SMART-X · PDF filealexey 18−Oct−2011 18:03 APSI,z=6,300ksec QSO Lx =1045 erg/s...
-
Upload
nguyencong -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of SMART-X · PDF filealexey 18−Oct−2011 18:03 APSI,z=6,300ksec QSO Lx =1045 erg/s...
SMART-X
Aim at a mission more compelling than IXO:
with significant cost savings
and big science gains via achieving Chandra-like angular resolution.
team at SAO, PSU, MIT, GSFC, MSFC, JHU, Stanford, U.Waterloo,Rutgers, NIST, Dartmouth
Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
Configuration
No extendable optical bench
M tot < 4,000 kg (including 30% growth contingency)
ATLAS V541 launch to L2; throw weight > 5,000 kg, 28%margin for SMART-X
Parameters very similar to Chandra andAXSIO
Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
Configuration
55 microcalorimeter with 1 pixels
(XMIS)
2222 CMOS imager with 0.33 pixels
(APSI)
insertable CAT gratings with R = 5000
(CATGS)
f =10 m, = 3 m mirrors with 0.5 HPD resolution and Aeff=2.3m2 at 1 keV
Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
Performance
Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
IXO Science
What Happens Close to a Black Hole? time-resolved Fe-K line spectra for 510 AGNs
How does matter behave at high ? high-res spectroscopy- no timing for 106 cnt/s sources
When and How Did SMBHs Grow? BH spins in ~40 low-z AGNs- (little area at E >10 keV)
BH spins for brightest z=3 AGNs
Observations of BHs to z=10 found in other wavebands or in SMART-X surveys
z = 10,MBH = 3 10
8M,
L
x
= 3 1044 erg/s
NH = 1.5 1024 cm2
NH = 0
10.5 2 510
610
510
410
30.
010.
1
norm
aliz
ed c
ount
s s
1 keV
1
Energy (keV)
data and folded model
alexey 19Oct2011 17:55
z = 3LX = 10
45 erg/sEWrel = 160 eV
App
rove
d fo
r pu
blic
rel
ease
, dis
trib
utio
n un
limite
d
SMART-X projections for high-z AGNs
IXO Science
How does Large Scale Structure Evolve? Precision Cosmology using ~1000 eRosita/ WFXT clusters:
= 0.02, w 0.02
Detection of WHIM in absorption (2 IXO efficiency)
Connection between SMBH and LSS Exquisite data on groups and clusters to high-z
Spatially-resolved turbulence measurements
High-res spectroscopy of AGN outflows,galaxywinds
2x4 arcsec diameterextraction region
Energy (keV)4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.80
0.5
1
1.5
2
Flux
(10-
5 ph/
cm2/
s/ke
V)
Perseus@z=0.5Fe K, 300 ksec
ThermalOnly
Best-$t: 35050km/s
App
rove
d fo
r pu
blic
rel
ease
, dis
trib
utio
n un
limite
d
SMART-X/XMIS simulation of Perseus-like clusters at z = 0.5
Adjustable mirrors
make segments for ~7 mirror quality (AXSIO-like), deposit PZT & electrodes
mount, calibrate and determine required piezo voltages on the ground, using available optical interferometry
apply voltage to correct the figure when in orbit (low power)
App
rove
d fo
r pu
blic
rel
ease
, dis
trib
utio
n un
limite
d
Adjustable mirrors: analytic modelingFinite element analysis of 410205mm conical elements with 2020 piezo adjusters, 10+2 point mount:
correction works for generic low-f distortions (e.g., gravity release)
up to 5% errors on correction coefficients can be tolerated
50 100 150 200
-0.20
-0.15
-0.10
-0.05
0.00
0.05
0.10
z@mmD
slopeerror@arcsecD
Residual Slope Center Strip, Primary, 1g
Simulations of 1-g gravity release correction an order of magnitude reduction in slope error
App
rove
d fo
r pu
blic
rel
ease
, dis
trib
utio
n un
limite
d
PZT film successfully deposited and energized. ~500ppm strain required, 700 900 ppm obtained;
Deposition on Corning Eagle glass
PZT lifetime, stability, repeatability studies on-going
first move measurement: 6060mm, ~2m displacement
Adjustable mirrors: current state
App
rove
d fo
r pu
blic
rel
ease
, dis
trib
utio
n un
limite
d
PZT deposition on D263 vs Corning Eagle
Adjustable mirrors: current state
App
rove
d fo
r pu
blic
rel
ease
, dis
trib
utio
n un
limite
d
Corning Eagle glass, single cell energized, 690ppm strain
PZT film successfully deposited and energized. ~500ppm strain required, 700 900 ppm obtained;
Deposition on Corning Eagle glass
PZT lifetime, stability, repeatability studies on-going
Adjustable mirrors: development plan
$45M, 7-yr development program (SAO, GSFC, PSU, MSFC, Industry) TRL6 by 2019 through a rocket flight
Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
ID Task Name
1 PZT Development
2 Extend to conical mirrors
3 Optimize Influence Function
4 Improve mid frequency figure
5 Flight-like Alignment and Mounting
6 Sounding Rocket Program
7 Sounding Rocket Launch
8 Metrology development
9 Lifetime testing
10 Technology Readiness Level
SAO, PSU
SAO, PSU, Industry, GSFC,
SAO, PSU, MSFC
SAO, GSFC
SAO, GSFC, Industry
SAO, MIT, PSU, MSFC, GSFC
10/2
SAO, Industry
SAO, MSFC, PS
TRL 2 TRL 3 TRL 6TRL 5TRL4
2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 41 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
Task
Split
Progress
Milestone
Summary
Project Summary
External Tasks
External Milestone
Deadline
Page 1
Project: Smart-X Tech Development - Date: Mon 12/12/11
Science instruments status
CATGS see Bautz et al.,Heilmann et al.
