Skull,orbit temporal bones,facial bones,paranasal sinuses,mandible and opg
-
Upload
lalit-chandrawanshi -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
1.011 -
download
0
Transcript of Skull,orbit temporal bones,facial bones,paranasal sinuses,mandible and opg


SKULL, ORBIT, TEMPORAL BONE,FACIAL BONES AND PARANASAL SINUSES, MANDIBLE AND OPG

SKULL (22 BONES)
CRANIUM (21 BONES)
MANDIBLE
CRANIAL VAULT (NEUROCRANIUM) FACIAL SKELETON (VISCEROCRANIUM)
(8 BONES) (14 BONES INCLUDING MANDIBLE)

CRANIAL VAULT/ CALVARIA/ BRAIN BOX/NEUROCRANIUM (8 BONES)
PAIRED BONES 1. PARIETAL 2. TEMPORAL
UNPAIRED BONES 1. FRONTAL 2. OCCIPITAL 3. ETHMOID 4. SPHENOID

FACIAL BONES/ VISCEROCRANIUM (14 BONES)
PAIRED
1. MAXILLA 2. ZYGOMATIC 3. NASAL 4. LACRIMAL 5. PALATINE 6. INFERIOR NASAL CONCHA
UNPAIRED
1. VOMER 2. MANDIBLE






FOR GOOD POSITIONING IN SKULL RADIOGRAPHY CERTAIN REFERENCES ARE UTILIZED.
LANDMARKS LINES PLANES

LANDMARKS
NASION - The articulation between nasal and frontal bones GLABELLA - A bony prominence on frontal bone immediately superior to
the nasion VERTEX - Highest point of skull in median sagittal plane EXTERNAL AUDITORY - Opening of external ear leading into external
MEATUS auditory canal EXTERNAL OCCIPITAL - A bony prominence on the occipital bone usually
PROTUBERANCE coincident with the median sagittal plane INFRAORBITAL - The inferior rim of the orbit MARGIN INFRAORBITAL POINT - The lowest point on inferior orbital rim OUTER CANTHUS - Point where upper and lower eyelids meet laterally OF THE EYE


Lines Inter-orbital (inter-pupillary) line: joins the centre of the
two orbits or the centre of the two pupils when the eyes are looking straight forward.
Infra-orbital line: joints the two infra-orbital points.
Anthropological baseline: passes from the infra-orbital point to the upper border of the external auditory meatus (also known as the Frankfurter line).
• Orbito-meatal base line (radiographic baseline): extends from the outer canthus of the eye to the centre of the external auditory meatus. This line is angled approximately 10 degrees to the anthropological baseline.


Planes Median sagittal plane: divides the skull into right and left halves.
Landmarks on this plane are the nasion anteriorly and the external occipital protuberance (inion) posteriorly.
Coronal planes: these are at right-angles to the median sagittal plane and divide the head into anterior and posterior parts.
Anthropological Plane: a horizontal plane containing the two anthropological baselines and the infra-orbital line. It is an example of an axial plane. Axial planes are parallel with this plane.
Auricular plane: perpendicular to the anthropological plane. Passes through the centre of the two EAM.



SKULL RADIOGRAPHY TECHNIQUES
ISOCENTRIC NON-ISOCENTRICUTILIZES SKULL UNITS ADVANTAGES- 1. Highest quality image with reduced distortion 2. More comfortable to patient 3. Less dose and minimized secondary radiationsDISADVANTAGES- 1.Unsuitable for patients who are unable to cooperate 2.Technically demanding 3.Expensive
UTILIZES CONVENTIONAL EQUIPMENTS INCLUDING X-RAY TABLE, BUCKY, GRID CASSETTES, SIMPLE X-RAY TUB ADVANTAGES- 1. Cheaper 2. More versatile DISADVANTAGES- 1. Poorer image quality 2. Less close collimation


SKULL: PROJECTIONS
STANDARD PROJECTIONS LATERAL (SUPINE/ERECT) OCCIPITOFRONTAL/POSTEROANTERIOR HALF –AXIAL ANTEROPOSTERIOR 30 degree CAUDED(TOWNE’S) SUBMENTOVERTICAL/BASAL

Lateral-supine with horizontal beam
Supine with head raisedImmobilized
MSP –L trolley & IOP-L cassette
Cassette lat to head & //MSP
CR directed //IOP &-L MSPb/w glabella & EOP to 5cmSuperior to EOM
COLLIMATION:to skull size
Kvp 80-90 mAS 80-100
FFD 40”(120cm)
24*30cm(10*12”)
ATLS screening - #; sinus fluid levels ; free intracranial air

