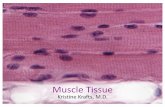
Smooth Muscle
description
Transcript of Smooth Muscle

Smooth MuscleSmooth Muscle CharacteristicsCharacteristics
Not striatedNot striated Dense bodies instead Dense bodies instead
of Z disks as in skeletal of Z disks as in skeletal musclemuscle
Have noncontractile Have noncontractile intermediate filamentsintermediate filaments
CaCa2+2+ required to required to initiate contractionsinitiate contractions
TypesTypes Visceral or unitaryVisceral or unitary
Function as a unitFunction as a unit MultiunitMultiunit
Cells or groups of Cells or groups of cells act as cells act as independent unitsindependent units


Smooth Muscle Smooth Muscle ContractionContraction

Electrical Properties of Electrical Properties of Smooth MuscleSmooth Muscle

Functional Properties Functional Properties of Smooth Muscleof Smooth Muscle
Some visceral muscle exhibits Some visceral muscle exhibits autorhythmic contractionsautorhythmic contractions
Tends to Tends to contract in responsecontract in response to to sudden stretch but no to slow sudden stretch but no to slow increase in lengthincrease in length
Exhibits Exhibits relatively constantrelatively constant tension: tension: Smooth muscle toneSmooth muscle tone
Amplitude of contractionAmplitude of contraction remains remains constant although muscle length constant although muscle length variesvaries

Smooth Muscle Smooth Muscle RegulationRegulation
Innervated Innervated by autonomic nervous by autonomic nervous systemsystem
NeurotransmitterNeurotransmitter are acetylcholine are acetylcholine and norepinephrineand norepinephrine
Hormones important as Hormones important as epinephrine epinephrine and oxytocinand oxytocin
ReceptorsReceptors present on plasma present on plasma membrane which neurotransmitters or membrane which neurotransmitters or hormones hormones bindbind determines determines responseresponse



Cardiac MuscleCardiac Muscle
Found only in Found only in heartheart StriatedStriated Each cell usually has Each cell usually has one nucleusone nucleus Has intercalated disks and gap junctionsHas intercalated disks and gap junctions AutorhythmicAutorhythmic cells cells Action potentials of longer duration and Action potentials of longer duration and
longer refractory periodlonger refractory period CaCa2+2+ regulates contraction regulates contraction

Cardiac MuscleCardiac Muscle
Elongated, branching cells containing 1-2 centrally located nucleiElongated, branching cells containing 1-2 centrally located nuclei Contains actin and myosin myofilaments Contains actin and myosin myofilaments Intercalated disksIntercalated disks: Specialized cell-cell contacts: Specialized cell-cell contacts Desmosomes hold cells together and gap junctions allow action Desmosomes hold cells together and gap junctions allow action
potentialspotentials Electrically, cardiac muscle behaves as single unitElectrically, cardiac muscle behaves as single unit


Cardiac myocyte action Cardiac myocyte action potential:potential:

Refractory PeriodRefractory Period
AbsoluteAbsolute: Cardiac muscle cell : Cardiac muscle cell completely insensitive to further completely insensitive to further stimulationstimulation
RelativeRelative: Cell exhibits reduced : Cell exhibits reduced sensitivity to additional stimulationsensitivity to additional stimulation
Long refractory period prevents Long refractory period prevents tetanic contractionstetanic contractions

AP-contraction AP-contraction relationship:relationship:
AP in skeletal muscle is AP in skeletal muscle is very short-livedvery short-lived AP is basically over before AP is basically over before
an increase in muscle an increase in muscle tension can be measured.tension can be measured.
AP in cardiac muscle is AP in cardiac muscle is very long-livedvery long-lived AP has an extra AP has an extra
component, which extends component, which extends the duration.the duration.
The contraction is almost The contraction is almost over before the action over before the action potential has finished.potential has finished.

Functions of the HeartFunctions of the Heart Generating Generating bloodblood pressure pressure Routing Routing bloodblood
Heart separates pulmonary and Heart separates pulmonary and systemic circulationssystemic circulations
Ensuring one-way Ensuring one-way bloodblood flow flow Heart valves ensure one-way flowHeart valves ensure one-way flow
Regulating Regulating bloodblood supply supply Changes in contraction rate and Changes in contraction rate and
force match blood delivery to force match blood delivery to changing metabolic needschanging metabolic needs


Orientation of cardiac Orientation of cardiac muscle fibres:muscle fibres:
Unlike skeletal Unlike skeletal muscles, cardiac muscles, cardiac muscles have to muscles have to contract in more than contract in more than one direction.one direction.
Cardiac muscle cells Cardiac muscle cells are striated, meaning are striated, meaning they will only contract they will only contract along their long axis.along their long axis.
In order to get In order to get contraction in two contraction in two axis, the fibres wrap axis, the fibres wrap around.around.

