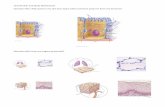
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. COMPONENTS OF THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Figure 5-1.
Skin and the Integumentary System. A. Functions… 1. protective covering 2. homeostasis 3. regulate...
-
Upload
aubrie-wheeler -
Category
Documents
-
view
212 -
download
0
Transcript of Skin and the Integumentary System. A. Functions… 1. protective covering 2. homeostasis 3. regulate...

HAP CHAPTER 6Skin and the Integumentary System

I. SKIN AND ITS TISSUES
A. Functions…1. protective covering2. homeostasis3. regulate body temp.4. prevents water loss5. sensory receptors6. excretes wastes (sweat)

B. Layers of the Integumentary System1. Epidermis – outer layer
a. Stratified squamous epithelium2. Dermis – inner layer
a. Connective tissueb. Epithelial tissuec. Muscle tissued. Nervous tissue e. Blood tissue
*basement membrane anchors dermis and epidermis

3. Subcutaneous Layer (Hypodermis)*(not a true layer of skin)a. Adipose tissueb. Loose connective tissue

II. EPIDERMIS
A. Layers1. Stratum Basale – deepest layer
a. Nourished by dermal blood vesselsb. Mitosis – rapidc. Push cells towards the surfaced. Older cells keratinize (keratin)
become tough, fibrous, waterproof 2. Stratum Corneum
a. Dead cells…shed or eaten

3. Stratum Lucidum a. Thickened skin of the palms and
solesb. Calluses / corns
B. Functions1. Prevents…
a. Water lossb. Mechanical injuryc. Harmful chemicals from
enteringd. Pathogens from entering

C. Special Cells1. Melanocytes – produce melanin
a. Dark pigment…absorbs UVb. Prevents DNA mutationsc. Lie deep in epidermisd. Pass melanin to other cells
cytocrine secretion


2. Skin Colora. Based on melanin produced…b. Genetically determinedc. O2 levels
d. Diet – yellow veg. orange/yellow skin
β-carotenee. Age – jaundice
build up of bilirubin

III. DERMIS
A. Location1. Deep of epidermis2. Uneven (pg.114)
dermal papillae (bumps)fingerprints
B. Characteristics1. Binds epidermis2. Blood supply3. Nerve cell processes4. Hair follicles5. Sebaceous glands6. Sweat glands

IV. SUBCUTANEOUS (HYPODERMIS) LAYER
A. Location1. Deep of dermis2. Level varies (no distinct boundary)
B. Characteristics1. loose and adipose connective tissue2. major blood vessels3. conservation of heat

V. ACCESSORY ORGANS OF SKIN
A. Nails1. components
a. Nail plate – covers surface of skin
b. Nail bed – specialized epithelial cells
c. Lunula – white ½ moon shapedactive keratinized

B. Hair Follicles1. present almost everywhere2. componentsa. Hair follicle – tubelike depressionb. Hair root – extends into dermisc. Keratinizedd. Arrector pili muscle – “goose bumps”3. Hair colora. Based on melanocytes b. No melanine
c. Trichosiderin Red hair
White…albinism

C. Sebaceous Glands1. associated w/ hair follicles2. type of holocrine gland
a. Produce sebumoily mixture with cellular debris
3. plugged pores acne/pimples

D. Sweat Glands1. Type of exocrine gland2. Eccrine gland – most common type
a. Forehead, neck, back3. Sweat…
a. Mostly waterb. Small quantities of…
-salt, wastes, and urea4. Other sweat glands
a. Apocrine glands – pubertyb. Mammary gland – secrete milk

VI. BODY TEMPERATURE REGULATION
A. Warm environment…1. nerve impulses react…send message to brain2. blood vessels vasodialate, sweat glands open3. heat escapes
B. Cold environment…1. nerve impulses react…send message to brain2. muscles fire; blood vessels constrict; sweat glands close3. skeletal muscles contract…shiver

VII. WOUND HEALING
A. Body’s Response1. Swelling2. Red3. Warm4. Pain
B. Why?1. Increased blood flow

C. Wounds1. Superficial Break
a. Epithelial cells divideb. Fill in broken space
2. Deep Breaka. Blood clotsb. Forms scabc. Fibroblasts and phagocytes migrated. Scab falls offe. Possibly forms scar
3. Large and Deep Breaka. Granulations form