Where patient is more cooperative Bone malignancyMetabolic bone disease
Sits facing erect bucky ;MSP//bucky &IOP 90*bucky
CR directed //IOP &-L MSPb/w glabella & EOP to 5cmSuperior to EOM
COLLIMATION:to skull size
Kvp 80-90 mAS 80-100
FFD 40”(120cm)
CASSETTE- 24*30cm(10*12”)

Image should contain-All cranial bones-1st cervical vertebra-Both inner & outer tables TRUE LATERAL VIEW;-Superimposition of both lateral portionOf floors of ACF & PCF-superimposition of clinoid processes Of sella turcica

Fig. 53.2 (A) X-ray film of skull taken in standard lateral projection.B) Diagram to illustrate the standard lateral view. 1 = coronal suture;2 = meningeal vascular marking, anterior branch; 3 = anterior border ofmiddle fossa4lambdoid suture 5dorsum of sella 6 clivus 7lat sinus 8sq parietal suture 9 EOM

1Frontal bone.2Parietal bone.3Occipital bone.4Squamous portion, temporal bone.5Petrous portion, temporal bone.6Middle meningeal artery.7Frontal sinus;;8Ethmoid sinus9Maxillary sinus.10Sphenoid sinus.11Mastoid air cells.12Transverse venous sinus.13Sella turcica.14Internal occipital protuberance.15External occipital protuberance.16Inner table.17Diploe.18Outer table.19Parietal star20Pinna of the ear.21Internal auditory meatus.22Temporomandibular joint.23Nasopharynx.24Hard palate.25Orbit.26Odontoid process.

CLINICORADIOLOGICAL CORRELATION
Lateral, Skull, Parietal Fracture. A linear fracture extends though the parietal bone (arrows). E. Lateral Skull, Multiple Myeloma. Multiple, well-defined radiolucent lesions are visible throughout the parietal and frontal bones.

OCCIPITOFRONTAL
kVp: 85 (80 to 90).mAS-100Film Size: 10 × 12 inches (24 × 30 cm), vertical orientation.Grid: Yes.TFD: 40 inches (102 cm); must correct for tube tilt with TFD to 37 inches (94 cm).Tube Tilt: NOPatient Position: Prone or upright. Part Position: Frontal bone in contact with the bucky. Remove all lateral head tilt and rotation. The orbitomeatal line should be perpendicular to the cassette.CR: Exits through the nasion. Collimation: To skull size.

Petrous ridges completely superimposed within the orbit
Petrous ridges appears in the middlethird Of the orbit
Petrous ridges appear just below the inferior orbital margin

kVp: 85 (80 to 90).mAS-100Film Size: 10 × 12 inches (24 × 30 cm), vertical orientation.Grid: Yes.TFD: 40 inches (102 cm); must correct for tube tilt with TFD to 37 inches (94 cm).Tube Tilt: 15° caudad.Patient Position: Prone or upright. Part Position: Frontal bone in contact with the bucky. Remove all lateral head tilt and rotation. The orbitomeatal line should be perpendicular to the cassette.CR: Exits through the nasion. Collimation: To skull size.
SKULL: PA Caldwell’s Projection

Indicated in evaluation of-sinus diseaseFrontal boneOrbits sphenoid
Essential image characteristics-all cranial bones-Equidistance from a point in midline of skullTo lateral margins-nasal septum & calcified penial gland in midline
1 Frontal bone.2 Frontal sinus.3 Ethmoid sinus.4 Maxillary sinus.5 Nasal septum.6 Petrous ridge.7 Greater wing of sphenoid.8 Infraorbital rim.9 Supraorbital rim.10 Nasal turbinates.11Mandible.

Clinicoradiologic Correlations
D. PA Caldwell’s, Skull, Frontal Bone Fracture. The fracture is visible as multiple radiolucent lines. The sinus is filled with hematoma (arrows). E. PA Caldwell’s, Skull, Frontal Sinus Osteoma. Dense, ivory-like new bone fills a frontal sinus.

kVp: 85 (80 to 90). mAS-100Film Size: 10 × 12 inches (24 × 30 cm), vertical orientation.Grid: Yes.TFD: 40 inches (102 cm); must correct TFD to 35 inches (89 cm) for tube tilt.Tube Tilt: 30 degree caudad.Patient Position: Supine or upright. Part Position: Centered, with removal of lateral head tilt and rotation. Orbito-meatal line is perpendicular to the cassette.CR: Passes through the midline at the external auditory meatus. Collimation: To skull size.
HALF-AXIAL FRONTO OCCIPITAL 30 DEGREE CAUDAD-INDICATED in evaluation of occipital bone Petrous ridges auditory meatus zygoma mandibular condyle

