spindle assembly checkpoint
-
Upload
mohammadhassanj -
Category
Documents
-
view
133 -
download
8
description
Transcript of spindle assembly checkpoint
Slide 1
Spindle assembly checkpoint with emphasis on role of Mad2 Mohammad.H.jafari1What we are followingIntroduction (Metaphase anaphase transition)
What s the spindle assembly checkpoint(SAC)?
When does the spindle assembly checkpoint can be active?
Whats its mechanism (MCC production)?
How does the SAC effector(MCC) inhibit the APC/C?
How does the cell can turn off the SAC on time?
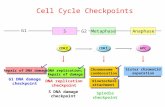
2Metaphase-anaphase transtionMitotic progression is controlled by the (APC/C+ cdc20)
Anaphase onset and mitotic exit by targeting two key proteins (securincyclinB)
Alberts, B., et al. (2015). Molecular biology of the cell. New York: Garland Science.
33Lara-Gonzalez, P., Westhorpe, F. G., & Taylor, S. S. (2012). The spindle assembly checkpoint. Current Biology, 22(22), R966-R980.
124Whats the SACCheckpoints are signaling pathways that detect cellular defects, stop cell-cycle progression, or initiate specic repair pathways
The spindle (assembly) checkpoint(the wait anaphase checkpoint, or the mitotic checkpoint) is a key regulator of chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis. Its function is to prevent precocious anaphase onset before chromosomes have achieved amphitelic attachment (bi-oriented) to the spindle
5SAC discovery
Artificial tentionDestroy kinetochoreLara-Gonzalez, P., Westhorpe, F. G., & Taylor, S. S. (2012). The spindle assembly checkpoint. Current Biology, 22(22), R966-R980.6Two central mechanisms ensure the formation of bi-oriented attachments
1- attachment OR microtubule binding
2- tension
3- Mitotic timer (NPC)
1 and 2 =kinetochore scaffold
3= NPC scaffold
When does the spindle assembly checkpoint can be activated?SAC triggers
AttachmentTension
77 Attachment-tension challengeWhen does the spindle assembly checkpoint can be activated?
8Whats its mechanism? (major components)
docking sitehubKinetochore and its proteins9Bub1,BubR1,Bub3,Mad1,and Mad2form three constitutive binary complexes: Bub1Bub3, BubR1Bub3, and Mad1Mad2Activates by conformation or enzymatic way and then collaborate in APC/C inhibitionRecruit to kinetochores during mitosis is in a KMN-dependent manner and a hierarchical method RZZ complex(RodZwilchZw10) in metazoans regulates Mad1 localization and a SAC silencer roleWhats its mechanism? (major components)Downstream spindle checkpoint proteins10Aurora B=destabilizing incorrect kinetochoremicrotubule attachments under certain conditions, such as a lack of tensionMPS1 =activates the checkpoint through recruitment of the checkpoint proteins BUB1,BUB3,MAD1,MAD2BUB1= phosphorylates histone H2A, which indirectly leads to Aurora B localization therefore has an indirect role
Whats its mechanism? (major components)
Checkpoint kinases11Whats its mechanism? (major components)MCC-A major checkpoint inhibitor of APC/C Is the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC), consisting of (BubR1Bub3)+ (Cdc20-C-Mad2).*Although Bub3:BubR1:Cdc20 and Cdc20-C-Mad2 alone are a potent inhibitor of APC
MCC Sequesters the mitotic APC/C activator Cdc20
1212P31comet by binding to Mad2 or cdc20 ubiquitination(MCC disassembly)
RZZ-spindly by dynein localization
PP1 is a phosphatase
Microtubule by displacement instead of Mad1
MPS1
Cdk1
Whats its mechanism? (major components)suppressor13Kinetochore scaffoldWhats its mechanism? (MCC production)
template model(prion-like template) related to c-mad2 making from o-mad2.14Conceptual Similarities betweenPrions and Mad2
15Mad2Mad2 has two topologically(o-mad2) and functionally(c-mad2) distinct native folds in equilibrium at physiological conditions and are diffrence in positioning of the 50 residue C-terminal segment (saftey belt)
Safety belt can be re-positioned around a binding partner
In the closed conformation, the safety belt wraps around the bound ligand and interacts with a different region of Mad2
Mad2 uses the same site to bind either Mad1 or Cdc20 and, thus, can only bind one of the two proteins at a time
16
17
scaffold NPCNPC-localized MAD1MAD2 assists the kinetochore based mechanisms Facilitating MCC production before mitotic entry , and by allowing more time for chromosomes to bi-orient (mitotic timer)
Whats its mechanism? (MCC production)18
MCC=Competitive inhibitor of substrate binding to APC/C or Anchors Cdc20 away from Apc10MCF2(unknown)Cdc20:C-Mad2, Bub3:BubR1:Cdc20
How does the SAC effector(MCC) inhibit the APC/C?
19How does the cell can turn off the SAC on time?
MCC production2020MCC disassemblyHow does the cell can turn off the SAC on time?
21The graded checkpoint response
22systems biology (why?)CCAN protein is 40 and connections between them are not visible through microscope techniques Theoretical analysis methods face with explosion of the amount of intermediate complexes and protein assembly statesThere are Various feedback loops
23Mad2-activation and its function in sequestering Cdc20 (module I)Autocatalytic amplication of Cdc20:C-Mad2 formation(module II)MCC formation (module III)APC inhibition (module IV-VI)
systems biology (How?)24
25ReferencesIbrahim, B. (2015). Toward a systems-level view of mitotic checkpoints. Progress in biophysics and molecular biology.
Jia, L., Kim, S., & Yu, H. (2013). Tracking spindle checkpoint signals from kinetochores to APC/C. Trends in biochemical sciences, 38(6), 302-311.
Lara-Gonzalez, P., Westhorpe, F. G., & Taylor, S. S. (2012). The spindle assembly checkpoint. Current Biology, 22(22), R966-R980.
London, N., & Biggins, S. (2014). Signalling dynamics in the spindle checkpoint response. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 15(11), 736-748.
Luo, X., & Yu, H. (2008). Protein metamorphosis: the two-state behavior of Mad2. Structure, 16(11), 1616-1625.
Pinsky, B. A., & Biggins, S. (2005). The spindle checkpoint: tension versus attachment. Trends in cell biology, 15(9), 486-493
2627Questions?Thank you for your attention