Sporogenesis and gametogenesis
Transcript of Sporogenesis and gametogenesis

SPOROGENESIS AND GAMETOGENESIS
Prepared by: Md khaja moinuddin s MSc Agri (genetics and plant breeding)


SPOROGENESIS• Production of microspores and megaspores is known as
sporogenesis. Microspores are produced in anthers(microsporogensis), while megaspores are produced are ovules (megasporogenesis).

MICROSPOROGENESIS• Each anther has four pollen sacs,which contain numerous POLLEN MOTHER
CELLS (PMC).each PMC undergoes meiosis to produce 4 haploid cells or microspores; this is known as microsporogenesis. The microspores mature into pollen grains mainly by thickening of their walls.

MEGASPOROGENESIS• Megasporogenesis occurs in ovules, which are present inside the
ovary. A single cell in each ovule differentiates into MEGASPORE MOTHER CELL, which undergo meiosis to produce 4 haploid megaspores. Three of the megaspores degenerate leaving one functional megaspore per ovule.

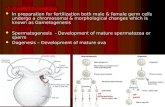
GAMETOGENESIS• The production of male and female gametes in microspores and the
megaspores,respectively, is known as gametogenesis.

MICROGAMETOGENESIS• This refers to the production of male gametes or sprems. During
maturation of pollen, the microspore nucleus divides mitotically to produce GENERATIVE and VEGETATIVE or TUBE NUCLEUS. Pollen is generally released in binucleate stage. When pollen lands onto stigma of a flower,it is known as pollination. Shortly after pollination, the pollen germinates, and pollen tube enters the stigma and grows through the style. The generative nucleus now undergoes a mitotic division to produce two MALE GAMETES or SPERMS. The pollen, along with the pollen tube, is known as microgametophyte. The pollen tube finally enters the ovule through a small pore,MICROPYLE, and discharge the sperms into the embryo sac.

MICROGAMETOGENESIS

MEGAGAMETOGENESIS• The nucleus of a functional megaspore dividews mitotically to produce
four or more nuclei. In most of the crop plants, megaspore nucleus undergoes three mitotic divisions to produce eight nuclei. Three of these nuclei move to one pole and produce a central EGG CELL and two SYNERGID CELLS situated on either side of the egg cell. Another three nuclei migrate to the opposite pole to give rise to ANTIPODAL CELLS, the two nuclei remaining in the centre, the POLAR NUCLEI, fuse to form a SECONDARY NUCLEUS. The megaspore thus develops into a mature MEGAGAMETOPHYTE or EMBRYO SAC. The development of an embryo sac from a megasporeis known as MEGAGAMETOGENESIS. An embryo sac generally contains one egg cell, two synergids, three antipodal cells(all haploid), and diploid secondary nucleus.

MEGAGAMETOGENESIS

FERTILIZATION• The fusion of one of the two sperms with the egg cell, producing a
diploid zygote, is known as fertilization. The fusion of the remaining sperm with the secondary nucleus,leading to the formation of a triploid primary endosperm nucleus, is termes as triple fusion. The zygote divides mitotically to produce a diploid embryo. The primary endosperm nucleus produces endosperm through repeated mitotic divisions. During seed development , endosperm providesnutrition to the developing embryo. The endosperm may become absorbed completely, e.g.,in legumes, or it may form the major portion of seeds, e.g.,in monocots like maize,wheat, etc., and some dicots, e.g.castor, Brassica spp.,etc.







![Gametogenesis [Frog] - nepeducation](https://static.fdocuments.in/doc/165x107/61d5d4f7008d0e67e9698b62/gametogenesis-frog-nepeducation.jpg)