Towne's projection. (B) Diagram to illustrate (A) 1 = lateral sinus; 2 = foramen magnum; 3 = dorsum sellae; 4 =i nternal auditory meatus; 5 = acuate eminence; 6 = superior semicircular canal; 7 = lambdoid suture

1 Occipital bone.2 Parietal bone.3 Lambdoidal suture.4 Sagittal suture.5 Internal occipital protuberance.6 Transverse venous sinus.7 Petrous pyramids.8 Mastoid air cells.9 Foramen magnum.10 Dorsum sellae.11 Mandibular condyle.12 Zygomatic arch.13 Cervical pillar.Essentials of image The dorsum sellae and posterior clinoid processes should project into the anterior portions of the foramen magnum.
All occipital bonem& posterior parts of parietal bone & lambdoid suture must be in included Skull shouldn’t be rotated

D. AP Towne’s, Skull, Occipital Bone Fracture. A linear fracture extends through the occipital bone (arrows). E. AP Towne’s, Skull, Occipital Bone Paget’s Disease. A sharply defined region of decreased bone density is visible in the occipital bone (arrows), an indication of the osteolytic phase Paget’s disease (osteoporosis circumscripta).
Clinicoradiologic Correlations

Erect/Pron,facing to buckySupported
MSP//midline-L cassetteOMP-L cassette
CR:30*Cranially to OMP
COLLIMATION:whole of occipital & parietal bones upto vertexAvoid eyes
Kvp 80-90
mAS-80-100
FFD 40”


Supine/erect; neck hyperextendedVertex in contact with cassette
EOM equidistant from cassetteMSP//midline&_LcassetteOMP//cassette
CR: 90* OMP & centered midway b/wEOMs
Kvp 80-90
mAS-90-100
Collimation ; to skull size
FFD 40”

Greater sphenoidal wing; 2 = sphenoidal sinus;3 = foramen ovale; 4 = foramen spinosum; 5 = foramen lacerum medium; 6 = foramen magnus: 7 = internal auditory meatus

Indicated in evaluation of-margins of skull base foramina-trauma- For fracture of zygomatic arch

Erect/Sitting, facing bucky & head is rotated soMSP//BUCKY & IOP 90* BUCKYSUPPORTED
CR:2.5cm vertically above a point 2.5cm along the baselineFrom EOMs nearer to xray tube kVp 80-90
mAS-90-100
FFD 40”
CASSETTE 10* 12”
COLLIMATION:to skull size

Positioning & cassette : as SMV
CR:20*caudally or 70*OMP Centred in midline b/w EOMs ORHead positioned with OMP at 20*to bucky,horizontal central ray at 70* to baseplane.


ORBIT PROJECTION
PA SKULLLATERAL SKULLPOSTEROANTERIOR OBLIQUE
INDICATED In evaluation of-bony orbit details-optic foramina for tumor-blunt ocular trauma-foreign bodies-malignancy


Erect/prone ;examined side in contact With bucky
Centre of examined side orbit shouldCoincide with centre of bucky
MSP 35* VERTICAL OR 55* table
CR: centred to middle of bucky & 7.5cm above & behind the upperMost EOM, CR emerges from Centre of orbit
KVp 80-90
mAS-90-100
FFD40”
CASSETTE 10*12”
OPTIC FORAMINA: POSTERO-ANTERIOR OBLIQUE



TEMPORAL BONE ANATOMY

TEMPORAL BONE :PROJECTIONS
FRONTO-OCCIPITAL 35* CAUDALMASTOID PROFILE: LATERAL OBLIQUE25*PETROUS PROFILE:ANTERO-OBLIQUE(STENVER’S VIEW) Indicated in evaluation of
-otitis media-basal tumors-fractures-changes in auditory canal -congenital maldevelopment-operative defects

supine/erect with back to bucky; head is adjusted soEOMs equidistant from table & MSP 90* tableOMP 90* table
CR:35*OMP;centred midway b/w EOMs
KVp 80-90
mAS- 90-100
FFD 40”
COLLIMATION:from lateral margins of skull & suprainferiorlyTo mastoid & petrous parts of temporal bone
Temporal bones


