spot.pcc.eduspot.pcc.edu/anatomy/232/232 supplemental package winter... · Web viewList the major...
Transcript of spot.pcc.eduspot.pcc.edu/anatomy/232/232 supplemental package winter... · Web viewList the major...
PCC-Sylvania BI 232 Laboratory Supplement
1. Upon entering the laboratory, please locate the exits, fire extinguisher, eyewash station, and clean up materials for chemical spills. Your instructor will demonstrate the location of fire blanket, safety kit, and showers.2. Read the general laboratory directions and any objectives before coming to lab.3. Food and drink, including water, are prohibited in laboratory. This is per Federal laboratory guidelines and per College Safety Policy. Do not chew gum, use tobacco products of any kind, store food or apply cosmetics in the laboratory. No drink containers of any kind may be on the benches.4. Please keep all personal materials off the working area. Store backpacks and purses at the rear of the laboratory, not beside or under benches. Some laboratory spaces have shelving in rear for this purpose.5. For your safety, please restrain long hair, loose fitting clothing and dangling jewelry. Hair ties are available, ask your instructor. Hats and bare midriffs are not acceptable in the laboratory. Shoes, not sandals, must be worn at all times in laboratory. You may wear a laboratory apron or lab coat if you desire, but it is not required.6. We do not wish to invade your privacy, but for your safety if you are pregnant, takingimmunosuppressive drugs or who have any other medical conditions (e.g. diabetes, immunological defect) that might necessitate special precautions in the laboratory must inform the instructor immediately. If you know you have an allergy to latex or chemicals, please inform instructor.7. Decontaminate work surfaces at the beginning of every lab period using Amphyl solution.Decontaminate bench following any practical quiz, when given, and after labs involving the dissection of preserved material.8. Use safety goggles in all experiments in which solutions or chemicals are heated or when instructed to do so. Never leave heat sources unattended: hot plates or Bunsen burners.9. Wear disposable gloves when handling blood and other body fluids or when touching items or surfaces soiled with blood or other body fluids such as saliva and urine. (NOTE: cover open cuts or scrapes with a sterile bandage before donning gloves.) Wash your hands immediately after removing gloves.10. Keep all liquids away from the edge of the lab bench to avoid spills. Immediately notify your instructor of any spills. Keep test tubes in racks provided, except when necessary to transfer to water baths or hot plate. You will be advised of the proper clean-up procedures for any spill.11. Report all chemical or liquid spills and all accidents, such as cuts or burns, no matter how minor, to the instructor immediately.12. Use mechanical pipetting devices only. Mouth pipetting is prohibited.
Students who do not comply with these safety guidelineswill be excluded from the Laboratory
2
Safe Disposal of Contaminated Materials
Place disposable materials such as gloves, mouth pieces, swabs, toothpicks and paper towels that have come into contact with blood or other body fluids into a disposable Autoclave bag for decontamination by autoclaving. This bucket is not for general trash.
Place glassware contaminated with blood and other body fluids directly into a labeled bucket of 10% bleach solution. ONLY glass or plastic-ware is to be placed in this bucket, not trash.
Sharp’s container is for used lancets only. It is bright red. When using disposable lancets do not replace their covers.
1. Properly label glassware and slides, using china markers provided.2. Wear disposable gloves when handling blood and other body fluids or when touching items or surfaces soiled with blood or other body fluids such as saliva and urine. (NOTE: cover open cuts or scrapes with a sterile bandage before donning gloves.) Wash your hands immediately after removing gloves.3. Wear disposable gloves when handling or dissecting specimens fixed with formaldehyde or stored in Carosafe/Wardsafe.4. Wear disposable gloves when handling chemicals denoted as hazardous or carcinogenic by your instructor. Read labels on dropper bottles provided for an experiment, they will indicate the need for gloves or goggles, etc. Upon request, detailed written information is available on every chemical used (MSDS). Ask your instructor.5. No pen or pencil is to be used at any time on any model or bone. The bones are fragile, hard to replace and used by hundreds of students every year. To protect them and keep them in the best condition, please use pipe cleaners and probes provided instead of a writing instrument.a. Probes may be used on models as well. The bones are very difficult and costly to replace, as are the models and may take a long time to replace.6. At the end of an experiment:a. Clean glassware and place where designated. Remove china marker labels at this time.b. Return solutions & chemicals to designated area. Do not put solutions or chemicals in cupboards!7. You cannot work alone or unsupervised in the laboratory.8. Microscopes should be cleaned before returning to numbered cabinet. Be sure objectives are clean, use lens paper. Place objectives into storage position, and return to the storage cabinet. Be sure cord has been coiled and restrained. Your instructor may require microscope be checked before you put it away. Be sure it is in assigned cupboard.9. Please replace your prepared slides into the box from which they came (slides and boxes are numbered), so students using them after you will be able to find the same slide. Before placing slides in box, clean it with Kimwipes if it is dirty or covered with oil. If you break a slide, please, inform you instructor so the slide can be replaced. Please be aware that there is hundreds of dollars worth of slides in each box and handle the boxes with care when carrying to and from your workbench.10. Be sure all paper towels used in cleaning lab benches and washing hands are disposed of in trash containerprovided.