XMIS some areas of development are specific to SMART-X (44 or 55Hydras, more pixels, energyvs. spatial resolution trade-off)
APSI straightforward development, but funding needed (seeD. Burrows talk):
- small pixel size + large depth- thin filter without hydrocarbon- fast readout + large arrays
Results for 33 Hydra (65 m absorbers vs. 46m for SMART-X)
Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
Cost
Use AXSIO as a basis
Add knowns and unknowns (conservatively)(e.g., 2 cost of module facilities, 50% instead of 30% reserves for mirror production)
from AXSIO = $430M$170M (mirrors) + $188M(instruments & spacecraft systems) + $52M(integration&test) + $20M (Atlas V-541)
End-to-end cost = $2,328M
App
rove
d fo
r pu
blic
rel
ease
, dis
trib
utio
n un
limite
d
High-resolution spectroscopy
Gas outflows in AGNs and starbursts
Spectroscopy / tomography of slightly extended sources
Active stars
Bondi radius in NGC3115
5 10 15 20Wavelength (Angstroms)
0
200
400
600
800
C
ou
nts
O VII
O V
III
O V
II
Fe
XV
II
Fe
XV
II
O V
III
Ne IX
Ne
X
Ne X
Fe
XX
IIN
e I
X
Ne
X
Mg
XI
Mg
XII
Si X
III
Si X
IVObservation
Shock Model
Coronal Model
Trumpler 14, Chandra X-ray spectral diagnostic of TW Hydrae with Chandra (Brickhouse et al 10)
App
rove
d fo
r pu
blic
rel
ease
, dis
trib
utio
n un
limite
d
Black holes and LSS from z = 6 to the present
Springel et al. 2005 simulations dark matter density
!rst quasar at z=6 nursing home at z=0
M87, Chandra, 1 pixels
XMIS, z = 0, 300 ks
GasT = 1.4 keV
HaloLX = 5 10
43 erg/sT = 2 keVr = 45kpc = 8
1 100.2 0.5 2 510
6
10
5
10
4
10
3
0.0
10
.1
no
rma
lize
d c
ou
nts
s
1 k
eV
1
Energy (keV)
data and folded model
alexey 18Oct2011 17:15
10.5 2 510
3
0.0
10
.11
no
rma
lize
d c
ou
nts
s
1 k
eV
1
Energy (keV)
data and folded model
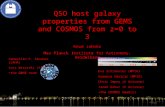
alexey 18Oct2011 18:03
APSI, z = 6, 300 ksec
QSOL
x
= 1045 erg/s
XMIS, z = 0, 300 ksec
Jet + gasT = 1.2 keV
App
rove
d fo
r pu
blic
rel
ease
, dis
trib
utio
n un
limite
d
T = 0.7 keVv = 400 km/s
50 kpc
T = 0.5 keVv = +400 km/s
10.5 210
4
10
3
0.0
10.1
110
norm
aliz
ed c
ounts
s
1 k
eV
1
Energy (keV)
data and folded model
alexey 18Oct2011 21:35
NGC 1961, XMIS, 300 ksec
NGC 1961, Chandra
HST+ALMA, z=0
Galaxy and star formation
Subaru, z=3C
old accretion
Ly-
Hot hal
os
SMART
-X
Observations of hot halos around SFR30M/yr galaxies at z ~ 2.5
Detailed study of hot phase at z = 0 Star-forming regions in the MW
Star
s, du
st,m
olec
ular
gas
optic
al,