Sitting facing erect bucky; head rotated so thatMSP// bucky & IOL 90* BUCKYAuricle adjacent to table folded forwardMastoid in middle of bucky
CR:25*cadual angulation & centred 5cm above &2.5cmBehind EOMs
KVp 80-90
mAS-90-100
FFD 40”
COLLIMATE to area under examination
Cassette 8*10”(18*24cm)


Prone/ sitting facing bucky,neck flexed so nose &Forehead in contact with table ;OML 90* table.-head rotated at45* so petrous part// cassette
CR:12* cephaled angulation,to saperate occiput From petrousCentred midway b/w EOP & EOM
KVp 80-90
mAS-90-100
FFD 40””
COLLIMATE to Mstoid & petrousParts of examined temporal
Cassette 8*10”(18*24cm)


an enlarged sella may be associated with a pituitary neoplasm, empty sella syndrome, or extrapituitary mass (neoplasm, aneurysm); it may even be a normal variant.


Average (°) Minimum (°) Maximum (°)
137 123 152
The measurement is an index of the relationship between the anterior skull and its base. The angle will increase beyond 152° in platybasia, in which the base is elevated in relation to the rest of the skull. This may or may not be associated with basilar impression. The deformity may be congenital (isolated impression, occipitalization) or acquired (Paget’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, fibrous dysplasia).
Basilar Angle


FACIAL BONES INCLUDING MANDIBLE

Facial bones
• Occipito-mental • Modified mento-occipital • Occipito-mental 30° caudad• Modified reverse occipito-mental 30°• Lateral• Zygomatic arches: infero-superior• Orbits: occipito-mental (modified)• Nasal bones: lateral

Occipito-mental

• Position:• Seated• No rotation• Orbitomeatal line @ 45° to cassette holder
• Centering :• Lower orbital margin
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80

Essential image characteristic:Petrous ridges must appear below the floors of the maxillary sinuses


Modified mento-occipital

• Patients who have sustained trauma
• Often present supine on a trolley,
• In a neck brace
• With the radiographic baseline in a fixed position

• Position:• Seated• No rotation• Orbitomeatal line @ 45° to cassette holder
• Centering :• Lower orbital margin• Top of cassette 5 cm above the top of head
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80

Occipito-mental 30° caudad

• Demonstrates lower orbital margins and orbital floors en face.
• Zygomatic arches are opened out compared with OM projection but they are still foreshortened.

• Position:• Seated• No rotation• Orbitomeatal line @ 45° to cassette holder• 30° caudad angulation
• Centering :• Upper symphysis menti
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80


Modified reverse occipito-mental 30°

• Position:• Supine• No rotation• Orbitomeatal line at 90° to table top
• Direction and Centering :• Tube is angled 20 degree to the horizontal • Upper symphysis menti• 100 cm FFD
• Exposure factor:• kVP 85• mAs 80

Lateral

• Position:• Supine/Erect• No rotation
• Centering :• 2.5 cm inferior to the outer canthus of the eye
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80


Zygomatic arches: infero-superior

• Position:• Supine• No rotation• Cassette’s long axis // to axial plane of body• Neck extended• Head tilted 10° towards opposite side
• Centering :• Midpoint of the zygomatic arch and thelateral border of thefacial bones
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80


Orbits: occipito-mental (modified)

• The projection is essentially an under-tilted occipito-mental with the orbito-meatal baseline raised 10 degrees less than in the standard occipito-mental projection
• Orbits circular rather than elliptical

• Position:• Seated• No rotation• Orbitomeatal line @ 30° to cassette holder
• Centering :• Lower orbital margin
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80


Nasal bones: lateral

• Position:• Erect• No rotation
• Centering :• Nose
• Exposure factor:• kVP 45• mAs 6

•Detected clinically & rarely treated actively.
•Considering the dose of radiation to the eye, this projection should be avoided.
• Severe nasal injuries will require only an occipitomental projection to assess the nasal septum and surrounding structures.

MANDIBLE•Mandible: lateral 30° cephalad •Mandible: postero-anterior•Mandible: postero-anterior oblique• Temporal-mandibular joints: lateral •25° caudad

Mandible: lateral 30° cephalad

• Position:• Supine• No rotation• MSP parallel to cassette
• Centering :• CR is angled 30° cranially at an angle of 60 ° to cassette • centred 5 cm inferior to angle of mandible
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80


Mandible: postero-anterior

• Position:• Erect• No rotation• Orbito meatal plane perp to cassette
• Centering :• Level of angle of mandible
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80


Mandible: Postero-anterior
oblique
Demonstrates symphysis menti

• Position:• Erect• No rotation• Orbito meatal plane perp to cassette • rotated 20°
• Centering :• CR is directed perp to cassette• centred 5 cm from the midline at level of angle of the
mandible.
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80