Students who do not comply with these safety guidelinesand directions will be excluded from the Laboratory
3
Please Read
You are beginning a very intense laboratory course. Before you come to class you will want to review what the study focus is for that day’s lab. This is important because you will be liable (tested) for the information listed in your study guide and manual. There are lists of terms that you are required to know, as well as tables and diagrams. These are testable as well. If there are slides listed in the study guide then you are also liable to identify these structures under the microscope on quizzes or on practicals. There will also be various models that are available in the classroom which will be used in the tests. It is up to the student to identify the structures on these models. Remember, majority of your practicals will be on these models. Please do not think that you will be able to look at the pictures in the book and do well on quizzes and practicals. YOU NEED TO SPEND TIME WITH THE MODELS!
Some labs will have exercises that are required. Please make sure that you understand what was learned in these exercises because these are also fair game to be used for questions in the tests.
Each lab will start with a 10 point quiz. You are required to be in attendance at the beginning of each lab. You will receive a zero on the quiz if you miss it. There will not be quizzes on the weeks we have a practical or the week after a practical. If you stay in lab only long enough to take the quiz and then leave soon after the lab will be counted as a missed lab.
Spelling can account for up to 10% off of your grade so please be careful. Also be aware of singular and plural usage because these mistakes will count as spelling errors.
Absences: You cannot miss more than two labs and still pass the course. Also you can only attend another instructor’s class once during the quarter. This must be approved by both instructors. If you attend another instructor’s lab without permission your quiz will be automatically thrown out.
There are review sheets at the end of each exercise that we recommend that you do. You will not receive credit for these pages but they will help you study the material and prepare for the tests.
Any material found in the lab manual can be used for the extra credit questions.
If you have any questions please contact Marilyn Thomas, Lab Coordinator ([email protected]) Thank you!
4
BI 232
Anatomy and Physiology 2
Lab 1:
Exercise 22: The Spinal Cord and Nerves and
Exercise 23: Nervous System Physiology-stimuli and Reflexes
Today’s Lab Objectives:1. Know the major regions in a cross section of the spinal cord and their functions2. Know the structure of the longitudinal aspect of the spinal cord3. Identify the nerve plexuses4. Identify the nerves listed on models5. List three things that cause a nerve to be stimulated6. Describe reflex arcs7. What is monosynaptic and polysynaptic?8. Define hyporeflexic and hyperreflexic9. Be able to identify structures on models and histology slides if available in lab.
