8
Urinuary System Revision Questions
1. Where in the nephron structure does filtration take place
2. Name 3 substances that do not pass through the glomerulus. Give a reason for this
3. When the content of the blood is passed through the glomerulus what does it become known as
4. In what part of the structure of the kidney does filtration occur
5. In what part of the structure of the kidney does reabsorption take place
6. List 3 ways in which the nephron has adapted to its role in absorption
7. What is excretion. How does it differ to egestion
8. Name three products that must be excreted from the body and state the location of excretion
9. Where in the structure of the nephron does reabsorption of food molecules occur
10. Name 3 types of food molecules reabsorbed at the location named in Q9
11. By what transport mechanism is 1. Water 2. Salt reabsorbed in the nephron
12. State a location in the nephron where 1. Water 2. Salt is reabsorbed
13. Name the blood vessel that supplies the kidney with food and oxygen. From what major blood
vesel in the body is blood vessel derived
14. Name a hormone which controls the amount of water reabsorbed into the body from the
nephron
15. Where is this hormone produced
16. Where is the site of action of this hormone in the nephron
17. What effect does this hormone have on the structure on the nephron that influences
reabsorption
18. Explain the role of ADH in water reabsorption from the kidney after a period of excercise
19. Describe the appearnace and volume of urine after excercise
20. What group of biomolecules do hormones belong to
21. How do hormones travel around the body
22. Draw and label a structure of the nephron
23. Is the kidney an example of an endocrine or an exocrine gland.give a reason for your answer
24. Draw and label the strucutre of a nephron
25. In what section of the kidney is the Bowman’s capsule located
26. Where in the structure of the nephron are Amino Acids reabsorbed
27. Large proteins are not passed throught the glomerulus. Given a reason for this
28. State two situations which may result in a drop in the water level of the blood
29. The kidney has a role to play in homeostasis. What is homeostasis
30. Why is glucose absent from urine
31. Why is the concentration of glucose the same in the plasma and glomerular filtrate
32. Is it normal to find proteins in urine. Give a reason for your answer
33. Why is the afferent arteriole larger than the efferent arteriole

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
9
The Urinary System Exam Paper Question 2018-Q6

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
10
2011 Q12
(a) (i) What is meant by the term excretion?
__________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) Mention one method of excretion in flowering plants.
__________________________________________________________________________________
(b) (i) Draw a large labelled diagram of a vertical section through a human kidney.
Label the following parts of your diagram: cortex, medulla, pelvis.
(ii) Indicate clearly on your diagram where re-absorption takes place.
(iii) 1. Name the blood vessel that supplies blood to a kidney. ________________________________
2. From which blood vessel does the blood vessel referred to in (iii)1 arise? _____________________
(iv) In which cavity of the body are the kidneys located? ____________________________________
(v) Name one substance, other than water, excreted in the urine.______________________________
(vi) Give a feature of the kidney which indicates that it is an exocrine gland.
__________________________________________________________________________________
(b) (i) The diagram
(c) above shows the structure of a nephron and its associated blood supply.
1. Name the parts numbered 1 to 6.
1. __________________ 2. _________________ 3. ________________ 4. _________________
5. _________________ 6. ________________ 7. __________________

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
11
2. Indicate clearly by number where filtration takes place. ____________________
3. Name the hormone associated with changing the permeability of the structure at 7. _____________
(ii) A sample of urine was found to contain protein.
1. Would you consider this to be normal? __________________________________
2. Explain your answer.
_________________________________________________________________________________
(iii) A sample of urine was found to contain glucose.
1. Would you consider this to be normal? _______________________________________________
2. Explain your answer. ______________________________________________________________
Homework 2008-Q13
(a) (i) What is meant by excretion?
_________________________________________________________________________________
(ii) Urea and carbon dioxide are excretory products of the human body. In the case of each
product name a substance from which it is derived.
Carbon Dioxide ___________________________________________________________________
Urea _____________________________________________________________________________
(b) The diagram shows the structure of a nephron and its associated blood supply.
(i) Name the parts A, B, C, D, E and F.
A _______________________ B________________ C________________ D __________________
E ____________________F__________________
(ii) From which blood vessel is A derived? ______________________________
(iii) Where in the kidney is B located? __________________________________
(iv) Give the part of the nephron in which each of the following takes place:
1. filtration, _____________________________________________________
2. reabsorption of amino acids. _________________________________________
(v) Give two features of the nephron that aid filtration.
1. ________________________________________________________________
2. ________________________________________________________________
(vi) Name a group of biomolecules in the blood which are too large to pass through the filtration system
of the nephron. ______________________________________________________

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
12
(b) (i) Suggest two situations which may result in a drop in the water content of the blood.
1.__________________________________________________________________________
2.__________________________________________________________________________
(ii) When the water content of the blood drops a hormone is released. Name this hormone and the
endocrine gland from which it is secreted.
Hormone _________________________ Gland ______________________
(ii) Give a precise target area for this hormone. How does the hormone reach the target area?
Target Area ________________________________________
How it reaches target area ____________________________
(iv) Explain the role of the hormone at its target area, when the water content of the blood is
low.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
Homework- 2006-13 (b)
(b) Use your knowledge of the human vascular and excretory systems to answer the following.
(i) Explain the terms, plasma, glomerular filtrate.
Plasma ___________________________________________________________________________
Glomerular Filtrate _________________________________________________________________
(iii) Explain why red blood cells are normally absent from glomerular filtrate.
_________________________________________________________________________________
(iii) The concentration of glucose is the same in plasma and glomerular filtrate. Why is
this? ____________________________________________________________________________
(iv) Why is glucose normally absent from urine?
__________________________________________________________________________________
(v) Following a period of heavy exercise an athlete may produce only a small volume of
concentrated urine. Explain this observation and give an account of the process that
concentrates the urine
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
13
2004 12 (a) and (b)
(a) What is homeostasis? State the role of the kidneys in homeostasis.
Homeostasis ______________________________________________________________________
Role of Kidney in Homeostasis _______________________________________________________
(b) (i) Draw a labelled diagram of a nephron. Include blood vessels in your diagram.
(ii) Filtration and reabsorption are vital processes that take place in the nephron. Describe how
each of these processes occurs.
Filtration
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
Reabsorption
_____________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
14
Homework- DEB 2005

Subject: Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level
Teacher: Ms. R. Doyle
Week: Week 19
Title: Excretion (kidney)
15
Homework – DEB 2015

![7 Catheter-associated Urinary Tract Infection (CAUTI) · UTI Urinary Tract Infection (Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection [CAUTI] and Non-Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/5c40b88393f3c338af353b7f/7-catheter-associated-urinary-tract-infection-cauti-uti-urinary-tract-infection.jpg)