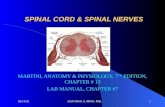
Spinal Cord
-
Upload
rabiatul-adawiyah-binti-mdyusof -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
770 -
download
5
description
Transcript of Spinal Cord

SPINAL CORD

INTRODUCTION Structure Function Tracts

STRUCTURE OF SPINAL CORDLong :- Men=45cm(18inch) Women=43cm(17inch)Width :- Cervical and lumbar = 1/2inch thick Thoracic area = 1/4inch thick Begins from occipital bone until L1&L2 the end of spinal cord = filum terminal




LAYERS OF SPINAL CORD Meninges
Epidural = External of dura(fat-fil) Subdural space = Serous fluid Subarachnoid = Between pia and arachnoid (CSF
filled)
Dura mater (dural sheath)=outermost
Arachnoid’s mater = thin,movable
Pia mater=forms filum terminal,denticulate ligament
Connective tissue
membranes
Subdural space
Subarachnoid
Epidural


Spinal segment = spinal nerve Spinal nerve has two roots Dorsal root ganglion = swelling like structure
Anterior root= ventral root
Posterior root=dorsal root
SPINAL NERVE



Spinal cord have 31 segment 8 Cervical 12 Thoracic 5 Lumbar 5 Sacral 1 Coccygeal
The spinal segments that contribute to the nerve of the upper are enlargement to the form cervical and lumbar enlargements

VERTEBRAE AND CORRESPONDING SPINAL SEGMENT RELATIONSHIP vertebrae spinal segments
C1 to C4 (upper cervical) same
C4 To C7 (lower cervical) +1
T1 to T7 +2
T7 to T9 +3
T10 L1,L2
T11 L3,L4
T12 L5,S1
L1 sacral and coccygeal nerve







ARTERIAL SUPPLY Spinal Arteries :- Anterior (1) & Posterior (2) Spinal Artery from
Vertebral artery Radicular Arteries :- Segmental arteries from Vertebral,Ascending
Cervical,Intercostal and Lumbar Artery Venous Drainage veins :- Longitudinal & Radicular Veins
Intervertebral veins Internal Vertebral Venous Plexus external vertebral venous plexus segmental veins

INTRODUCTION OF SPINAL TRACT Tract is a bundle of nerve fibers (within
CNS) having the same :- Origin Course Destination Function


The name of the tract = origin = destination
The axons within each tract are grouped according to the body region innervated
Long tracts at white matter Short tracts at gray matter There are 2 types of tract :- Ascending tract=Sensory Descending tract=Motor


CROSS OVER Decussation is the cross-over of the
tract from one side to the other. Therefore,there are instances where the
left side of the body is controlled by the right brain hemisphere.
Decussation occurs at different locations for each tracts.


ASCENDING TRACT



Ascending Spinal Tracts

SENSORY PATHWAYS Contain a sequence of 3 neurons
from the receptor to the cerebral cortex
1st order neuron: Sensory neuron that delivers
information from the receptor to the CNS.
2nd order: Has cell body in the spinal cord
or medulla oblongata Axon decussate
3rd order neuron: Has cell body in thalamus Axon terminates on cerebral
cortex ipsilaterally
1
2
3

Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation Conscious
Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings
Ist Neuron: Dorsal Root Ganglion (Spinal Ganglion) Dorsal Column Nuclei (Nucleus Gracilis Thalamus (VPLc) ,Corona Radiata
Termination: Primary Somesthetic Area (S I)
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway

LATERAL SPINOTHALAMIC TRACT
Modality:pain and thermal sensations.
Ist Neuron : dorsal horn 2nd Neuron: mostly in the
nucleus proprius), decussate within one segment by passing through the ventral white commissure
3rd Neuron: ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus
Thalamic neurons project to the somatosensory cortex

ANTERIOR SPINOTHALAMIC TRACT
Modality:non- discriminative touch and pressure
Ist Neuron : dorsal horn 2nd Neuron: nucleus
proprius,crossing to opposite side by passing through the ventral white commissure
3rd Neuron: in ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus
Thalamic neurons project to the somatosensory cortex

VENTRAL SPINOCEREBELLAR TRACTS
Ist Neuron neuron lie in base of the dorsal horn of the lumbosacral segments
cross to opposite side, ascend as far as the midbrain
2nd Neuron: terminating in the cerebellar cortex
Both spinocerebellar tracts convey sensory information to the same side of the cerebellum

POSTERIOR SPINOCEREBELLAR TRACTS
Info:Present only above level L3
Ist Neuron in Clark’s column
2nd Neuron: terminate ipsilaterally in the cerebellar cortex

DESCENDING TRACT
*PYRAMIDAL*EXTRAPYRAMIDAL

MOTOR PATHWAYS 2 Sequence of neuron(from cerebral
cortex/brain stem – muscle) Upper Motor Neuron(UMN)
o Spinal cord -> braino Cell body cross over before terminate on
lower motor neuron Lower Motor Neuron(LMN)
o Spinal cord -> muscle o Cell body pass through posterior root of
spinal nerve

DESCENDINIG TRACT
PYRAMIDAL TRACT(DIRECT)
ANTERIOR CORTICOSPINAL
TRACT
LATERAL CORTICOSPINAL
TRACT
EXTRAPYRAMIDAL TRACT
(INDIRECT)
RETICULOSPINAL
TRACT
VESTIBULOSPINALTRACT
TECTOSPINALTRACT
RUBROSPINALTRACT

PYRAMIDAL TRACT
(DIRECT PATHWAY)

CORTICOSPINAL TRACTFunction:voluntary movement
: fine skill movement Anterior corticospinal tract
o Origin:motor cortex (4,6)
:somatosensory cortex (1,2,3)o Course:pass through midbrain(cerebral peduncle) pyramid of medulla oblongatao Termination: anterior white column

Lateral corticospinal tracto Origin: motor cortex (4,6)
:somatosensory cortex (1,2,3)o Course: pass through midbrain(cerebral peduncle)
(cross over)
pyramid of medulla oblongata
o Termination: lateral white columno Corticobulbar innervate cranial nerves motor nuclei of CNS




EXTRAPYRAMIDAL TRACT(INDIRECT PATHWAY)

RETICULOSPINAL TRACT Function: coordination of voluntary and reflex movement
: control of muscle tone : control of respiration and diameter of blood vessel Origin: Reticular formation (pontine & medulla) Course :pass through medial pontine lateral medulla Termination: ventral funniculus


TECTOSPINAL TRACT Function: coordination of head and neck
to the visual & audio stimuli Origin : superior colliculus Course : pass through periaquductal (cross)
Dorsal tegmental
Termination: Anterior median fissure
(cervical area)


RUBROSPINAL TRACT Function : controls flexor muscle tone Origin : Red nucleus Course :cross to (lower cervical segment) Termination: lateral white column

VESTIBULOSPINAL TRACT Lateral vestibulospinal tract Function: control extensor muscle tone : antigravity maintenance of posture Origin : lateral vestibular (Derter’s) nucleus Termination :ventral funniculus

• Medial vestibulospinal tractFunction: control movement of head :maintain equilibrium Origin:medial vestibular nucleusTermination: ventral funniculus + medial funniculus