Longitudinal Aspect of the spinal cord:
Conus medullarisTerminal filumCauda equinaCervical enlargementLumbar enlargement
Cross Section of Spinal Cord (be able identify structures on models and slides)Multipolar neuron cell bodies*gray matter
*posterior gray horns*anterior gray hornsLateral gray horns*gray commissure*Central canal
5
*White matter*Tracts (funiculi)
*Anterior column*Posterior column*Lateral columnAscending tracts Descending tracts
*Posterior median sulcus*Anterior median fissure
MeningesDura mater
Epidural spaceArachnoid mater
Subarachnoid spaceCerebrospinal fluid
Pia materDenticulate ligaments
Nerves associated with the spinal cordAnterior (ventral) root: motorPosterior (dorsal) root: sensory
Posterior (Dorsal) root ganglionSpinal nerve (mixed)
Intervertebral foramenAnterior ramus (mixed)Posterior ramus (mixed)
Nerve Structure Nerves (PNS) (be able to id on microscope)
EndoneuriumPerineuriumepineurium
Spinal Nerves and PlexusesSpinal nerves (31) mixed
8 pairs cervical nerves 12 pairs thoracic 5 pairs lumbar 5 pairs of sacral nerves1 pair coccygeal
6
PlexusesCervical
PhrenicBrachial
RadialMedianUlnarMusculocutaneousAxillary
LumbarFemoralObturator
SacralSciatic (branches into the tibial and common fibular)
Communicating rami (innervate sympathetic ganglia)Thoracic Nerves
Fundamental properties of neuronsExcitabilityConductivity
Saltatory propagation in myelinated Reflexes
Spinal reflexesCranial reflexes
Reflex arcsReceptorAfferent (sensory) neuronIntegrating center (brain or spinal cord)Efferent (motor) neuroneffector
Somatic reflexExample: ___________________________
Visceral or autonomic reflexExample: ___________________________
Polysynaptic reflex arcExample: ____________________________
Monosynaptic reflex arcExample: ____________________________
Hyporeflexic
Hyperreflexic
7
Stretch reflexesMuscle spindle
Practice patellar, triceps and biceps brachii reflexes, calcaneal reflexes on partnersAre these reflexes somatic or visceral?
Are these reflexes spinal or cranial?
Practice eye reflexesIs this reflex somatic or visceral?
Which cranial nerve is tested with this test?
Plantar response (babinski reflex)Is this reflex Spinal or cranial?
8
Lab 2
Exercise 21: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
Quiz #1: spinal cord and reflexes
Objectives1. Name the three meninges of the brain and their location relative to one another2. Locate the three major regions of the brain3. Name the main structures of each of the four regions4. Know the main function of the listed structures in the brain5. Trace the path of CSF through the brain6. Know the major blood vessels that take blood to or from the brain
Major Brain Regions
CerebrumDiencephalon
ThalamusHypothalamus
Brain Stem MidbrainPonsMedulla Oblongata
Cerebellum
MeningesDura mater
Periosteal layerMeningeal layer
Falx cerebriArachnoid mater
Subarachnoid spaceCerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Pia mater
Blood Supply to the BrainVertebral arteriesInternal carotid
9
Basilar arteryArterial circle (circle of Willis)Venous sinuses
Superior sagittal sinusInferior sagittal sinus
Internal jugular veins
Ventricles of the BrainLateral ventricles
Choroid plexusesInterventricular foramina
Third ventricleMesecephalic (cerebral) aqueduct
Fourth ventricleHydrocephalyCentral canal
Surface View of the BrainForebrain
*CerebrumGyri
Precentral gyrusPostcentral gyrus
SulciCentral sulcus
FissuresFalx cerebri
Frontal lobeCentral sulcusPrecentral gyrus (primary motor cortex)
Parietal lobePostcentral gyrus (primary somatic sensory cortex)
Occipital lobeTransverse fissure
Temporal lobesLateral fissurePrimary auditory cortexOlfactory centersGustatory centers
Cerebral HemispheresLongitudinal fissure
10
Left and right cerebral hemispheresInferior Aspect of the brain
Pituitary gland (may be removed)Optic chiasmMammillary bodiesPonsMedulla oblongata
Decussation of the pyramidsCerebellum
FoliaVermis (midline band)
Midsagittal section of the BrainCorpus callosum
Septum pellucidumDiencephalon
ThalamusHypothalamus
Pituitary glandPineal gland
MelatoninMidbrain
Cerebral pedunclesMesencephalic (cerebral) aqueductCorpora quadrigemina
Superior colliculiInferior colliculi
*CerebellumCerebellar cortexArbor vitae
Coronal Section of the Brain*Cerebral cortex
Superficial Gray matterTracts
White matterBasal nuclei (basal ganglia)
Limbic System (region)Cingulate gyrus
11