Temporo-mandibular joints: lateral 25° caudad

• Position:• Erect• No rotation• Orbito meatal plane // to cassette. • 1 cm along the OMB anterior to the external auditory meatus.
• Centering :• CR is angled 25° caudally and will be centred to a point 5 cm superior to the joint remote from the cassette so the central ray passes through the joint nearer the cassette.
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80



PNS
•Occipito-mental•Occipito-frontal 15° caudad •Lateral

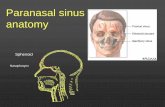
PARANASAL AIR SINUSES ARE A SERIES OF AIR FILLED CAVITIES LINED BY MUCOUS MEMBRANE IN SOME OF THE BONES OF THE CRANIUM
APPEARS OF HIGHER RADIOGRAPHIC DENSITYTHAN SURROUNDING TISSUES
SINUSES COLLECTIVELY CONSISTS OF THE FOLLOWING STRUCTURES-
• MAXILLARY SINUSES (MAXILLARY ANTRA)- PAIRED, PYRAMIDAL SHAPED ,LARGEST
• FRONTAL SINUSES- PAIRED, VARIABLE IN SIZE• SPHENOID SINUSES- IMMEDIATELY BENEEATH SELLA TURCICA AND
POSTERIOR TO ETHMOID SINUSES• ETHMOID SINUSES- SMALL AIR SPACES THAT COLLECTIVELY FORM PART OF
THE MEDIAL WALL OF THE ORBIT AND THE UPPER LATERAL WALLS OF THE NASAL CAVITY


Occipito-mental

THIS PROJECTION IS DESIGNED TO PROJECT THE PETROUS PART OF THE TEMPORAL BONE BELOW THE FLOOR OF THE MAXILLARY SINUSES SO THAT FLUID LEVELS OR PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE LOWER PART OF THE SINUSES CAN BE VISUALIZED CLEARLY

• Position:• Seated/ prone• No rotation• Orbitomeatal line @ 45° to cassette holder
• Centering :• Lower orbital margin
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80

• Essential image characteristic: Petrous ridges must appear below the floors of the maxillary sinuses


Clinicoradiologic correlation

To distinguish a fluid level from mucosal thickening, an additional projection may be undertaken with the head tilted, such that a transverse plane makes an angle of about 20 degrees to the floor.

Occipito-frontal 15° caudad Demonstrates the frontal and ethmoid sinuses

• Position:• Seated• No rotation• Orbitomeatal line @15° to the horizontal
• Centering :• Nasion
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80
Essential characteristics: The petrous ridges should be projected just above the lower orbital margin.

An OF10°↓ or occipito-frontal projection would not be suitable for demonstration of the ethmoid sinuses, as the petrous ridges would obscure the region of interest.


Lateral

• Position:• Erect• No rotation
• Centering :• 2.5 cm post. to outer canthus of the eye
• Exposure factor:• kVP 75• mAs 80
Essential image characteristics: Lateral portions of the floors of the anterior cranial fossa are superimposed



OPGRotational panoramic radiography
orthopantomography (OPT) Dental panoramic tomography (DPT)
Panoral

Indications• Orthodontic assessment of the teeth• Detection # mandible• Assessment of TMJ pathology• Assess pathological lesions • When intra-oral radiography is impossible• Assessment of 3rd molars before surgical removal

Simultaneous rotationalmovement
Slit-collimatedvertical X-ray beam
8° upward inclinationfocal trough
Principle

Factors reducing diagnostic quality of image• magnification variation• tomographic blur• overlap of adjacent teeth• superimposition of soft tissue and secondary shadows• limitations of resolution imposed by the image
receptor• exposure parameters and processing conditions

10 to 30%
Objects lying closer to the X-ray source (i.e. situated inside the focal trough) will display a greater degree of horizontal magnification
Variability in horizontal shape is apparent by examining the appearance of anatomical structures within the focal trough (thetongue, hyoid bone) and those outside it (the zygomatic arch).

12- 20 s exposureski position60 Kvp20 mAs

Positioning of Frankfort plane upward
If the frankfort plane is rotated upward,it results in overlapping of the images of the teeth and an opaque shadow obcuring the root of the max teeth

Superimposition of soft tissue and secondary shadows
Superimposition of soft tissue and secondary shadows

Limitations of resolution imposed by image receptor, exposure parameters and processing conditions
• Rushton et al. 1999 “one-third of all panoramic films taken were diagnostically unacceptable”

Thank you