Structure of eye and instillation of opthalmic sol. in eye ppt
Click here to load reader
-
Upload
ali7070 -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
136 -
download
5
description
Transcript of Structure of eye and instillation of opthalmic sol. in eye ppt


Structure of an eye


Pupil:The Pupil is an opening at the centre of the Iris. It permits light to enter the eye.
Iris:This is a pigmented layer of muscular tissue which gives the eye its colour.
Cornea:This is the see-through skin that covers the eye. It is clear like glass (transparent)
and has no blood vessels in it.
Sclera:This is known as the "white of the eye." The Sclera protects the inner structure of
the eye
Aqueous Humour:A clear, watery fluid (produced by the Ciliary body) that fills the area between the
Lens and the Cornea. It supplies nutrients that nourishes the Cornea and Lens
and maintains the convex shape of the Cornea along with refracting light onto the
pupil.
Vitreous Humour:A transparent, jelly-like substance that forms the main bulk of the eyeball.
maintains the shape of the eye.

Lens:The Lens is a transparent, round, biconvex structure. It is elastic so that its
curvature can be changed to adjust its refractive or focusing power.
Ciliary body:A circular band of tissues at the front of the Choroid that supports the Lens. It
contains Ciliary Muscles.
Conjunctiva:Transparent membrane that covers the sclera and lines the inner surface of the
eyelids. Also secretes mucous and a small volume of tears for the eye to be moist
Choroid:Black-pigmented layer under the Sclera that prevents the internal reflection of
light rays. Filled with blood capillaries.
Retina :The inner-most, light sensitive layer of the eyeball, on which images are formed.
Photoreceptors:
Rods are responsible to detect light in dim light (black and white) enabling night
vision.Cones are responsible to detect coloured light.
Optic Nerve:It transmits nerve impulses from photoreceptors to the brain.

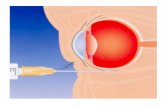
INSTILLATION OF EYE DROPS:To instill the eye drops, follow these steps:
1. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
2. Check the dropper tip to make sure that it is not
chipped or cracked.
3. Avoid touching the dropper tip against your eye or
anything else; eye drops and droppers must be kept
clean.
4. While tilting your head back, pull down the lower lid
of your eye with your index finger to form a pocket.
5. Hold the dropper (tip down) with the other hand, as
close to the eye as possible without touching it.
6. Brace the remaining fingers of that hand against your
face.

7. While looking up, gently squeeze the dropper so
that a single drop falls into the pocket made by the
lower eyelid. Remove index finger from the lower eyelid.
8. Close your eye for 2 to 3 minutes and tip your head
down as though looking at the floor. Try not to blink or
squeeze your eyelids.
9. Place a finger on the tear duct and apply gentle pressure.
10. Wipe any excess liquid from your face with a tissue.
11. If you are to use more than one drop in the same eye, wait
at least 5 minutes before instilling the next drop.
12. Replace and tighten the cap on the dropper bottle. Do not
wipe or rinse the dropper tip.
13. Wash your hands to remove any medication.

SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS:Before using pilocarpine eye drops or eye gel,
•Tell your doctor and pharmacist if you are allergic to pilocarpine or any other
drugs.
•Tell your doctor and pharmacist what prescription and nonprescription
medications you are taking, including vitamins.
•Tell your doctor if you have or have ever had asthma, intestinal disease,
ulcers, high blood pressure, heart disease, an overactive thyroid gland,
seizures, Parkinson's disease, or an obstruction in the urinary tract.
•Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-
feeding. If you become pregnant while using pilocarpine eye drops or eye gel,
call your doctor immediately.
•If you are having surgery, including dental surgery, tell the doctor or dentist
that you are using pilocarpine eye drops or eye gel.
•If you are using another topical eye medication, instill it at least 10 minutes
before or after you instill pilocarpine eye drops.

THANKS