Cranial Nerves (be able to identify on models and know their specific functions)I Olfactory SensoryII Optic SensoryIII Oculomotor Motor (mainly)IV Troclear Motor (mainly)V Trigeminal BothVI Abducens Motor (mainly)VII Facial BothVIII Vestibulocochlear SensoryIX Glossopharyngeal BothX Vagus BothXI Accessory Motor (mainly)XII Hypoglossal Motor (mainly)
Be able to give both name and number
should be able to identify these on histology slides
12
Lab 3: Exercise 20Introduction to Sensory Receptors
Quiz 2: Brain and CN
Objectives:1. List the major receptor types in the body2. Define adaptation to a stimulus3. Define referred pain
Terms to understand:Punctate distributionModalityReceptors (know the modalities of each of the following)
PhotoreceptorsThermoreceptorsProprioreceptorsPain receptors (nociceptors)MechanoreceptorsBaroreceptorsChemoreceptors
Tonic receptorsPhasic receptors
Touch Receptors (Know functions)*Meissner corpusclesMerkel discs*Pacinian (lamellated) corpuscles
13
Do the following tests (Make sure that you understand the tests because may be questions on quizzes and practicals concerning your understanding of the test results)
Two-Point Discrimination TestWarm and Cool ReceptorsMap Temperature ReceptorsMap light-tough receptorsAdaptation to TouchLocating stimulus with ProprioceptionTemperature JudgmentReferred pain
Exercise 26: Eye and Vision
Objectives:1. Identify major structures listed on eye models2. Identify the six extrinsic muscles of the eye and the Cranial nerves that innervate
them3. Describe the function of the rods and cones of the eye4. Determine the near point of the eye5. Define the near point of the eye6. Demonstrate the Snellen vision tests and those for accommodation, color
blindness and astigmatism
External Features of the EyePupilIrisSclera
CorneaLateral and medial commissureExtrinsic Eye muscles (know direction eyes turn)
Lateral rectus – CN VI- (abducens)Medial rectus – CN III (oculomotor)Superior rectus –CN III (oculomotor)Inferior rectus – CN III (oculomotor)Inferior oblique – CN III (oculomotor)Superior oblique -- CN IV (trochlear)
14
Lacrimal apparatusLacrimal glandNasolacrimal ductLacrimal sac
Interior of the EyeConjunctivaAnterior cavity
Anterior chamberPosterior chamberAqueous humor (produced by ciliary body)Venous sinus (canal of Schlemm)
IrisCircular muscles of irisRadial muscles of iris
Pupil
Posterior CavityVitreous body (Vitreous humor)Tunics
*Fibrous layerScleraCornea
*Vascular layer (Uvea)ChoroidCiliary bodyIris
*Neural layerOptic Nerve (CN II)Pigmented epitheliumretina
*Photoreceptor cellsRods and cones
*bipolar cells*ganglion cells
Macula lutea (yellow spot)Fovea centralis
15
*should be able to identify these on histology slides
Lab activitiesDissection of sheep or cow eye (these can be used for testing purposes)Do the following Vision tests:
Visual tracking exerciseWhich cranial nerves are being tested?
Determine your near pointMeasurement of the distribution of rods and conesMeasure binocular visual fieldMeasurement of Visual acuity (Snellen Test)Astigmatism testOphthalmoscopePupillary reactionColor blindnessAfterimagesDetermination of the blind spot
Make sure that you understand these tests because questions may be asked on the quizzes and practicals
16
Lab 4: Exercise 25 & 27Ear, Hearing and Equilibrium and Taste and smell
Quiz 3: Vision & sensory receptors
Objectives:
1. Identify structures of the outer, middle, and inner ear2. Describe the structure of the cochlea3. Perform conduction deafness tests, such as the Rinne and Weber tests4. Compare dynamic and static equilibrium and the structures involved in their perception5. Explain how mechanical sound vibrations are translated into nerve impulses6. What are the two major chemoreceptors located in the region of the head?7. Identify a taste bud on a slide8. Know the functions of listed structures
Anatomy of the EarOuter Ear
Pinna (auricle)Helix (elastic cartilage)Earlobe Auditory canal
Middle EarTympanic membrane (border between outer and middle ear)Tympanic cavity
OssiclesMalleusIncusStapes
Auditory tube (Eustachian tube)Inner Ear
Bony labyrinth
17
PerilymphMembranous labyrinth
EndolymphCochlea (hearing)
Oval windowRound window*Scala vestibule (vestibular duct)*cochlear duct (scala media)*scala tympani (tympanic duct)*vestibular membrane*basilar membrane*tectorial membrane
VestibuleUtricleSacculeMaculae
OtolithsSemicircular Ducts (inside canals)
AmpullaCrista ampullarisCupula
Do the following tests and make sure that you understand them:
Webber TestRinne TestBing TestSound locationPostural Reflex testBarany’s Test
nystagmusRomberg Test
What cranial nerve is being tested in these tests?
