Skeletal System. Bones: 22 skull22 skull 27 hand27 hand 26 foot26 foot.
-
Upload
xzavier-snipes -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Skeletal System. Bones: 22 skull22 skull 27 hand27 hand 26 foot26 foot.

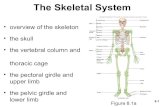
Skeletal System

Skeletal System
Bones:•22 skull•27 hand•26 foot

Skeletal System (cont.)
# of bones:•Adults 206•Babies 300

Function of Bones1. Support
for body and organs2. Protection
for the brain, spinal cord, and
vital organs3. Movement
levers for muscles4. Mineral storage – Ca, P5. Blood cell formation
occurs in the marrow of bones

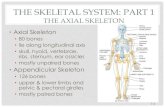
Division of Bones:1. Axial skeleton –
skull, vertebral column, sternum, rib cage
2. Appendicular skeleton –upper & lower limbs, shoulder, hip

Axial Skeleton

Appendicular
Skeleton

Classification of Bones:
• Long bones:Arm and leg bones
• Short bones:Wrist bones
• Flat bones:The bones of the skull
• Irregular bones: Facial bones or vertebrae

Structure of Bones:
• Bones are solid networks of living cells and protein fibers that are surrounded by deposits of calcium salts.

Compact & Spongy Bone

• Dense & strong• Provides strength & protection
• Outermost part of the bone
Compact Bone:

• Less dense & contains bone marrow
• Found in short, flat, and long bones
• Surrounded by compact bone
Spongy Bone:

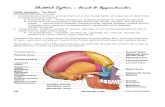
Structure of Long Bone
Figure 6.3a,b

Structure of Long Bone• Periosteum- tough layer of connective tissue
• Compact bone- found beneath periosteum
• Haversian canals- network of tubes that run through compact bone & contain blood vessels and nerves.

Structure of Long Bone:• Spongy bone- ends of long bones & middle of short, flat bones. Adds strength w/o mass!
Within bones are cavities that contain a soft tissue called bone marrow.

Structure of Long Bone:• Two types of bone marrow: Yellow bone marrow- made up of fat cells
Red bone marrow- produces red blood cells, white blood cells, & platelets

Structure of Long Bone

Bone Cells:• Osteocytes- mature bone cells that are embedded in the matrix
• Osteoclasts- break down bone
• Osteoblasts- produce bone
Stop growing- late teens! Our Bones are continuously remodel throughout our lives.

OsteoporosisOsteoclast activity is faster than osteoblast activity!

Osteoporosis

Development of Bones:
• Skeleton of embryo almost entirely cartilage:Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that is made up of a network of protein fibers (both tough collagen & flexible elastin).

Development of Bone Cont’d: • Cartilage does not contain
blood vessels!• Cartilage is replaced by bone during the process called ossification:Osteoblasts secrete mineral deposits that replace cartilage with bone.
Osteoblasts surrounded by bone tissue – now osteocytes

Growth:• Long bones contain growth plates called epiphyseal lines at either ends

Growth: •Growth of cartilage at these plates causes the bones to lengthen.
•Gradually cartilage replaced by bone- a.k.a. ossification
•Late adolescence/ early adulthood growth plates replaced by bone- stop growing!
•Cartilage in adults found:
- nose, external ears, attach ribs to sternum

Epiphyseal Fracture

Bone Connections• Joints- place where one bone attaches to anotherClassified by movement:ImmovableSlightly movableFreely movable
• Ligaments hold bone to bone

Immovable Joints: •Allow no movement•Bones are interlocked and held together by connective tissue or fusedExample: skull bones

fixed

Slightly Movable Joints:
• Permit a small amount of restricted movement
• Bones are separated from each other
• Example:Joints between lower leg Joints between adjacent vertebrae

inter-vertebral
joints

Freely Movable Joints:
• Permit movement in one or more directions
• Grouped according to shapes of the surfaces of the adjacent bones. Ball- and- Socket JointHinge JointPivot JointSaddle Joint

Ball-and-Socket Joint:
• Permits movement in many directions
• Allows for widest range of motion
• Example:Humerus bone and scapula

ball & socket

Hinge Joint:
•Permits back and forth motion
•Example:Femur and tibia/fibula
Like open and closing a door!

hinge joint

Pivot Joint:
•Allow one bone to rotate around
another. •Example:
Humerus and radius/ulna

pivot joint

Saddle Joints:
• Permits one bone to slide in two directions.
• Example:Metacarpals with your carpals

saddle joint

Structure of Joints: • Cartilage covers the surfaces where two bones come together (protects bones)
• Joint capsule helps hold bones together & consists of two layers:LigamentsSynovial fluid

Structure of Joints Cont’d: • Ligaments- hold bones together in a joint
• Synovial fluid- produced by cells enables surfaces of the joint to slide over each other smoothly.

Skeletal Conditions•Bursitis•Scoliosis•Osteoporosis
•Arthritis•Sprain•Fracture

Bursitis
• Inflammation of the bursa (sac)

•Curvature of the spine
Scoliosis

Osteoporosis
• Inefficient bone replacement
• 5-10% of bone mass lost every 10 years past age of 40
Rate of bone eating cells exceeds bone building cells!

Arthritis• Joint inflammation
•Lose strength & functionEx. Rheumatoid arthritis

Rheumatoid arthritis

Sprain•Over stretching of ligaments or tendons
•Torn ligaments require surgery

Fracture
•Broken bone
•Multiple types

• Simple fracture:Bone breaks but does not come through the skin
Types of Fractures:

• Compound fracture:Bone protrudes through the skin
Types of Fractures:

• Stress fracture:A thin crack in the bone
Types of Fractures: