Soft connective pain'
-
Upload
ganesamurthi-rathinam -
Category
Education
-
view
317 -
download
0
Transcript of Soft connective pain'
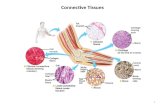
INTRODUCTION
derived largely from embryonic mesoderm
composed of cells,fibres and amorphous substance
(intercellur substance secreted by cells
Connective tissue fibers, which are made of protein, are of three kinds:
collagenous fibers
elastics fibers
reticular fiber
Connective tissue pain
Introduction
Connective tissue pain :
Pain due to inflammation of the connective tissue of the body..
Soft connective pain – more constant then muscle pain
Follow inflammatory time frame
Pain – pulsatile quality
in intensity
Cellulitis is a example of Connective tissue pain
An acute, diffuse, and suppurative inflammation of loose connective tissue, particularly the deep subcutaneous tissues, and sometimes muscle, which is most commonly seen as a result of infection of a wound, ulcer, or other skin lesions.
Purulent inflammatory conditions
Deeper soft tissue
Intensity of pain depends acute , spreading, distensions of tissue
Confinement inflammatory exudate
Differential diagnosis
Muscle pain
Vascular pain
Glandular pain
Other condition
1. cysts
2. tumor
both begin and malignant
Physical therapy
deep heat therapy diathermy is used for this deep heat therapy
When heat is not helpful ice can be tried
Deep massage can be used
Ultrasound