Taste and Smell
Chemoreception*taste buds
Supporting cellsTaste cells
18
Taste poresGustation (taste)
Olfactory bulbs (ID on brains)Cribriform plate
*must be able to identify these structures on the microscope
Do the following tests and make sure that you understand them:
Taste Determination of solid materialsMapping the Tongue for taste receptors
Olfactory bulbs (ID on brains)
Olfactory reflex What cranial nerve causes this?
Visual cues in smell interpretationOlfactory discrimination
What cranial nerves are innervated?Adaptation to smellTaste and olfaction tests
Lab Practical I will be next week (Week 5)
The practical will cover all the material covered in the package for the last 4 weeks of lab
75 questionsModelsMicroscopesImages
Also this week:Instructors will determine 4 student volunteers who will be testing their blood glucose levels in week six!
19
Lab 6
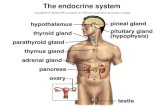
Endocrine System Exercise 28
No Quiz
Objectives: 1. List the major endocrine organs of the human body2. Name the hormones produced by these endocrine organs3. Discuss how the secretions of the endocrine glands differ from exocrine glands4. Identify endocrine organs in histological slides5. Identify endocrine glands and organs on models in lab6. Do glucometer experiment and be able to discuss the outcomes
Endocrine systemHormones
Exocrine glandsSweat, salivary, ovary, testes, pancreatic acini
Anatomy of the major endocrine organs
Pineal glandMelatoninFunction:
Hypothalamus and pituitary gland (hypophysis)infundibulum
*Anterior lobe (adenohypohysis)Intermediate lobe (part of the anterior lobe)
Melanocyte stimulating hormone
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)Function:
Growth hormone (GH)
20
Function:
Prolactin (PRL)Function:
Gonadotropins:
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)Function:
Luteinizing hormone (LH)Function:
Adrenocorticotropin (ACTH)Function:
*Posterior Lobe (neurohypophysis)
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)Function:
OxytocinFunction:
*Thyroid Gland*Follicle cells
Thyroid hormone (T3 & T4)Function:
*Colloid *Parafollicular cells
CalcitoninFunction:
*Parathyroid glands*Chief cellsParathyroid hormone (PTH)
Function:
*ThymusThymosin
Function:
21
*PancreasPancreatic islets
Glucagon (alpha cells)Function:
Insulin (beta cells)Function:
Delta cellsFunction:
*Adrenal Glands*Zona glomerulosa
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone)Function:
*Zona fasciculataGlucocorticoids (cortisol)
Function:
*Zona reticularisSex hormones (androgens and estrogens)
Function:
Glucocorticoids
*Adrenal MedullaEpinephrine and norepinephrine
Function:
Gonads
*TestesTestosterone
Function:
InhibinFunction:
*seminiferous tubules*interstitial cells
22
Nurse cellsSperm
*OvariesEstrogen
Function:
ProgesteroneFunction:
*Oocyte*Follicle*stroma
Detection of hormones:Was Luteinizing hormone (LH) detected on samples? _____________________What does a raised level of LH represent on a sample? _______________________
Make sure that you understand the results of the Glucometer exercise.
23
Lab 7
Exercise 29 & 30: Blood & Blood tests and typing
Quiz 4: Endocrine system
Lab Objectives:1. Distinguish among the various formed elements of blood and their functions2. Know the major components of plasma3. Determine the percent of each type of leukocyte in a differential white cell count4. Know the significance of an elevated level of a particular WBC and what it may indicate about a
disease state or an allergic reaction5. Determine the antigens present in a particular ABO blood type6. Know the antibodies present in a particular ABO blood type7. Relate Rh-positive or Rh-negative blood to antigens present8. Correlate hematocrit with erythrocyte counts9. Know the universal donor and universal receiver and why
BloodPlasmaBlood cells
*ErythrocytesHemoglobin
*Platelets (thrombocytes)Megakaryocytes
LeukocytesGranular leukocytes
*Neutrophils*Eosinophils*Basophils
Agranular leukocytes*Lymphocytes
B cellsPlasma cellsAntibodies
T cellsCell-mediated immunityNatural killer (NK) cells
24
*MonocytesMacrophage
Differential Leukocyte Count
Determine differential leukocyte count and compare your cell count with normal valuesNeutrophils (60-70%)
% in your sample _________________________Cause for increase ____________________________________________
Eosinophils (2-4%)% in your sample _________________________Cause for increase _______________________________________________
Basophils (0.5-1%)% in your sample _________________________Cause for increase ______________________________________________
Lymphocytes (25-33%)% in your sample _________________________Cause for increase ______________________________________________
Monocytes (3-8%)% in your sample __________________________Cause for increase ______________________________________________
LeukopeniaLeukemia
Blood TypingAntigens (agglutinogens)
Type AType BType ABType O
Antibodies (agglutinins)Transfusion reactions
Rh factorRh-positiveRh-negative
Hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)What is your blood type? _______________________________
25
Hemoglobin concentration
What was your hemoglobin concentration? _______________
Is this within normal range? _________________
HematocritPolycythemiaAnemia
Genetics of ABO blood types:
There are 4 blood group phenotypes that occur in the ABO system:
Phenotype GenotypeO OOA AA, AOB BB, BOAB AB
A Punnett Square can be used to help determine potential children. Place one parent’s blood type across the top and the other parent’s downward, then fill out the combinations.