Circulation circuits:Circulation circuits:



Heart WallHeart Wall
Three layers of tissueThree layers of tissue EpicardiumEpicardium: This serous membrane : This serous membrane
of smooth outer surface of heartof smooth outer surface of heart MyocardiumMyocardium: Middle layer composed : Middle layer composed
of cardiac muscle cell and of cardiac muscle cell and responsibility for heart contractingresponsibility for heart contracting
EndocardiumEndocardium: Smooth inner surface : Smooth inner surface of heart chambersof heart chambers





Valve function:Valve function:


Coronary circulation:Coronary circulation:

Pacemaker potential:Pacemaker potential:

Cardiac conducting Cardiac conducting system:system:



EKG:EKG:

Heart SoundsHeart Sounds
First heart sound or “lubb”First heart sound or “lubb” Atrioventricular valves and surrounding fluid Atrioventricular valves and surrounding fluid
vibrations as valves close at beginning of vibrations as valves close at beginning of ventricular systoleventricular systole
Second heart sound or “dupp”Second heart sound or “dupp” Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary Results from closure of aortic and pulmonary
semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular semilunar valves at beginning of ventricular diastole, lasts longerdiastole, lasts longer
Third heart sound Third heart sound (occasional)(occasional) Caused by turbulent blood flow into ventricles and Caused by turbulent blood flow into ventricles and
detected near end of first one-third of diastoledetected near end of first one-third of diastole

Heart sounds:Heart sounds:

Cardiac ArrhythmiasCardiac Arrhythmias
TachycardiaTachycardia: Heart rate in excess of : Heart rate in excess of 100bpm100bpm
BradycardiaBradycardia: Heart rate less than 60 : Heart rate less than 60 bpmbpm
Sinus arrhythmiaSinus arrhythmia: Heart rate varies 5% : Heart rate varies 5% during respiratory cycle and up to 30% during respiratory cycle and up to 30% during deep respirationduring deep respiration
Premature atrial contractionsPremature atrial contractions: : Occasional shortened intervals between Occasional shortened intervals between one contraction and succeeding, one contraction and succeeding, frequently occurs in healthy peoplefrequently occurs in healthy people

Mean Arterial Pressure Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)(MAP)
Average blood pressure in aortaAverage blood pressure in aorta MAP=CO x PRMAP=CO x PR
CO is amount of blood pumped by heart CO is amount of blood pumped by heart per minuteper minute CO=SV x HRCO=SV x HR
SVSV: Stroke volume of blood pumped during each : Stroke volume of blood pumped during each heart beatheart beat
HRHR: Heart rate or number of times heart beats per : Heart rate or number of times heart beats per minuteminute
Cardiac reserve: Difference between CO at Cardiac reserve: Difference between CO at rest and maximum COrest and maximum CO
PR is total resistance against which PR is total resistance against which blood must be pumpedblood must be pumped

Pressure relationships:Pressure relationships:

Cardiac CycleCardiac Cycle
Heart is two pumps that work Heart is two pumps that work together, right and left halftogether, right and left half
Repetitive contraction (Repetitive contraction (systolesystole) and ) and relaxation (relaxation (diastolediastole) of heart chambers) of heart chambers
Blood moves through circulatory Blood moves through circulatory system from areas of higher to lower system from areas of higher to lower pressure.pressure. Contraction of heart produces the Contraction of heart produces the
pressurepressure


Factors Affecting MAPFactors Affecting MAP

Regulation of the HeartRegulation of the Heart Intrinsic regulationIntrinsic regulation: Results from : Results from
normal functional characteristics, not normal functional characteristics, not on neural or hormonal regulationon neural or hormonal regulation Starling’s law of the heartStarling’s law of the heart
Extrinsic regulationExtrinsic regulation: Involves neural : Involves neural and hormonal controland hormonal control Parasympathetic stimulationParasympathetic stimulation
Supplied by vagus nerve, decreases heart rate, Supplied by vagus nerve, decreases heart rate, acetylcholine secretedacetylcholine secreted
Sympathetic stimulationSympathetic stimulation Supplied by cardiac nerves, increases heart rate Supplied by cardiac nerves, increases heart rate
and force of contraction, epinephrine and and force of contraction, epinephrine and norepinephrine releasednorepinephrine released

Heart HomeostasisHeart Homeostasis Effect of blood pressureEffect of blood pressure
Baroreceptors monitor blood pressureBaroreceptors monitor blood pressure Effect of pH, carbon dioxide, oxygenEffect of pH, carbon dioxide, oxygen
Chemoreceptors monitorChemoreceptors monitor Effect of extracellular ion concentrationEffect of extracellular ion concentration
Increase or decrease in extracellular KIncrease or decrease in extracellular K++ decreases heart ratedecreases heart rate
Effect of body temperatureEffect of body temperature Heart rate increases when body temperature Heart rate increases when body temperature
increases, heart rate decreases when body increases, heart rate decreases when body temperature decreasestemperature decreases

Baroreceptor and Baroreceptor and ChemoreceptorChemoreceptor
ReflexesReflexes