Structure, Function and Homeostasis for the cell •What structure controls which proteins, lipids &...
Transcript of Structure, Function and Homeostasis for the cell •What structure controls which proteins, lipids &...

Cells
Structure, Function and Homeostasis

Characteristics of Cells • Basic unit of life
– anything alive is made of cells • Plasma membrane (skin) that separates them
from the environment. • Skeletonsfor protection & support (proteins) • Move (via proteins) • Communicate (via hormones) • Harness & use Energy (produce enzymes, heat) • Reproduce (maintain & copy blueprint for life)

Cells are small
• 10 – 100µm • Small to minimize energy
needs… • But large enough to
house specialized organelles and to minimize heat loss

Size determines rate of life
• Large enough to house organelles needed to eat, grow, reproduce
• Small enough that verylittle energy & time is needed for transport of nutrients & waste
Soviet Russia

Simple, Prokaryotic cells
• Lack nuclei (have nucleoid region), few organelles • Circular DNA (with just 1 copy of each gene)

Bacteria & Archaea - Prokaryotes • Wildly diverse
– ~ 500 species in your mouth alone • Abundant (numerous)
– 1012 on your skin; 1014 in G. I. tract; 1 teaspoon of soil contains billions
• Ubiquitous – O2-free mud; salt flats; boiling hot springs;
bedrock 1500 m deep; 10 km beneath ocean’s surface; 0˚- 121˚C

2/3 major evolutionary lineages

Types of Eukaryotic cells

Eukaryotic Animal cell • Endomembrane System
– Nucleus – Smooth & Rough Endoplasmic
Reticulum – Golgi Apparatus – Lysosomes ** – Plasma membrane
• Ribosomes • Peroxisomes • Mitochondria • Centrioles ** • Flagellum ** • Cytoskeleton

Eukaryotic Plant cell • Vacuole • Cloroplasts (&
other plastids: amyloplasts)
• Cell wall

Nucleus: Control center (brain) Cytoplasm - organelles, free proteins, ions (guts)
Cell (plasma) membrane - barrier between inside and outside (skin)

Questions for the cell • What structure controls which proteins, lipids
& RNA are produced & when? • Where do cells get Energy? Which structures
harness it? • What structures move stuff around the cell? • Where are proteins and lipids built? • How do cells move molecules in and out? • How do cells eat, drink & defend themselves?

Nucleus: Control center • Holds DNA, and
“machinery” for replicating DNA and transcribing it into proteins
• Surrounded by nuclear envelope (phospholipid bilayer)
•Nuclear pores •Chromatin •Chromosomes

• Genetic code = DNA, coiled into chromosomes
• Chromosomes? – Hypercoiled
chromatin • Chromatin?
– DNA coiled around protein

Where and what is the cytoplasm?
• Between cell membrane & nuclear membrane
• Consists of: – Cytosol: intracellular fluid (mostly H20, ions
& buffering proteins) – Organelles: structures with specific
functions; suspended in cytosol – Inclusions: Insoluble material (e.g. lipids)

Ribosomes • Organ of protein
synthesis • Made of 2 subunits; each
made of rRNA + protein • Two varieties
– Free ribosomes: produce proteins that travel to nucleus
– Fixed ribosomes: produce proteins for export to Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)

Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) • Network of membranes
connected to nuclear envelope
• 4 major functions 1. Synthesis (pro, carbs,
lipids) 2. Storage 3. Transport 4. Detoxification
• Two types 1. Smooth 2. Rough

Smooth ER (SER) • Why is it called smooth? • Responsible for the synthesis and storage of: – Phospholipids and cholesterol for
maintenance & growth of cellular membranes (ER, nucleus, Golgi apparatus (GA)) What type of molecules?
– Steroid hormones: estrogens and androgens – Triglycerides in liver and fat cells – Glycogen in skeletal muscle and liver cells
What type of molecules?

Rough ER (RER) • Workshop • Site ofprotein
synthesis (it has fixed ribosomes!!) Some chemical modification. – Polypeptide chains
migrate into cisternae, assume tertiary structure + additional modification
• Ships proteins to GA via transport vesicles

Golgi Apparatus • Packing & shipping depot • Consists of 5-6
flattened membranous disks (cisternae)
• Functions – Modifies (adds parts) &
packages secretions – Renews cell membrane – Packages special enzymes

• Produces 3 type of vesicles: 1. Secretory - exocytosis 2. Membrane renewal – replacement & remodeling 3. Lysosomes - “Primary” contain inactive digestive enzymes
Functions of GA

Lysosomes digest!

Show “Lysosomes”

Abnormal lysosomes
• Lack, or have malfunctioning enzymes – Normal cell products accumulate & stifle
(suffocate) cells • Tay-Sachs disease
– Lysosomes lack enzymes that break down lipids in nerve cells
• Pompe’s disease – Lysosomes lack hydrolytic enzyme that splits
glycogen

The endomembrane system allows membrane flow
• Phospholipid bilayer is maintained! • Nuclear envelope continuous network of SER
& RER transport vesicles Golgi Apparatus secretory vesicles cell membrane

Peroxisomes metabolize dangerous material
• Functions: – Absorb and breakdown fatty acids and
nucleic acids - produces H2O2 (danger!) – Convert free radicals to H2O2 – Coverts H2O2 to harmless H2O and O2, using catalase
• Produced by division of existing peroxisomes
• Contain digestive enzymes; produced @ free ribosomes

Concept Check
a) The ribosomes on the rough endoplasmic reticulum are analogous to a production line in a factory.
b) The golgi apparatus is analogous to the packaging and shipping department.
c) The nucleus is analogous to management offices.
d) All of the above.
The cell is sometimes described as a protein factory. Using the cell-as-factory analogy, which of the following accurately describes the functions of the endomembrane system?

Mitochondria = Powerhouse

Mitochondria harness energy! • “powerhouse” of the
cell…makes ATP • Double membrane • Number per cell
varies with metabolic activity (0% volume of RBC, 20% volume of liver cell)
• Aerobic respiration • Anaerobic resp.

Chloroplasts make food! • Photosynthetic
organisms (Autotrophs) • Sunlight + CO2 + H20 =
sugars • Stroma: tubules &
membranous disks • Grana: stacks of disks;
membranes chock full of chlorophyll, which traps solar energy

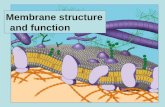
Cell Membrane = Fluid Mosaic

Structure of cell membrane • Contains lipids, proteins and
carbohydrates – Lipids
• Phospholipids; Cholesterol; Glycolipids – Proteins
• Integral; Peripheral – Carbohydrates
• Form glycocalyx (identity)

Cell Membrane Functions • Physical isolation - separates inner and
outer environments • Sensory receptor - receptor proteins
sense changes in external environment (encrusted with peripheral nerves)
• Regulates exchange with the environment - membrane channel proteins + carrier proteins
• Structural support - intercellular protein attachment