Fill out the following Punnet squares:
1. Parents: dad is AB & mom is AO
2. Parents: dad is BO & mom is AO
26
3. Which blood type is the universal donor? Why?
4. Which blood type is considered the universal recipient?
5. Could two parents have a child with Type O blood and a child with Type A blood?
6. Could two parents have a child with Type O blood and a child with Type AB blood?
7. What parental genetics are needed to yield a child with Type O blood?
27
Lab 8
Exercise 27: Structure of the Heart and
Exercise 32: Electrical conductivity of the Heart
Quiz 5: Blood
Objectives1. Identify the three layers of the heart wall2. Find and name the anatomical features on models of the heart and in the sheep heart3. Describe the blood flow through the heart and the function of the internal parts of the
heart4. Know the functioning of the atrioventricular valves and the semilunar valves and their
role in circulating blood through the heart5. Be able to read an electrocardiogram (waves and intervals)6. Distinguish between systole and diastole7. Associate the P wave, QRS complex and T wave of an ECG with electrical events that
occur in the heart
Heart Wall
MediastinumFibrous pericardium
Parietal pericardiumPericardial cavity
Serous fluidSerous pericardium (epicardium)
*MyocardiumEndocardium
Endothelium
OverviewRight atriumRight ventricleLeft atriumLeft ventricle
Exterior of the HeartApexBase
AortaPulmonary trunk
Interventricular sulcus (groove)
28
Anterior interventricular sulcusAnterior interventricular arteryGreat cardiac vein
Posterior interventricular sulcusPosterior interventricular arteryMiddle cardiac vein
AuriclesAtrioventricular sulcus (groove) (coronary sulcus)
Right coronary arteryLeft coronary arteryCircumflex arteryGreat cardiac veinCoronary sinus
Major vesselsPulmonary arteries
Ligamentum arteriosumAscending aortaPulmonary veinsSuperior vena cavaInferior vena cavaAorta (ascending, arch, descending)
Interior of the HeartInterventricular septumInteratrial septum
Fossa ovalisForamen ovale
Pectinate musclesRight atrioventricular valve (tricuspid valve)
Chordae tendineaePapillary musclesTrabeculae carneae
Pulmonary semilunar valveLeft atrioventricular valve (Bicuspid valve or mitral valve)
Also has chordae tentineae and papillary musclesAortic semilunar valve
29
Electrical Conductivity of the Heart
TerminologySystole
Atrial systoleVentricular systole
DiastoleAtrial diastoleVentricular diastole
Sinoatrial (SA) nodePacemaker
Atrioventricular (AV) nodeAtrioventricular bundle (bundle of His)Right and left bundle branchesPurkinje (conduction) fibers
Electrocardiograph (ECG)Electrocardiogram (ECG, or EKG)
P waveQRS complexT wave
Analysis of the ECGIrregularities in Heart Rate
TachycardiaBradycardia
PR Intervals (normally about 0.16 second)Heart blocks
QRS complex (normally about 0.08-0.10 second)Right or left bundle branch block
QT interval (normally 0.30 second)Cardiac Arrhythmias
30
Lab 9
Exercise 34: Introduction to Blood Vessels and Arteries of the Upper BodyExercise 35: Arteries of the Lower BodyExercise 36: Veins and Special CirculationsExercise 38: Blood Vessels and Blood Pressure
Quiz 6: Heart structure and Conductivity of the heart
Lab Objectives:
1. Be able to identify layers of blood vessels on microscopes and models2. Be able to distinguish between arteries, veins and capillaries3. Identify the arteries and veins listed on models in the lab4. Distinguish the systemic circulation from the pulmonary circulation5. Describe the major digestive organs and vessels that supply blood to the hepatic portal vein6. Describe the pathway of fetal circulation and discuss how it varies from the adult circulation
General Circulatory PatternsPulmonary circulation
Pulmonary trunkRight and left pulmonary arteriesPulmonary veinsLeft atrium
Systemic circulation
Cross Sections of Arteries and Veins*Tunica externa (tunica adventitia)
Vaso vasorum*Tunica media
Smooth muscle (thicker in arteries)Elastic fibers (large arteries)
*Tunica interna (tunica intima)Endothelium (simple squamous epithelium)Inner elastic lamina (in arteries)
*Valves (only found in veins)
Know the difference between arteries and veins
31
Aortic Arch ArteriesBrachiocephalic trunk
Right common carotidRight subclavian artery
Left common carotidLeft subclavian
Descending aortaThoracic aorta
Intercostal arteriesAbdominal aorta
Arteries that feed the upper extremitiesAxillary
Brachial arteryRadial
Palmar arch arteriesDigital arteries
UlnarPalmar arch arteries
Digital arteriesArteries of the Head and Neck
Vertebral arteriesBasilarCircle of Willis
Common carotid arteriesExternal carotid (face)
FacialTemporalMaxillaryOccipital
Internal carotid (brain)Abdominal arteries
Abdominal aortaCeliac artery (celiac trunk)Splenic arteryLeft gastric arteryCommon hepatic arterySuperior mesenteric arteryRenal arteriesGonadal arteriesInferior mesenteric
Common iliac arteriesExternal iliac arteries
Femoral arteryPosterior and anterior tibial arteriesFibular (peroneal artery)
Tibial and fibular arteries anastomose in the foot and supply blood to
32
Plantar arteriesDorsal pedal arteryDigital arteries
Internal iliac arteriesPelvic region
Veins of the Upper ExtremitiesDigital veinsPalmar arch veinsMajor superficial veins
Basilica veinCephalic vein
Median cubital veinDeep veins of the forearm
Radial veinUlnar veinBrachial veinsBasilic veinAxillaryCephalic
SubclavianBrachiocephalic veins (union of internal jugular and subclavian veins)Superior vena cava
Veins of the Head and NeckInternal Jugular veinExternal jugular veinVertebral vein
Veins of the Lower extremitiesPlantar venous archDorsal venous archAnterior tibial veinGreat saphenous veinSmall saphenous veinPosterior tibial veinPopliteal veinFemoral veinFemoral veinDeep femoral veinExternal iliac vein
Veins of the Abdomen and PelvisInternal iliac veinCommon iliac veinInferior vena cava
Abdominal veins that take blood directly to the inferior vena cavaRenal veinsSyorarebak veubsGonadal veins
Hepatic Portal CirculationInferior mesenteric vein
33
Splenic veinGastroepiploic vein
Superior mesenteric veinHepatic portal veinLiverHepatic vein
Thoracic VeinsIntercostal veinsAzygos veinHemiazygos vein
Fetal CirculationPlacentaUmbilical vein
Umbilical cordDuctus venosus
Inferior vena cava to right atriumForamen ovalePulmonary trunkDuctus arteriosusAortic arch (bypassing the lungs)Systemic arteriesInternal iliac arteriesUmbilical arteriesFossa ovalis
Be able to identify on histology slides
Lab 10 – Practical #2The practical will cover all the material discussed in the last 4 weeks of lab
75 questions Models Microscopes images Timed stations Any materials found in this guide can be on the practical
34








































![Team : Alfa Faridh Suni [232 07 052] Alvani Wiwoho [232 07 163] Harold Harriman [232 07 088] Uray Lunar Meiviar [232 07 164]](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/56649c7b5503460f9492ee5a/team-alfa-faridh-suni-232-07-052-alvani-wiwoho-232-07-163-harold-harriman.jpg)